Imagine a world where factories run seamlessly, energy grids operate efficiently, and transportation systems function without a hitch. This is the reality created by industrial control systems. These sophisticated networks manage everything from assembly lines to power plants, ensuring that processes are streamlined and safe.
In this article, you’ll discover various examples of how industrial control systems play a crucial role in different sectors. From monitoring environmental conditions in agriculture to optimizing production in manufacturing, these systems are vital for enhancing productivity and safety. Have you ever wondered how smart technology influences our everyday lives?
Join us as we explore the fascinating world of industrial control systems and uncover their impact on modern industry. You’ll gain insights into real-world applications that showcase their importance in today’s technological landscape.
Overview of Industrial Control Systems
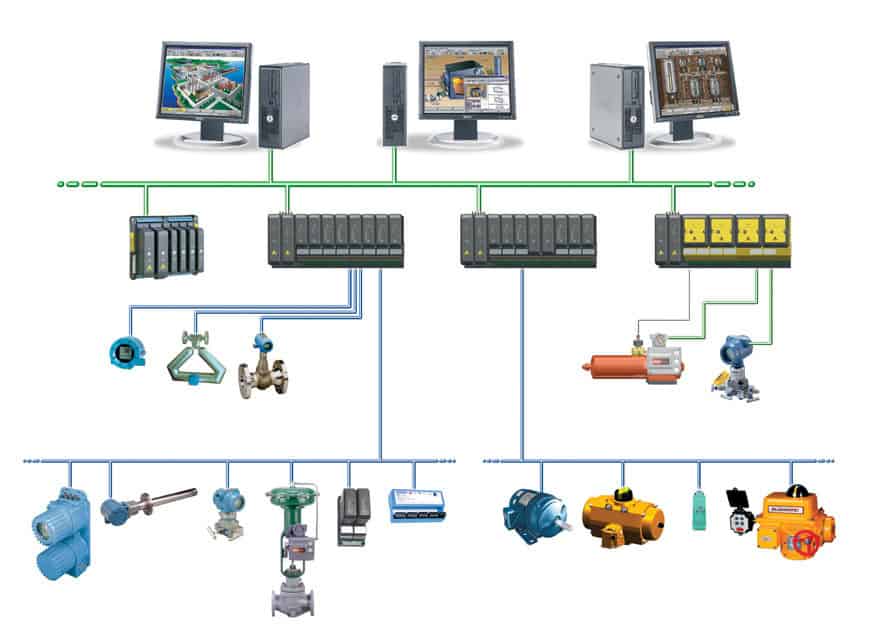
Industrial control systems (ICS) play a critical role in various sectors, ensuring efficient and safe operations. These systems manage processes ranging from manufacturing to energy distribution.
- SCADA Systems: Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems monitor and control industrial processes. They collect real-time data, enabling operators to make informed decisions quickly.
- DCS: Distributed Control Systems (DCS) offer centralized monitoring for complex processes. They provide automated control, improving precision and reliability in operations.
- PLC: Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC) are essential for automation in manufacturing. They’re designed to handle multiple inputs and outputs, making them adaptable for different tasks.
Real-world applications showcase the effectiveness of ICS. For instance, oil refineries use SCADA systems to optimize production efficiency while reducing safety risks. Similarly, water treatment facilities utilize DCS technology to manage chemical dosing accurately.
You might wonder how these technologies impact daily life. Consider smart grids—these utilize ICS to enhance electricity distribution through real-time data analysis, thereby minimizing outages.
Understanding how industrial control systems function can highlight their importance across various industries. Each system type contributes uniquely to operational success and safety standards.
Components of Industrial Control Systems
Industrial control systems (ICS) consist of various essential components that work together to ensure efficient and safe operations. Understanding these components provides insight into how ICS function effectively across different industries.
Sensors and Actuators
Sensors play a critical role in industrial control systems. They collect real-time data from the environment, monitoring variables such as temperature, pressure, and flow rate. For instance:
- Temperature sensors monitor heating processes in manufacturing.
- Pressure sensors track gas levels in pipelines.
- Flow sensors measure fluid movement in water treatment facilities.
Actuators are equally important. They respond to signals from the control system to perform physical actions. Examples include:
- Electric motors driving conveyor belts in assembly lines.
- Pneumatic actuators controlling valves for gas distribution.
- Hydraulic cylinders moving heavy machinery parts.
These components work together to maintain optimal performance within an industrial setting.
