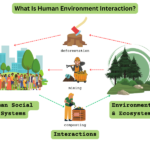
Imagine walking through a bustling city where towering skyscrapers meet lush parks. This dynamic relationship between people and nature is known as human environment interaction. It shapes our daily lives, influencing everything from urban planning to conservation efforts.
In this article, you’ll explore various examples of how humans interact with their surroundings. From agriculture transforming landscapes to the impact of climate change on communities, these interactions reveal both challenges and opportunities. Ever wondered how your choices affect the environment?
Get ready to dive into real-world scenarios that highlight the delicate balance we must maintain between development and sustainability. Understanding human environment interaction isn’t just academic; it’s essential for building a better future for ourselves and the planet.
Overview of Human Environment Interaction
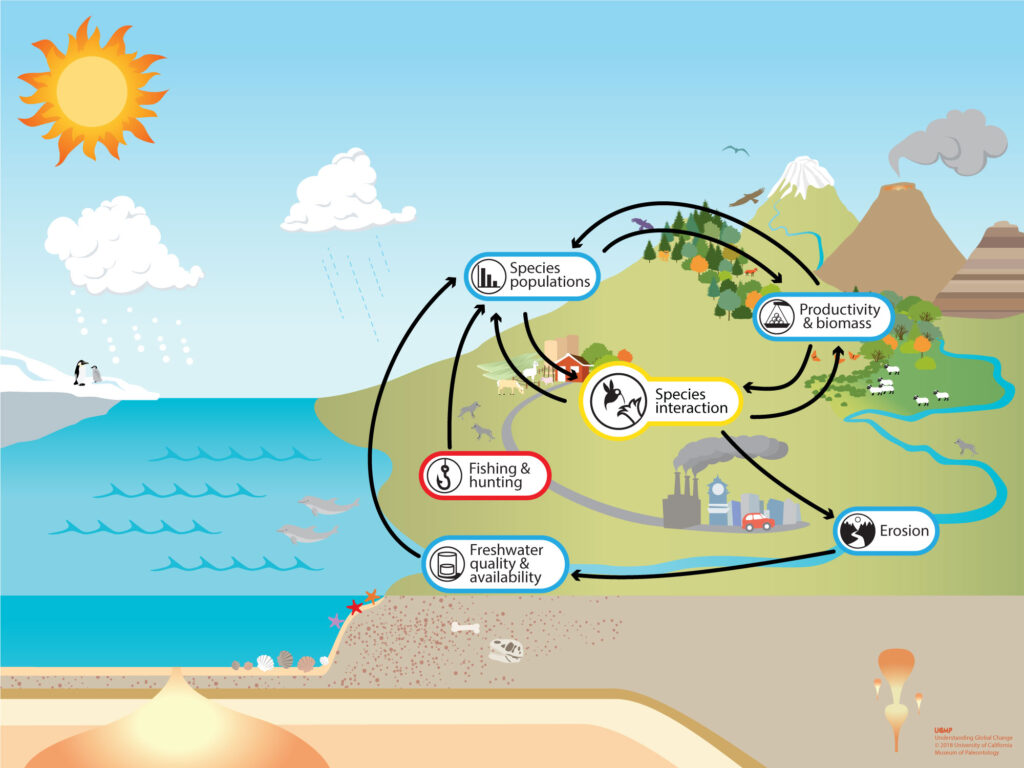
Human environment interaction encompasses various activities that highlight how people affect and are affected by their surroundings. Urban development shapes city landscapes as infrastructure like roads, bridges, and buildings emerge. These developments often lead to increased pollution and habitat loss.
Agriculture serves as another prime example. Cultivating crops alters local ecosystems. Farmers clear forests for fields, which impacts biodiversity. Crop choices also dictate water usage and soil health.
Moreover, climate change exemplifies the effects of this interaction on communities. <strong Rising temperatures influence weather patterns, leading to severe droughts or floods in certain areas. Communities face challenges adapting to these changes while striving for sustainable solutions.
Conservation efforts represent a proactive response to human-environment interactions. Preserving natural habitats supports wildlife and maintains ecological balance. Initiatives like reforestation help combat deforestation’s effects.
Human environment interactions showcase a dynamic relationship with complex implications for society and nature alike. Each decision made today influences tomorrow’s environmental landscape significantly.
Historical Context
Human-environment interaction has evolved significantly over time, shaping societies and ecosystems. Understanding this history provides insight into current challenges and opportunities.
