Have you ever wondered how human activities shape the world around you? Human geography examples reveal the intricate ways people interact with their environment, influencing everything from urban development to cultural landscapes. This fascinating field explores the relationship between humans and their surroundings, highlighting patterns in population distribution, migration, and land use.
Overview Of Human Geography
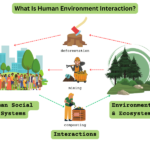
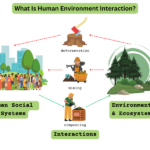
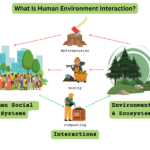
Human geography examines how people interact with their environments. It focuses on various aspects, such as cultural landscapes, which reflect the beliefs and practices of societies. For instance, cities often showcase architecture that represents local history and values.
Population distribution plays a significant role in human geography. You can observe patterns in urban versus rural areas. Urban areas tend to have higher population densities due to economic opportunities and services.
Migration is another crucial aspect of human geography. People move for numerous reasons, including employment, education, or escaping conflict. This movement shapes cultural diversity within regions.
Land use illustrates how humans modify natural landscapes for agriculture, industry, or recreation. For example, agricultural practices vary widely based on climate and terrain but significantly impact local ecosystems.
Economic activities also feature prominently in human geography. Different regions may specialize in specific industries based on available resources or geographic advantages. These economic differences influence social structures and community interactions.
Understanding these elements provides insight into how societies develop over time while shaping their environments uniquely and dynamically.
Key Human Geography Examples
Human geography includes various examples that illustrate how people interact with their environments. Here are some key areas of focus:
Cultural Geography
Cultural geography examines the ways culture shapes and is shaped by geographic spaces. For example, different regions showcase unique architectural styles reflecting local history and traditions. Cities like Paris exhibit Gothic cathedrals, while Tokyo features modern skyscrapers alongside traditional temples. Additionally, festivals such as Rio Carnival or Diwali highlight cultural practices tied to specific locations, emphasizing the connection between culture and place.
Economic Geography
Economic geography studies how economic activities are distributed across different regions. For instance, Silicon Valley in California serves as a global tech hub, concentrating innovative companies like Apple and Google due to favorable conditions for growth. Similarly, oil-rich areas in the Middle East show a concentration of industries reliant on petroleum resources. Regions specializing in agriculture—like Midwest cornfields—demonstrate how land use varies based on available natural resources.
Political Geography
Political geography investigates the relationship between politics and space, shaping boundaries and governance structures. Countries like Canada and the United States exemplify political divisions defined by borders that impact trade relations. Moreover, urban areas often exhibit distinct political districts influenced by socioeconomic factors; for example, New York City has varied voting patterns across its boroughs based on demographics. Lastly, conflicts over territorial claims can be seen in regions like Kashmir where geopolitics drive tensions between nations.
Importance Of Human Geography Examples
Human geography examples play a crucial role in understanding societal dynamics. They provide insights into how people interact with their environments, shaping cultures and economies. You can see this clearly in urban development patterns where cities reflect the social values of their inhabitants.
Population distribution offers another key example. Urban areas often attract larger populations due to job opportunities and better services. For instance, cities like New York and Los Angeles illustrate these trends with their high densities compared to rural settings.
Moreover, migration showcases the fluidity of human geography. People move for various reasons—work, education, or escaping conflict—which enriches cultural diversity. Regions that experience significant migration tend to develop unique cultural blends.
Land use also highlights human impact on geography. Agricultural practices differ based on climate; for example, rice paddies dominate in Southeast Asia while wheat fields are prevalent in North America. These variations affect local ecosystems significantly.
Economic activities further enhance your understanding of human geography examples. Areas like Silicon Valley specialize in technology due to resource availability and skilled labor pools, impacting regional growth and community interactions profoundly.
Political geography reveals how governance structures shape trade relationships and power dynamics between nations. Look at Canada and the U.S.; their shared border influences commerce extensively while regions like Kashmir highlight conflicts arising from territorial disputes.
Recognizing these human geography examples helps you appreciate how societies evolve over time and adapt uniquely to their surroundings.
Applications Of Human Geography In Real Life
Human geography plays a vital role in various aspects of daily life. For instance, consider urban planning. Urban planners utilize human geography to design cities that meet the needs of residents. They analyze population density and cultural patterns to create efficient public transport systems and recreational spaces.
Another example is environmental sustainability. Organizations apply human geography principles to address climate change impacts on communities. By studying land use patterns, they develop strategies for sustainable agriculture or conservation efforts, ensuring resource preservation.
Economic development also benefits from human geography insights. Businesses analyze geographic data to identify market trends and customer demographics. This information influences location decisions, helping companies thrive in specific regions based on local demands.
In education, human geography enhances curriculum development. Teachers incorporate geographical concepts to explain societal issues like migration or urbanization. Students gain a deeper understanding of global interconnections and cultural diversity through these lessons.
Public health initiatives also rely heavily on human geography. Health departments map disease outbreaks geographically to allocate resources effectively. Understanding population distribution aids in targeting healthcare services where they’re most needed.
Additionally, disaster management utilizes human geography for risk assessment. A comprehensive analysis of geographical features allows authorities to prepare better for natural disasters. Planning evacuation routes becomes more effective by knowing which areas are prone to flooding or earthquakes.
Through these applications, you see how relevant human geography remains across different sectors. Its influence shapes policies and practices that directly affect your community and environment every day.