Have you ever wondered how your subconscious beliefs shape your actions? Implicit attitudes can influence everything from your daily choices to your interactions with others, often without you even realizing it. These hidden preferences play a crucial role in how we perceive the world around us and can lead to surprising behaviors.
Understanding Implicit Attitudes
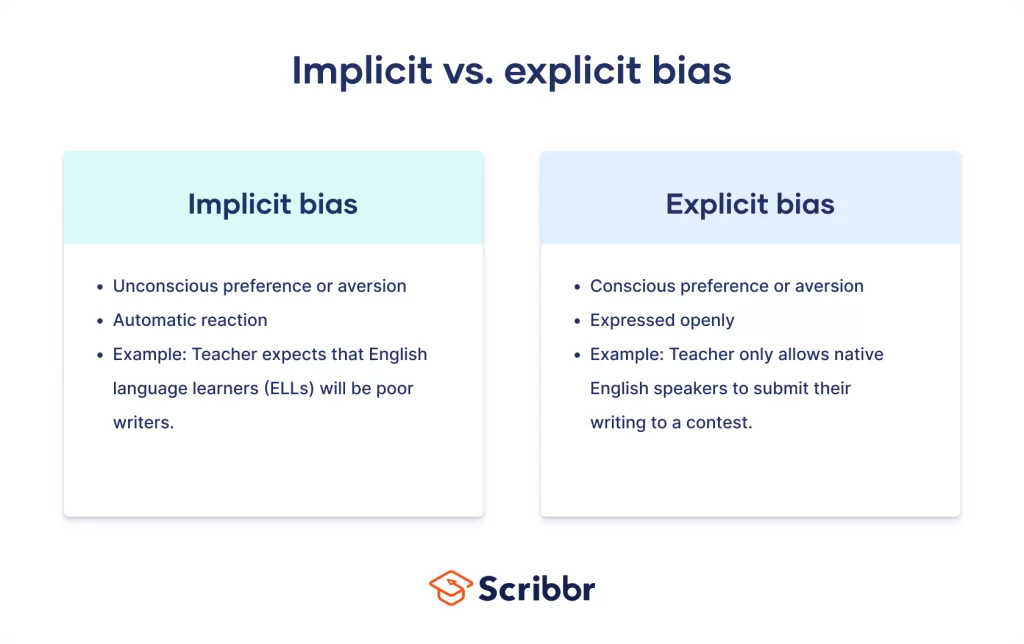
Implicit attitudes refer to the subconscious beliefs that influence your thoughts and behaviors. These attitudes often operate outside of your conscious awareness, impacting decisions you make daily.
Definition and Importance
Implicit attitudes are evaluative judgments about people or situations that occur without conscious thought. They shape how you react to others, influencing everything from hiring practices to social interactions. Recognizing these hidden biases is crucial because they affect societal dynamics and personal relationships, often leading to unintended discrimination or favoritism.
Measurement of Implicit Attitudes
Researchers measure implicit attitudes using various techniques, with the Implicit Association Test (IAT) being among the most common. This test assesses the strength of associations between concepts by analyzing reaction times in pairing words or images. Other methods include:
Understanding these measurement tools helps you gain insight into your own implicit biases and fosters greater self-awareness.
Types of Implicit Attitudes
Implicit attitudes manifest in various contexts, influencing behavior and decision-making. Understanding these types helps recognize their impact on daily life.
Implicit Attitude Example in Social Contexts
In social situations, implicit attitudes often shape how you perceive others. For instance, if you unconsciously associate certain ethnic groups with negative traits, your interactions may reflect that bias. Research shows that these biases can lead to unfair treatment during conversations or group activities. For example, studies indicate that individuals with implicit biases are less likely to engage positively with people from those groups. Recognizing this pattern is crucial for fostering inclusive environments.
Implicit Attitude Example in Consumer Behavior
In consumer settings, implicit attitudes significantly affect purchasing decisions. You might prefer brands associated with positive imagery without realizing it. For example, if a brand uses diverse models in its advertising, research suggests you may develop a more favorable attitude toward the brand itself. Additionally, implicit preferences can influence your choice of products based on packaging or color associations rather than actual quality. These examples illustrate how subconscious beliefs drive consumer choices and market dynamics.
Implicit Attitudes in Psychology Research
Implicit attitudes are critical in understanding how subconscious beliefs shape behavior. These attitudes influence decisions without conscious awareness, impacting everything from workplace dynamics to interpersonal relationships.
Key Studies and Findings
Several studies highlight the significance of implicit attitudes:
- The Implicit Association Test (IAT) demonstrates that people often associate certain groups with positive or negative traits even if they consciously reject these biases.
- Research on hiring practices shows that evaluators may favor candidates who share similar backgrounds, reflecting implicit preferences for familiarity.
- Studies on social interactions reveal that individuals unknowingly exhibit less warmth toward those belonging to stigmatized groups.
These findings illustrate how deeply ingrained implicit biases manifest in everyday situations.
Implications of Findings
Understanding implicit attitudes offers valuable insights into societal issues.
- Recognizing these hidden biases can guide organizations to implement more equitable hiring practices.
- Awareness of your own implicit preferences may foster better communication and collaboration across diverse teams.
- Societal change hinges on addressing these subconscious influences, promoting inclusivity, and reducing discrimination.
By acknowledging and analyzing implicit attitudes, you contribute to a more equitable society.
Real-World Applications
Implicit attitudes play a significant role in various sectors, influencing decisions and behaviors without conscious awareness. Understanding these examples helps you grasp how deeply embedded biases can affect outcomes.
Implicit Attitude Example in Marketing
In marketing, implicit attitudes significantly shape consumer behavior. For instance, consider how advertisements often use diverse representations to resonate with audiences. You might find that when brands showcase people from various backgrounds, they foster positive feelings among consumers.
Additionally, research shows that individuals tend to prefer brands associated with positive imagery or familiarity. This preference occurs even if they consciously believe in equality and inclusivity. Brands like Nike and Dove have effectively leveraged these implicit associations to strengthen their market presence.
Implicit Attitude Example in Education
Education offers another domain where implicit attitudes manifest clearly. Studies reveal that teachers may unconsciously favor students who resemble them based on race or socioeconomic status. This tendency can lead to disparities in academic support and opportunities for minority groups.
Furthermore, classroom dynamics can be influenced by implicit biases regarding gender. For example, girls might receive less encouragement in STEM subjects due to stereotypes about their abilities. Addressing these hidden preferences is crucial for creating equitable educational environments where every student thrives regardless of background or identity.