Ancient Civilizations
Ancient civilizations exemplified early human-environment interactions. For instance, the Mesopotamians developed irrigation systems to manage water from rivers for agriculture. They modified landscapes, enabling crop cultivation in arid regions. Similarly, the Mayan civilization practiced slash-and-burn agriculture, impacting tropical forests while supporting their communities.
You can also observe how Egyptians utilized the Nile River for farming. The river’s predictable flooding enriched soil, fostering a thriving agricultural society that relied heavily on this natural resource.
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution marked a turning point in human-environment interaction. This period saw rapid urbanization as factories emerged, leading to increased pollution and habitat destruction. Cities expanded quickly due to migration from rural areas seeking work in industries.
Additionally, advancements in transportation transformed landscapes. Railroads facilitated timber extraction and mining activities that decimated forests and ecosystems. Urban air quality declined sharply due to emissions from coal-burning factories, affecting public health drastically.
Overall, both ancient civilizations and the Industrial Revolution reflect significant shifts in how humans interact with their environments—shaping our modern world while posing ongoing environmental challenges.
Modern Impacts
Human-environment interaction has evolved significantly, with modern impacts shaping both urban landscapes and natural ecosystems. This section explores two critical aspects: urbanization and climate change.
Urbanization
Urbanization dramatically alters environments. As cities expand, they consume land that once supported diverse ecosystems. Urban sprawl leads to habitat destruction, forcing wildlife into smaller areas. For instance, in the United States, over 80% of the population lives in urban areas, resulting in increased pressure on surrounding habitats. The construction of roads and buildings contributes to air pollution and heat islands while reducing green spaces essential for biodiversity. What happens when cities grow without planning? Increased flooding risks arise due to inadequate drainage systems overwhelmed by stormwater runoff.
Climate Change
Climate change presents significant challenges linked to human actions. Rising global temperatures disrupt weather patterns, leading to extreme events like hurricanes and droughts. For example, studies show that sea levels have risen about 8 inches since 1880 due to melting ice caps and thermal expansion of seawater. These changes threaten coastal communities and agriculture alike. Additionally, changing rainfall patterns affect water availability for farming—what does this mean for food security? It may lead to increased prices or shortages as farmers struggle to adapt their practices amid shifting conditions.
Understanding these impacts helps you see how your daily choices intersect with broader environmental issues.
Cultural Perspectives
Cultural perspectives significantly influence human-environment interactions. Different societies adapt uniquely to their surroundings, demonstrating this relationship through various practices and beliefs.
Indigenous Practices
Indigenous communities often showcase sustainable methods that respect natural ecosystems. For instance, the Hopi tribe in Arizona employs dryland farming techniques, using traditional knowledge to cultivate crops like corn and beans without depleting water resources. Similarly, the Maasai people of East Africa practice rotational grazing, which allows grasslands to recover while supporting livestock health. These practices highlight a deep understanding of local environments and foster biodiversity conservation.
Western Approaches
Western approaches often reflect industrialization’s impact on nature. Urban planning emphasizes infrastructure development but frequently overlooks environmental consequences. For example, cities like Los Angeles prioritize automobile use, leading to significant air pollution and urban sprawl. In contrast, initiatives such as green architecture promote eco-friendly designs in buildings that minimize energy consumption and maximize natural light. This shift towards sustainability indicates a growing awareness of balancing development with ecological preservation.
By examining both indigenous practices and western approaches, you can appreciate how diverse cultural perspectives shape our interactions with the environment.
Future Challenges and Solutions
Human-environment interaction faces numerous challenges that demand innovative solutions. Rapid urbanization, resource depletion, and climate change shape the future landscape. Addressing these issues requires a multifaceted approach.
Sustainable Development
Sustainable development focuses on meeting present needs without compromising future generations. This involves balancing economic growth with environmental protection. For instance:
- Green infrastructure: Cities increasingly adopt green roofs and permeable pavements to manage stormwater effectively.
- Renewable energy sources: Solar and wind power reduce reliance on fossil fuels, decreasing carbon emissions.
- Sustainable agriculture practices: Techniques like agroforestry enhance biodiversity while maintaining productivity.
These initiatives illustrate how communities can adapt sustainably.
Technological Innovations
Technological innovations drive progress in human-environment interactions. Emerging technologies offer tools for reducing negative impacts. Consider these examples:
- Smart cities: Utilizing sensors and data analytics optimizes energy use and improves traffic management.
- Precision agriculture: Drones and soil sensors enable farmers to monitor crop health closely, minimizing waste.
- Waste-to-energy processes: Converting waste into energy reduces landfill usage while generating power.
These advancements highlight the potential for technology to facilitate sustainable practices in everyday life.