In today’s fast-paced business world, understanding your workforce is crucial for success. That’s where HR metrics come into play. These powerful tools help you measure and analyze employee performance, engagement, and retention, allowing you to make informed decisions that drive organizational growth.
But what exactly are HR metrics? Think of them as the key indicators that reveal how well your human resources strategies are performing. From tracking turnover rates to assessing training effectiveness, these metrics provide invaluable insights into your company’s health. Are you ready to unlock the potential of your workforce?
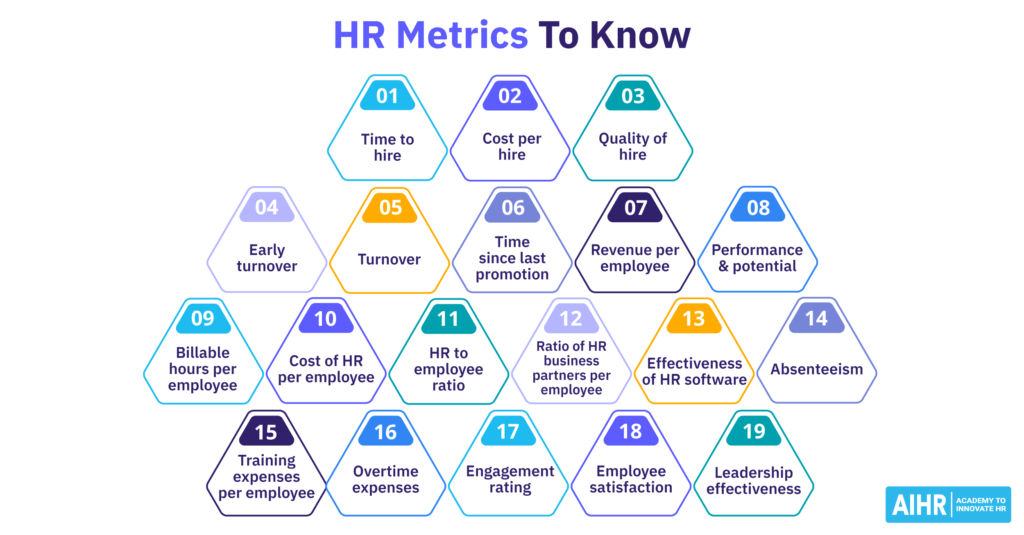
Overview of HR Metrics
HR metrics serve as essential tools for understanding workforce dynamics. They provide valuable insights into employee performance, engagement, and retention. For example, consider the following key HR metrics:
- Turnover Rate: This measures the percentage of employees leaving within a specific period. A high turnover rate might indicate issues with workplace culture or job satisfaction.
- Employee Engagement Score: Surveys can gauge how motivated employees feel at work. Higher scores typically correlate with better productivity and lower absenteeism.
- Training Effectiveness: By assessing improvements in employee skills post-training, organizations can determine if their training programs are beneficial.
These examples show how each metric contributes to more informed decision-making in human resources. With clear data, you can identify areas for improvement and implement strategies that enhance overall organizational performance.
Importance of HR Metrics
HR metrics play a crucial role in shaping effective human resource strategies. These metrics provide insights that drive organizational success by highlighting trends and areas for improvement.
Enhancing Decision-Making
HR metrics empower you to make data-driven decisions. For instance, tracking turnover rates helps identify patterns related to employee departures and potential cultural issues. By analyzing these trends, you can implement targeted retention strategies, such as improving onboarding processes or enhancing employee engagement initiatives. Additionally, monitoring employee performance scores allows for better allocation of resources and identifying high-potential employees for leadership roles.
Measuring Employee Performance
Measuring employee performance through specific HR metrics provides clarity on workforce effectiveness. For example, using the employee engagement score derived from regular surveys gives a clear picture of motivation levels within the team. Higher engagement typically translates into increased productivity and lower absenteeism. Furthermore, assessing training effectiveness through pre- and post-training evaluations ensures that your training programs deliver value. This systematic approach allows you to refine programs continually based on measurable outcomes.
Types of HR Metrics
HR metrics can be categorized into several types that provide insights into different aspects of workforce management. Understanding these metrics helps you make informed decisions and enhances organizational effectiveness.
Recruitment Metrics
Recruitment metrics evaluate the efficiency of your hiring processes. Examples include:
- Time to Fill: Measures the number of days taken to fill a position, reflecting the efficiency of recruitment.
- Cost per Hire: Calculates total hiring costs, including advertising, agency fees, and candidate travel expenses.
- Quality of Hire: Assesses new employee performance over time to determine how well they fit within the organization.
Employee Engagement Metrics
Employee engagement metrics gauge how committed and motivated your employees are. Key examples consist of:
- Employee Engagement Score: Derived from surveys assessing job satisfaction and commitment levels among staff.
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): Evaluates whether employees would recommend your company as a workplace to others.
- Participation Rate in Surveys: Indicates how many employees engage in feedback processes, providing insights into overall sentiment.
Retention Metrics
Retention metrics focus on employee turnover and retention strategies. Important examples include:
- Turnover Rate: Measures the percentage of employees leaving within a specific timeframe, indicating potential issues in workplace culture or job satisfaction.
- Retention Rate: Reflects the percentage of employees who remain with the company over time, highlighting successful retention strategies.
- Average Tenure: Calculates the average duration employees stay at your organization, helping identify trends related to employee loyalty.
By monitoring these HR metrics closely, you can gain valuable insights that guide strategic planning and improve overall workforce management.
Implementing HR Metrics
Implementing HR metrics involves systematic steps to ensure accurate data collection and insightful analysis. These steps empower organizations to enhance their human resources strategies effectively.
Data Collection Methods
Effective data collection sets the foundation for meaningful HR metrics. Consider these methods:
- Surveys: Use employee engagement surveys to gather feedback on job satisfaction.
- Interviews: Conduct one-on-one interviews for in-depth insights into employee experiences.
- Performance Reviews: Analyze performance evaluations to track individual progress over time.
- HR Software: Utilize integrated HR systems that automatically record relevant data, such as attendance and turnover rates.
Each method serves a specific purpose in building a comprehensive view of your workforce dynamics.
Analyzing HR Metrics
Analyzing HR metrics transforms raw data into actionable insights. Focus on these key areas:
- Trend Analysis: Examine changes in turnover rates over multiple quarters to identify potential issues.
- Benchmarking: Compare your employee engagement scores against industry standards to gauge competitive positioning.
- Predictive Analytics: Use historical data trends to forecast future retention challenges or hiring needs.
By employing these analytical techniques, you can tailor your strategies based on concrete evidence rather than assumptions. This approach enhances decision-making and drives organizational success through focused interventions.
Challenges in HR Metrics
Challenges in HR metrics impact how effectively organizations can utilize data to drive decisions. Understanding these challenges helps you navigate the complexities of workforce management.
Data Privacy Concerns
Data privacy concerns present significant challenges when collecting and analyzing HR metrics. Organizations must protect sensitive employee information while maintaining compliance with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA. For instance, if an employee’s engagement score is linked to identifiable information, sharing that data without consent may lead to legal repercussions. Thus, implementing secure data handling practices becomes essential for safeguarding personal information.
Interpretation of Data
Interpreting data correctly poses another challenge in leveraging HR metrics effectively. Misinterpretation can lead to misguided conclusions about workforce dynamics. For example, a high turnover rate might seem alarming at first glance; however, it could indicate a positive change if many employees are moving on for better opportunities elsewhere. Therefore, context plays a crucial role in understanding what the metrics reveal about your organization’s health and performance trends.