Have you ever wondered why some people seem to navigate life’s challenges with confidence while others struggle? The answer often lies in their internal locus of control. This psychological concept refers to the belief that you can influence your own life outcomes through your actions and decisions, rather than attributing them solely to external forces.
Understanding Internal Locus of Control
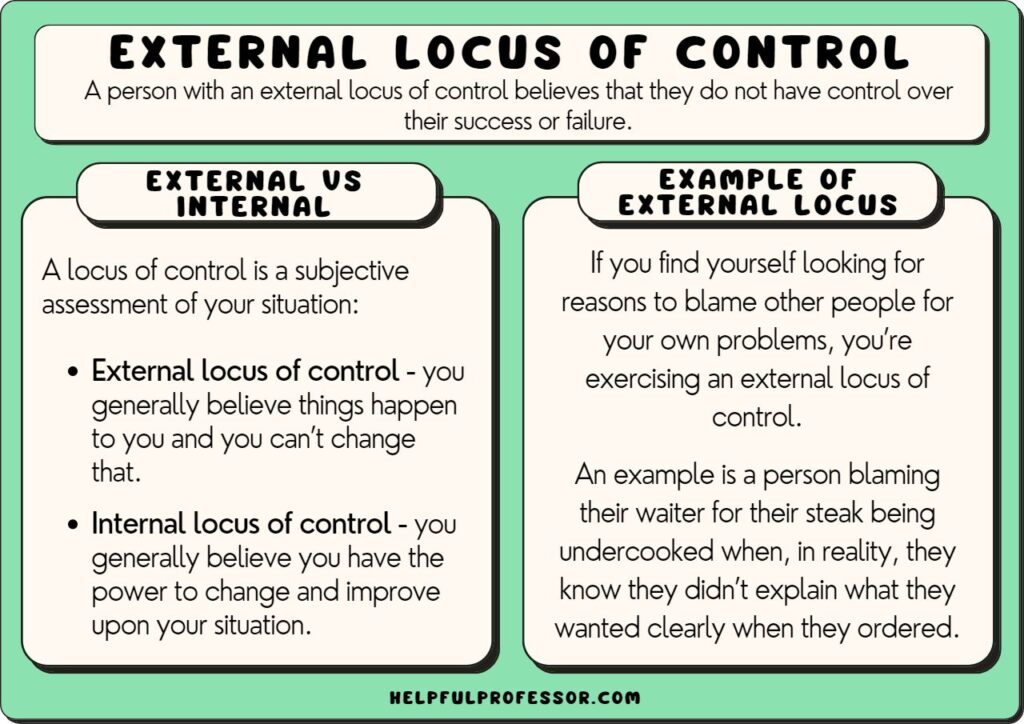
An internal locus of control reflects the belief that you shape your life through your choices and actions. This perspective empowers individuals to take responsibility for their outcomes, fostering resilience.
Definition and Concept
An internal locus of control refers to the perception that you can influence events and outcomes in your life. People with this mindset believe they are responsible for their successes and failures. For example, if you achieve a goal at work, you attribute it to your hard work rather than external factors like luck or fate. This sense of agency promotes motivation and determination.
Historical Background
The term “locus of control” was introduced by psychologist Julian Rotter in 1954. He categorized it into two types: internal and external. An internal locus focuses on personal influence over one’s environment, while an external locus emphasizes outside forces dictating outcomes. Research has shown that people with an internal locus tend to perform better academically and professionally due to their belief in personal efficacy.
Importance of Internal Locus of Control
An internal locus of control significantly impacts various aspects of life. It shapes how you approach personal development, academic success, and career advancement.
Personal Development
An internal locus of control encourages self-improvement. Individuals with this mindset actively seek opportunities to grow through their choices. For example, you might pursue new skills or hobbies because you believe your efforts will yield results. Engaging in self-reflection helps identify areas for improvement, leading to a more fulfilling life. It fosters resilience during setbacks since you view challenges as chances to learn rather than obstacles.
Academic Success
<strong.An internal locus of control correlates strongly with academic achievement. Students who believe they can influence their grades often perform better than those who see outcomes as determined by external factors. When faced with poor exam results, these students analyze what went wrong and adjust their study strategies accordingly. This proactive attitude not only boosts grades but also enhances overall learning experiences.
