Imagine having a treasure trove of information right at your fingertips. Internal data examples can unlock insights that drive strategic decisions and enhance operational efficiency. From sales figures to employee performance metrics, the data you collect within your organization holds immense value.
In this article, you’ll discover various internal data examples that can transform how you understand your business landscape. By leveraging these examples, you can identify trends, improve customer satisfaction, and boost overall productivity. Curious about how companies use their internal data effectively? Get ready to explore practical applications and real-world scenarios that show just how powerful this information can be for achieving your goals.
Understanding Internal Data Examples
Internal data encompasses various metrics and information that organizations generate from their operations. You can leverage these examples to enhance decision-making and boost efficiency.
Sales Figures are one of the most common internal data examples. Tracking monthly sales helps identify trends in customer preferences and seasonal demand shifts. For instance, if you notice an increase in sales during the holiday season, it could prompt targeted marketing efforts.
Employee Performance Metrics provide insight into workforce productivity. Analyzing individual performance reviews helps discern strengths and weaknesses within your team. This enables tailored training programs to enhance skills where necessary.
Customer Feedback collected through surveys or support tickets offers another vital example of internal data. By analyzing this feedback, you can pinpoint areas for improvement in products or services, thus increasing customer satisfaction.
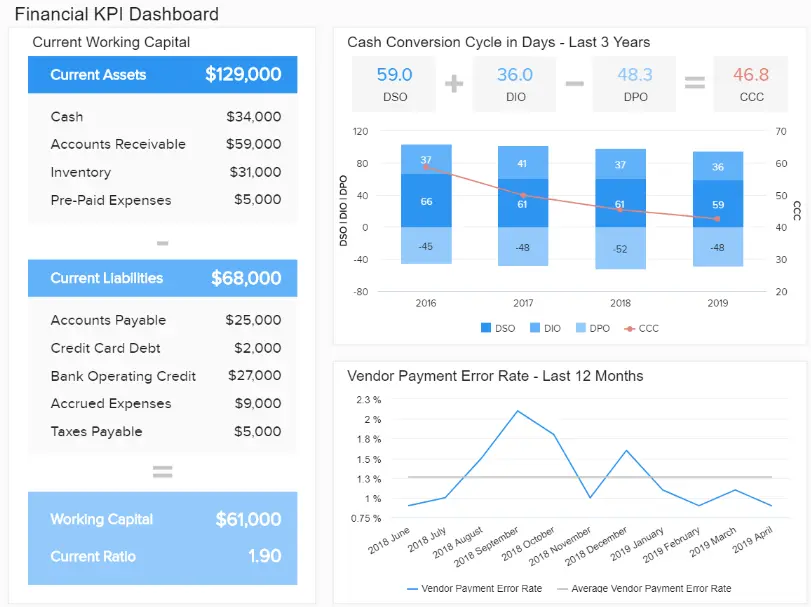
Additionally, Financial Reports, including income statements and balance sheets, illustrate your organization’s financial health over specific periods. Regularly reviewing these reports aids in budget planning and forecasting future growth.
Lastly, Inventory Levels serve as crucial internal data points for businesses with physical products. Monitoring inventory turnover rates ensures you maintain optimal stock levels while minimizing holding costs.
Types of Internal Data Examples
Understanding the various types of internal data helps organizations leverage their resources effectively. Here are some key examples:
Customer Data
Customer data provides insights into preferences and behaviors. You can gather details such as:
- Purchase history: Track what products customers buy over time.
- Demographics: Collect information on age, gender, and location.
- Feedback scores: Analyze customer satisfaction ratings and reviews.
Utilizing this data enhances targeting strategies and improves overall customer experience.
Operational Data
Operational data reflects the efficiency of your processes. Examples include:
- Production metrics: Monitor output levels and production timelines.
- Employee performance records: Assess individual contributions to daily tasks.
- Supply chain statistics: Review inventory turnover rates and delivery times.
This type of internal data enables you to streamline operations and reduce costs.