Control Logic and Human-Machine Interfaces
Control logic forms the backbone of industrial control systems. It consists of algorithms that process data from sensors and make decisions based on predefined rules. For example:
- A PLC can turn off a machine if it detects overheating.
- SCADA systems adjust energy output based on demand fluctuations.
Human-machine interfaces (HMIs) enable operators to interact with the system easily. HMIs display vital information such as system status or alarms, allowing for quick decision-making. Common features include:
- Touchscreen displays showing real-time data trends.
- Push buttons for manual overrides during emergencies.
You might find that effective HMIs enhance user experience by providing intuitive controls, ultimately improving operational efficiency.
By understanding these core components—sensors, actuators, control logic, and HMIs—you gain valuable insights into how industrial control systems operate seamlessly across various applications.
Types of Industrial Control Systems
Industrial control systems (ICS) come in various forms, each designed to meet specific operational needs. Understanding these types helps you appreciate their roles in enhancing efficiency and safety.
Distributed Control Systems (DCS)
Distributed Control Systems (DCS) manage complex processes across multiple locations. These systems provide centralized monitoring while distributing control functions throughout the network. For example, a chemical plant may use a DCS to monitor reactor temperatures and flow rates from different units, allowing for seamless operation adjustments. This setup minimizes downtime and enhances system reliability by localizing issues quickly.
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC)
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC) play an essential role in automating manufacturing processes. They execute specific control tasks based on programmable instructions. A classic example is automotive assembly lines where PLCs automate robotic arms for tasks like welding or painting. By using PLCs, manufacturers achieve higher precision and productivity while reducing the potential for human error.
Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA)
Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems are vital for real-time monitoring of industrial operations. SCADA collects data from sensors installed throughout facilities, enabling operators to make informed decisions promptly. For instance, water treatment plants utilize SCADA to monitor chemical levels in tanks, ensuring safe drinking water production. This immediate access to data allows for quick responses to any irregularities or equipment failures.
Importance of Industrial Control Systems
Industrial control systems (ICS) play a vital role in enhancing operational processes across various sectors. These systems streamline operations, improve efficiency, and contribute to safety standards.
Enhancing Operational Efficiency
ICS significantly boost productivity by automating various tasks. For example, Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) handle repetitive tasks on assembly lines, allowing for faster production rates. Additionally, Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems monitor multiple processes in real-time, enabling quick adjustments that optimize performance. By using these technologies, industries can reduce waste and lower operational costs.
Furthermore, Distributed Control Systems (DCS) manage complex processes across different locations seamlessly. They centralize monitoring and data analysis which leads to quicker decision-making. As a result, companies experience reduced downtime and improved resource allocation.
Ensuring Safety and Compliance
Safety is paramount in industrial operations. ICS enhance safety measures by closely monitoring environmental conditions. For instance, SCADA systems are used in oil refineries to track pressure levels and prevent dangerous leaks or explosions. This real-time data collection allows for immediate action when issues arise.
Moreover, compliance with industry regulations becomes easier with the implementation of ICS. DCS provide detailed logs of operations that help ensure adherence to safety standards set by authorities like OSHA or EPA. Thus, organizations not only protect their workers but also avoid costly fines associated with non-compliance.
Industrial control systems are essential for improving efficiency while maintaining high safety standards across sectors like manufacturing and energy management.
Future Trends in Industrial Control Systems
Industrial control systems (ICS) are evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancements and changing industry demands. These trends will enhance efficiency, safety, and data management across various sectors.
Integration with IoT and AI Technologies
Integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices and artificial intelligence (AI) technologies is reshaping ICS. IoT enables real-time monitoring by connecting sensors to the internet, allowing for immediate data access. For instance, smart factories utilize IoT devices to track equipment performance and predict failures before they occur. Similarly, AI algorithms analyze large datasets from ICS to optimize processes. An example includes predictive maintenance in manufacturing plants where AI forecasts machinery breakdowns based on historical data.
Cybersecurity Challenges and Solutions
Cybersecurity remains a significant concern for ICS due to increasing connectivity. As more devices connect online, the risk of cyberattacks escalates. Notably, ransomware attacks can disrupt operations or compromise sensitive information. To combat these threats, organizations implement several strategies:
- Regular software updates protect against vulnerabilities.
- Network segmentation limits exposure by isolating critical systems.
- Employee training enhances awareness about phishing schemes.
For example, oil refineries use advanced firewalls and intrusion detection systems to safeguard their networks while ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. Addressing cybersecurity challenges is essential for maintaining operational integrity in industrial environments.