Career Advancement
<strong.An internal locus of control plays a crucial role in career progression. Employees who feel empowered to shape their work environment are more likely to take initiatives that lead to promotions or new opportunities. They seek feedback and act on it, demonstrating commitment and adaptability. By setting clear goals and working diligently towards them, you can create pathways for professional growth that align with your aspirations.
Factors Influencing Internal Locus of Control
Various factors play a significant role in shaping your internal locus of control. Understanding these influences can help you cultivate this mindset further.
Personality Traits
Certain personality traits strongly correlate with an internal locus of control. For instance, individuals who display high levels of self-efficacy tend to believe they can influence their outcomes. Additionally, traits such as assertiveness and resilience contribute positively. You might notice that people who score high on the Big Five personality traits, especially conscientiousness and openness, often exhibit a stronger internal locus.
Environment and Upbringing
Your environment during childhood significantly impacts your beliefs about control. Supportive parents or guardians encourage independence and decision-making, fostering an internal locus of control. Conversely, overly controlling environments may lead you to adopt an external perspective over time. Research indicates that children raised in nurturing settings with opportunities for autonomy develop confidence in their ability to navigate challenges.
Education and Learning Experiences
Education plays a crucial role in developing your internal locus of control. Engaging learning experiences that promote critical thinking enable you to see the connection between effort and results. For example:
- Active participation in class discussions fosters ownership of learning.
- Constructive feedback helps refine skills and strategies.
- Goal-setting exercises teach you how personal actions lead to achievements.
Such educational practices empower students to recognize their influence over academic success, reinforcing a strong internal locus of control throughout life stages.
Measuring Internal Locus of Control
Measuring internal locus of control involves using specific tools and interpreting the results effectively. You can gain insights into personal beliefs about influence over life events through these assessments.
Assessment Tools
Several assessment tools exist to measure your internal locus of control. Common instruments include:
- Rotter’s Locus of Control Scale: This 29-item questionnaire evaluates whether you perceive outcomes as a result of your actions or external factors.
- Nowicki-Strickland Internal-External Locus of Control Scale: This tool focuses on children and adolescents, offering insights into younger individuals’ perspectives.
- Locus of Control Inventory: A detailed inventory that assesses various dimensions related to how you view control in different life areas.
These tools provide structured ways to reflect on your beliefs and behaviors regarding control.
Interpretation of Results
Interpreting the results from these assessments is crucial. If you score high on an internal locus scale, it suggests that you believe your actions significantly impact outcomes. Conversely, low scores indicate a tendency towards external locus thinking, where you might attribute success or failure to luck or other external forces.
Consider the implications of your scores:
- High internal scores may correlate with greater motivation and resilience.
- Low internal scores could highlight areas for personal development, such as building self-efficacy or decision-making skills.
Understanding these results can guide you toward strategies for personal growth and improvement in various aspects of life.
Strategies to Enhance Internal Locus of Control
Fostering an internal locus of control involves specific strategies that empower you to take charge of your life. These strategies encourage personal responsibility and the belief that your actions significantly influence outcomes.
Goal Setting Techniques
Utilizing effective goal-setting techniques can strengthen your internal locus of control. Start by setting SMART goals—Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. This approach ensures clarity in what you want to achieve.
- Write down your goals: Documenting them keeps you accountable.
- Break goals into smaller steps: Smaller tasks make large objectives more manageable.
- Track progress regularly: Reviewing achievements reinforces your sense of control.
By following these techniques, you’ll develop a stronger belief in your ability to shape outcomes.
Cognitive Behavioral Approaches
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) offers valuable tools for enhancing an internal locus of control. CBT focuses on changing negative thought patterns that may undermine self-efficacy.
- Challenge negative beliefs: Identify thoughts like “I can’t do this” and replace them with positive affirmations.
- Practice self-reflection: Regularly assess your responses to events; understanding triggers helps modify reactions.
- Visualize success: Imagining achieving goals fosters confidence in taking action.
These approaches allow you to reshape perceptions about control over life’s challenges, reinforcing the belief that you drive your destiny.