When it comes to financing your home, understanding whether a mortgage is installment or revolving can make all the difference in your financial planning. Are you aware of how these two types of loans function? Each has its unique characteristics and implications for your budget and long-term financial health.
Understanding Mortgages
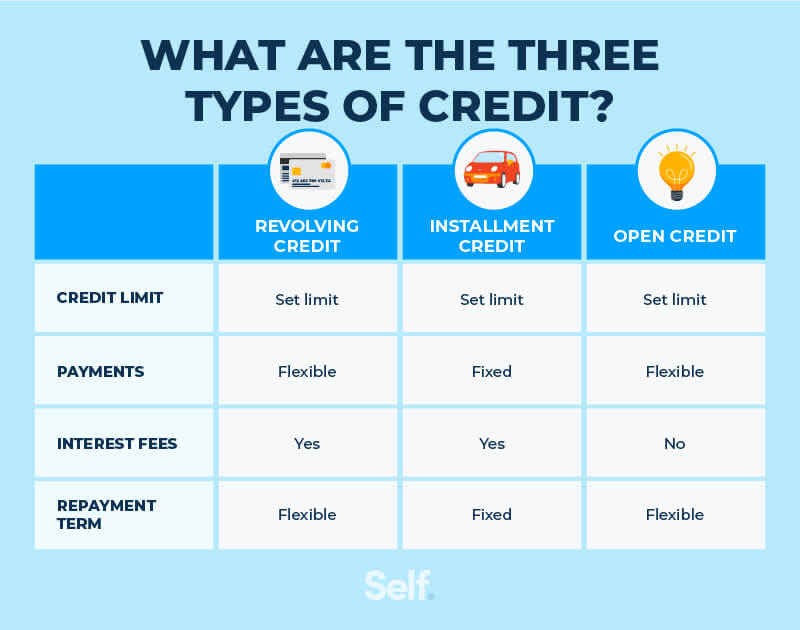
Mortgages can be categorized into two main types: installment loans and revolving loans. It’s crucial to grasp the distinctions between them for effective financial planning.
Installment mortgages involve fixed payments over a set period. For instance, a 30-year fixed mortgage means you’ll pay the same amount each month for 30 years until the loan is fully repaid. This predictability aids in budgeting.
Revolving mortgages, like home equity lines of credit (HELOCs), offer flexibility. You can borrow up to a certain limit and repay it as needed. This type allows you to access funds repeatedly without reapplying for a new loan.
Consider how interest rates differ. With installment loans, interest rates are typically locked in at the start. Conversely, revolving loans often have variable rates that can fluctuate based on market conditions.
Think about your financial goals when choosing between these options. If stability matters most, an installment mortgage may suit you better. But if you prefer flexibility and anticipate fluctuating expenses, consider a revolving option like HELOCs.
Ultimately, knowing what each type offers helps you make informed decisions that align with your financial situation and long-term plans.
Mortgage Types
Understanding mortgage types is crucial for making informed financial decisions. Two primary categories exist: Installment Mortgages and Revolving Mortgages. Each type serves different needs and preferences in home financing.
Installment Mortgages
Installment mortgages provide fixed payments over a specific period. For example, a 30-year fixed-rate mortgage allows you to pay the same amount each month, which aids in budgeting. This predictability helps homeowners plan their finances effectively.
Examples of installment loans include:
- Conventional loans
- FHA loans
- VA loans
Each has unique eligibility criteria and benefits, catering to various borrower situations.
Revolving Mortgages
Revolving mortgages offer flexibility with borrowing and repayment. A common example is a Home Equity Line of Credit (HELOC), where you can draw funds as needed up to a credit limit. This setup allows you to borrow only what you require at any given time.
Key features of revolving mortgages include:
- Variable interest rates that fluctuate based on market conditions.
- The ability to withdraw funds multiple times during the loan period.
These characteristics suit borrowers who prefer adaptable payment options or need funds for ongoing projects like renovations or education expenses.
Key Differences Between Installment and Revolving Mortgages
Understanding the key differences between installment and revolving mortgages helps in making informed financial decisions. Each type possesses unique features that cater to different borrowing needs.
Payment Structure
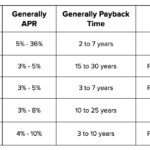
Installment mortgages require fixed monthly payments over a specified term, typically 15 to 30 years. This predictability aids in budgeting since you know exactly how much to pay each month. For example, if you take out a conventional loan for $200,000 at a 3% interest rate for 30 years, your monthly payment remains constant.
On the other hand, revolving mortgages, like home equity lines of credit (HELOCs), allow more flexibility. You draw funds as needed within a set limit and only pay interest on what you borrow. If your HELOC has a $50,000 limit but you only use $20,000 one month, you’ll only owe interest on that $20,000 during the draw period.
Interest Rates
Interest Rates differ significantly between these two mortgage types. With an installment mortgage, rates are often fixed. This means they stay the same throughout the life of the loan. For instance, if your fixed-rate mortgage is locked at 4%, it won’t change regardless of market fluctuations.
Conversely, revolving loans usually have variable rates influenced by market conditions. If you’re using a HELOC with an initial rate of 5%, it could increase or decrease based on changes in prime lending rates. This variability can lead to unpredictable payment amounts over time.
By understanding these distinctions—payment structures and interest rates—you can better align your mortgage choice with your financial goals and lifestyle preferences.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of installment and revolving mortgages helps in making informed financial decisions.
Benefits of Installment Mortgages
Installment mortgages provide predictable monthly payments. This predictability aids in budgeting effectively over the loan term. You know exactly how much to pay each month, which simplifies managing your finances.
Another advantage is fixed interest rates, especially common with traditional loans like FHA or VA loans. Fixed rates protect you from market fluctuations. Additionally, many lenders offer various terms, typically ranging from 15 to 30 years, allowing you to choose one that fits your financial goals.
Drawbacks of Revolving Mortgages
Revolving mortgages come with some drawbacks. Variable interest rates can lead to unpredictable monthly payments. If market conditions change, so does your interest rate—and this unpredictability might strain your budget.
Moreover, while flexibility is a key feature—allowing you to borrow as needed—it can also lead to overspending. The temptation to withdraw more than necessary can create long-term debt challenges. Lastly, if not managed well, these loans could impact your credit score negatively due to high balances on revolving credit lines.