Financial Data
Financial data is crucial for evaluating organizational health. Key components consist of:
- Revenue reports: Examine sales figures across different periods or segments.
- Expense tracking: Identify where money is spent within departments.
- Budget forecasts: Project future financial scenarios based on historical trends.
Importance of Internal Data Examples
Internal data examples play a crucial role in guiding organizations toward informed decisions and efficient operations. They not only enhance strategic planning but also improve overall performance outcomes.
Decision-Making
Internal data examples provide actionable insights for decision-making. For instance, sales figures can highlight which products are performing well or underperforming. With this information, you can adjust your marketing strategies effectively. Similarly, customer feedback allows you to identify areas needing improvement, ensuring that you’re meeting customer expectations consistently.
Consider these internal data examples for better decision-making:
- Sales Trends: Monthly reports reveal shifts in consumer demand.
- Customer Feedback: Surveys help pinpoint service weaknesses.
- Market Analysis: Competitor benchmarks guide product positioning.
Performance Measurement
Performance measurement relies heavily on internal data examples. Tracking employee productivity metrics helps identify top performers and those needing additional training. This approach leads to a more engaged workforce and higher output levels. Financial reports also serve as essential tools for assessing the effectiveness of various initiatives within your organization.
Key internal data examples for performance measurement include:
- Employee Metrics: Attendance rates indicate engagement levels.
- Project Timelines: Completion rates reflect team efficiency.
- Budget Reports: Expense tracking aids financial health assessments.
Using these internal data examples enables you to create targeted strategies that drive growth and operational success.
How to Collect Internal Data Examples
Collecting internal data examples requires a structured approach that focuses on relevant metrics. Start by identifying key data points essential for your organization. You can consider the following steps:
- Define Objectives: Establish clear goals for what you want to achieve with the internal data.
- Select Sources: Choose reliable sources like customer relationship management (CRM) systems, financial software, or employee performance tools.
- Gather Data: Use surveys, feedback forms, and automated reporting tools to collect information.
Next, analyze the data gathered to extract meaningful insights. For instance:
- Sales Figures: Track daily or monthly sales trends to identify peak purchasing times.
- Employee Performance Metrics: Evaluate productivity rates through regular performance reviews.
- Customer Feedback: Collect and categorize feedback from various channels such as social media or direct surveys.
While collecting this data, ensure consistency in measurement methods for accuracy. You might also want to implement software solutions that automate data collection processes, minimizing human error.
In addition, regularly review and update your internal data collection strategies to adapt to changing business needs. This practice ensures ongoing relevance and reliability of the information collected.
Ultimately, effective internal data examples not only help in decision-making but also drive strategic initiatives within your organization.
Best Practices for Using Internal Data Examples
Using internal data examples effectively can transform your organization’s decision-making process. Here are some best practices to consider:
- Define Your Objectives: Always start by understanding what you want to achieve with the data. Clear goals guide your analysis and ensure you’re focusing on relevant metrics.
- Select Relevant Data Sources: Choose sources that provide accurate and timely information. This might include sales databases, customer feedback platforms, or financial reporting systems.
- Analyze Trends Over Time: Instead of looking at data in isolation, track trends over weeks or months. For instance, monitoring monthly sales figures shows seasonal patterns and shifts in consumer behavior.
- Segment Your Data: Break down data into meaningful segments, such as demographics or purchase history. This segmentation helps tailor marketing strategies to specific audience groups.
- Visualize the Data: Use charts or graphs to present complex data visually. This makes it easier for stakeholders to grasp key insights quickly.
- Regularly Review Insights: Conduct periodic reviews of your findings to adapt strategies based on new information and changing market conditions.
- Incorporate Feedback Loops: Create mechanisms for gathering ongoing feedback from employees and customers about how they’re using the internal data provided.
- Train Employees on Data Utilization: Ensure team members understand how to interpret and leverage internal data examples effectively in their roles.
By applying these best practices, you’ll maximize the value derived from internal data examples while enhancing overall organizational performance.