Every day, you interact with your environment in ways that shape both your life and the world around you. From urban development to agriculture, these interactions reveal a fascinating dynamic between humans and nature. Understanding human environment interaction examples can help you appreciate the impact of our choices on ecosystems.
This article explores various real-world scenarios showcasing how people modify their surroundings and adapt to environmental changes. Whether it’s through sustainable practices or industrial advancements, each example highlights our role in shaping the planet. Have you ever considered how your daily actions influence local wildlife or contribute to climate change? Dive into this exploration of human-environment interactions and discover insights that might inspire you to make more conscious decisions for a better future.
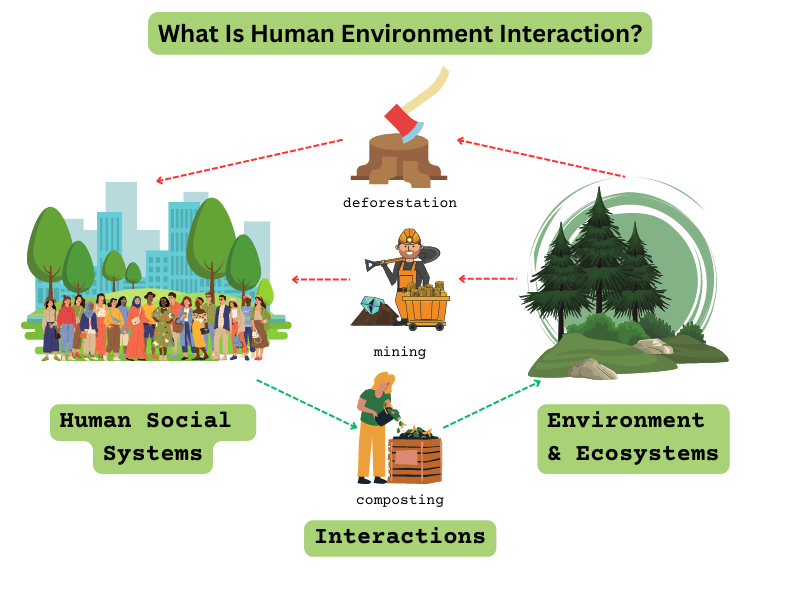
Human Environment Interaction Examples
Human-environment interactions shape our world in many ways. Here are several examples to illustrate this dynamic relationship:
- Urban Development: Cities expand into natural habitats, altering ecosystems. Urban planning involves creating infrastructure like roads and buildings, often displacing wildlife.
- Agricultural Practices: Farming modifies land for food production. Techniques such as crop rotation and organic farming aim to reduce environmental impact while improving soil health.
- Deforestation: Cutting down forests for timber or agriculture significantly affects biodiversity. This practice contributes to habitat loss and can lead to climate change by increasing carbon emissions.
- Water Management: Humans manage water resources through dams and irrigation systems. These structures help control flooding but can disrupt aquatic ecosystems.
- Renewable Energy: Solar panels and wind turbines represent a shift towards sustainable energy sources. They reduce reliance on fossil fuels, lowering greenhouse gas emissions.
- Waste Management: Recycling programs encourage responsible disposal of materials, minimizing landfill use. Proper waste management reduces pollution and its impact on local environments.
These examples highlight how human actions influence the environment, showcasing both positive advancements and negative consequences. Understanding these interactions can drive more sustainable choices in daily life.
Types of Human Environment Interactions
Human interactions with the environment vary significantly across different contexts. Each type demonstrates unique adaptations and impacts that shape both ecosystems and human societies.
Agriculture and Land Use
Agriculture significantly transforms land for food production. Farmers clear forests or wetlands to create arable land, often leading to habitat destruction. However, sustainable practices like crop rotation and organic farming aim to minimize negative effects on the environment. For instance, agroforestry integrates trees into agricultural landscapes, enhancing biodiversity while providing crops.
Urban Development and Infrastructure
Urban development reshapes natural landscapes through infrastructure projects. Cities expand by constructing roads, buildings, and other facilities. This expansion often disrupts local ecosystems but can also lead to improved public services. Green spaces within urban areas help mitigate pollution and provide habitats for wildlife. Additionally, smart city initiatives focus on integrating technology with sustainability goals.
Conservation and Environmental Protection
<strongConservation efforts address environmental degradation caused by human activities. Protected areas such as national parks preserve biodiversity while allowing for recreational use. Initiatives like reforestation enhance carbon sequestration, combating climate change effects. Community-led conservation programs empower local populations to manage resources sustainably, ensuring ecological balance while promoting economic growth.
Impact of Human Environment Interactions
Human-environment interactions significantly shape both your life and the ecosystem. Understanding these impacts is crucial for making informed decisions.
Positive Effects
Human activities can lead to beneficial changes in the environment. For instance, sustainable agriculture practices, like crop rotation and organic farming, enhance soil health while producing food. Additionally, urban green spaces, such as parks and community gardens, improve air quality and provide habitats for wildlife. You might also notice that renewable energy initiatives, including solar and wind farms, reduce reliance on fossil fuels, lessening pollution levels.
- Sustainable agriculture improves soil health.
- Urban green spaces enhance biodiversity.
- Renewable energy reduces carbon emissions.
Negative Effects
However, not all human-environment interactions are positive. Urban development often results in habitat destruction as cities expand. This leads to the loss of biodiversity and disrupts local ecosystems. Moreover, deforestation contributes to increased carbon emissions while diminishing natural habitats for many species. Water management projects like dams can alter river ecosystems, impacting fish populations and water quality.
- Urban expansion destroys habitats.
- Deforestation increases carbon footprint.
- Water management affects aquatic life.
Recognizing these impacts helps you appreciate the delicate balance between progress and preservation in your environment.
Case Studies of Human Environment Interaction
Human-environment interactions manifest in various ways. These case studies highlight specific practices that illustrate the dynamic relationship between people and their surroundings.
Forest Management Practices
Forest management practices aim to balance ecological health with human needs. Sustainable logging techniques, such as selective cutting, minimize environmental impact. They allow for forest regeneration while providing timber resources. Reforestation efforts also play a critical role by restoring degraded areas and improving biodiversity. Additionally, community-based forest management encourages local stewardship, ensuring that conservation aligns with economic benefits for the residents.
Coastal Zone Management
Coastal zone management focuses on protecting coastal ecosystems while accommodating development. Strategies include implementing buffer zones to reduce erosion and protect habitats. Integrated Coastal Zone Management (ICZM) promotes coordinated efforts among stakeholders to address issues like pollution and habitat loss. Moreover, restoring wetlands enhances water quality and provides flood protection. By balancing human activities with environmental preservation, effective coastal management fosters resilience against climate change impacts.