Have you ever felt overwhelmed by your own thoughts? Internal stressors can significantly impact your mental well-being, often lurking beneath the surface and affecting your daily life. Understanding these stressors is crucial for managing them effectively.
Understanding Internal Stressors
Internal stressors significantly impact mental well-being and can disrupt daily life. Recognizing these stressors is crucial for effective management.
Definition of Internal Stressors
Internal stressors are psychological or emotional factors that originate within you. These include negative thoughts, feelings of inadequacy, and self-doubt. They arise from personal beliefs and experiences rather than external circumstances. For example, perfectionism can create constant pressure to excel, leading to anxiety.
Importance of Identifying Internal Stressors
Identifying internal stressors plays a vital role in managing stress effectively. When you recognize what’s causing your distress, you can develop coping strategies. Awareness enables you to challenge negative thought patterns. Moreover, pinpointing these triggers helps in seeking appropriate support or therapy when necessary. By addressing internal sources of stress, you enhance your overall mental health and resilience against future challenges.
Common Internal Stressors Examples
Recognizing internal stressors can help you develop effective coping strategies. Here are some common examples of these stressors.
Psychological Stressors
Psychological stressors often stem from negative thought patterns or mental challenges. Examples include:
- Perfectionism: Setting unrealistically high standards can lead to chronic dissatisfaction.
- Fear of Failure: Worrying about not meeting expectations may prevent you from taking risks.
- Negative Self-Talk: Critiquing yourself harshly can diminish self-esteem and increase anxiety.
These psychological factors create a cycle of stress that’s hard to break without intervention.
Emotional Stressors
Emotional stressors arise from your feelings and emotional responses. Key examples include:
- Chronic Sadness: Ongoing feelings of sadness may contribute to depression.
- Anger Management Issues: Difficulty controlling anger can lead to conflicts and isolation.
- Overwhelming Guilt: Excessive guilt over past actions might hinder personal growth.
Addressing these emotions is vital for maintaining mental wellness.
Behavioral Stressors
Behavioral stressors relate to your actions and habits. They often manifest through:
- Procrastination: Delaying tasks creates unnecessary pressure as deadlines approach.
- Unhealthy Coping Mechanisms: Relying on alcohol or drugs for relief compounds problems rather than solving them.
- Poor Time Management: Struggling to prioritize tasks leads to feeling overwhelmed by responsibilities.
Identifying these behaviors provides an opportunity for change, empowering you toward healthier choices.
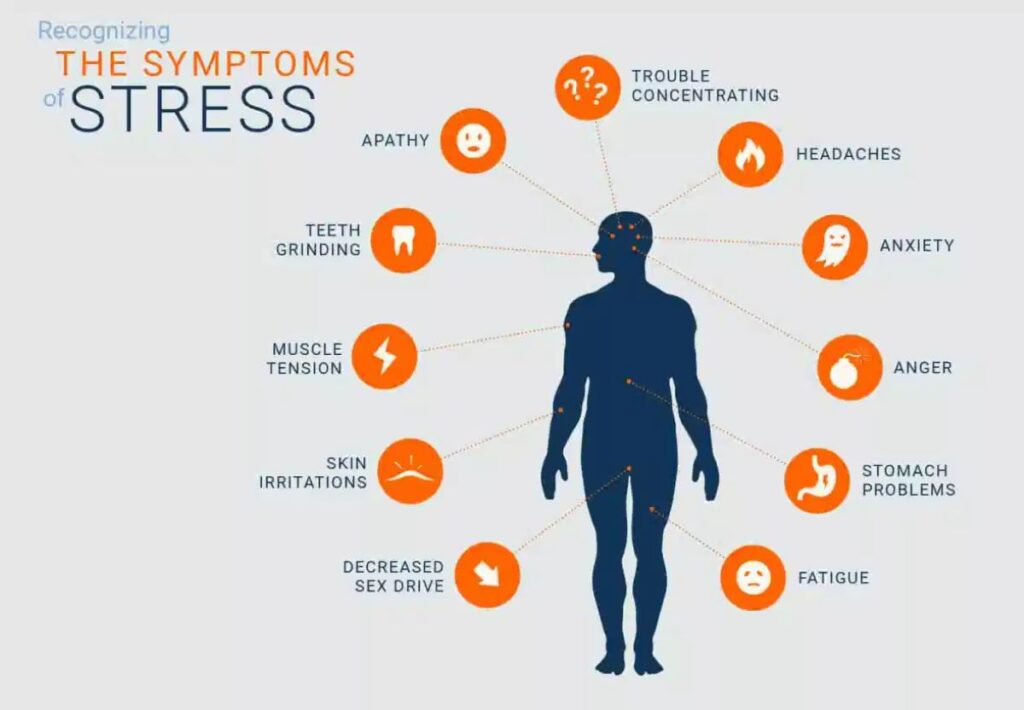
Effects of Internal Stressors on Well-Being
Internal stressors significantly impact your well-being, influencing both mental and physical health. Recognizing these effects helps in managing stress more effectively.
Mental Health Implications
Internal stressors can lead to various mental health issues. Strong negative thoughts may create feelings of inadequacy or hopelessness. You might experience heightened anxiety or depression due to perfectionism or fear of failure. Chronic self-doubt often results in low self-esteem, making daily tasks feel overwhelming. Additionally, emotional turbulence can arise from unresolved guilt or anger, leading to mood swings and irritability.
Physical Health Implications
Internal stressors also manifest physically. Increased tension often leads to headaches, muscle pain, and fatigue. You may notice changes in appetite—either overeating or loss of interest in food—due to emotional distress. Sleep disturbances frequently occur as racing thoughts disrupt rest patterns. Furthermore, prolonged exposure to internal stressors can weaken the immune system, increasing susceptibility to illnesses and infections.
Strategies for Managing Internal Stressors
Managing internal stressors effectively enhances mental well-being. Various strategies exist, including mindfulness practices and cognitive behavioral techniques.
Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques
Mindfulness and relaxation techniques promote awareness of the present moment. You can practice:
- Meditation: Spend 10-20 minutes daily focusing on your breath.
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Inhale deeply through your nose, hold for a few seconds, then exhale slowly through your mouth.
- Progressive Muscle Relaxation: Tense and relax different muscle groups to release physical tension.
These methods reduce anxiety levels by grounding you in the here and now, fostering a sense of calm. Consider incorporating these practices into your routine to combat the effects of negative thoughts.
Cognitive Behavioral Approaches
Cognitive behavioral approaches address negative thinking patterns directly. You might engage in:
- Identifying Negative Thoughts: Write down recurring negative thoughts instead of letting them linger unexamined.
- Challenging Distorted Beliefs: Ask yourself if there’s evidence supporting these beliefs or if they’re based on assumptions.
- Setting Realistic Goals: Break tasks into smaller steps, making them more manageable.
This approach empowers you to reshape your thought process, leading to improved emotional responses. By consistently applying these techniques, you can cultivate resilience against internal stressors.