Every relationship faces challenges, and interpersonal conflict is a common hurdle that can arise in any setting. Whether at work, home, or among friends, these conflicts often stem from differing opinions, values, or communication styles. Have you ever found yourself in a disagreement that escalated quickly? Understanding the nature of these conflicts is essential for resolving them effectively.
Understanding Interpersonal Conflict
Understanding interpersonal conflict is crucial for maintaining healthy relationships. Conflicts often arise from differing perspectives, and recognizing this can aid in resolution.
Definition of Interpersonal Conflict
Interpersonal conflict refers to a disagreement or struggle between individuals due to varying needs, values, or goals. This type of conflict occurs when one person’s actions interfere with another’s. For example, if two colleagues want the same promotion but have different ideas on how to achieve it, tension may develop. Identifying the core issues helps clarify misunderstandings.
Types of Interpersonal Conflict
Several types of interpersonal conflicts exist:
- Value-based conflicts: Disagreements stem from differing beliefs about morality or ethics. For instance, debates over political views often lead to heated arguments among friends.
- Interest-based conflicts: Conflicts arise when individuals pursue incompatible goals. Imagine two team members competing for limited resources; this situation creates friction.
- Relational conflicts: These occur when personal dynamics influence interactions. For example, jealousy between siblings can lead to ongoing disputes.
Recognizing these types enhances your ability to navigate disagreements effectively. Each scenario requires tailored strategies for resolution and understanding.
Causes of Interpersonal Conflict
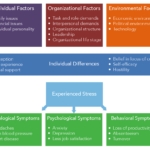
Interpersonal conflict arises from various factors that affect relationships. Understanding these causes helps in addressing and resolving conflicts effectively.
Individual Factors
Individual differences play a significant role in interpersonal conflict. These factors include:
- Personality Traits: For instance, someone with a high level of assertiveness may clash with a more passive individual due to differing communication styles.
- Values and Beliefs: Conflicts often occur when personal values differ, such as religious beliefs or ethical views on specific issues.
- Emotional States: When individuals are stressed or upset, their reactions can lead to misunderstandings and disagreements.
You might notice how these traits shape interactions, leading to potential conflicts if not managed properly.
Situational Factors
Situational contexts also contribute to interpersonal conflict. Key situational factors include:
- Environmental Stressors: High-pressure environments, like workplaces during tight deadlines, can increase tensions among colleagues.
- Cultural Differences: Variations in cultural backgrounds can cause misinterpretations in communication styles or social norms.
- Resource Scarcity: Limited resources, whether time or materials, often create competition among individuals which leads to conflicts.
Consider how each situation influences behavior and interactions among people. Understanding these elements enables you to navigate interpersonal dynamics more effectively.
Effects of Interpersonal Conflict
Interpersonal conflict significantly affects individuals and their relationships. Understanding these effects is crucial for navigating disagreements effectively.
Emotional Impact
Interpersonal conflicts trigger various emotional responses. Conflicts can lead to increased stress levels, anxiety, or even depression. For example, you might feel overwhelmed when facing persistent arguments with a coworker. Additionally, feelings of frustration may arise when personal values clash with those of a friend. Recognizing these emotional impacts helps you manage your reactions better.
Impact on Relationships
Conflicts strain relationships in multiple ways. Frequent disagreements can erode trust and create distance between individuals. For instance, ongoing tension with a family member may result in reduced communication or avoidance behaviors. Furthermore, unresolved issues often lead to resentment and bitterness over time. By addressing conflicts promptly and constructively, you can maintain healthier connections and foster stronger bonds with others.
Strategies for Managing Interpersonal Conflict
Effective strategies exist to manage interpersonal conflict, allowing you to navigate disagreements constructively. Recognizing the right approach can significantly improve your relationships and reduce tension.
Communication Techniques
Active listening is crucial in resolving conflicts. It involves truly hearing what the other person says without formulating a response while they speak. This technique fosters understanding and shows respect for differing viewpoints.
Using “I” statements helps express feelings without placing blame. For instance, instead of saying, “You never listen,” try stating, “I feel ignored when you don’t respond.” This encourages open dialogue rather than defensiveness.
Clarifying misunderstandings prevents escalation. If something isn’t clear, ask questions or paraphrase what you heard. This ensures both parties are on the same page and minimizes assumptions that could lead to further conflict.
Conflict Resolution Methods
Collaborative problem-solving focuses on finding solutions. Both parties work together to identify common goals and brainstorm potential resolutions that satisfy everyone involved.
Mediation can be effective in complex situations. Involving a neutral third party allows for objective input and guidance. They facilitate communication, helping each side articulate their concerns clearly.
Establishing ground rules during discussions assists in maintaining respect. Agreeing beforehand that personal attacks are off-limits creates a safer environment where constructive conversation can thrive.