Ever wondered how tiny organisms can impact your health? Good bacteria vs bad bacteria is a fascinating battle playing out in our bodies every day. These microorganisms are more than just invisible invaders; they play crucial roles in digestion, immunity, and overall well-being. Understanding the difference between these two types of bacteria can empower you to make better choices for your health.
Good Bacteria vs Bad Bacteria: An Overview
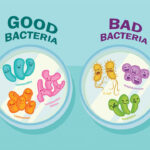
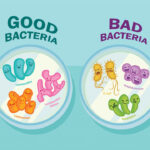
Good bacteria, known as probiotics, play a vital role in your body. They help with digestion and strengthen your immune system. For example, Lactobacillus is found in yogurt and helps break down lactose, making dairy easier to digest for many people. Another beneficial strain is Bifidobacterium, which supports gut health by balancing harmful bacteria.
In contrast, bad bacteria can cause illness and infections. Escherichia coli (E. coli) includes some strains that lead to food poisoning if ingested through contaminated food or water. Furthermore, Staphylococcus aureus can result in skin infections and respiratory issues when it enters the body.
You might wonder how to maintain a healthy balance between these microorganisms. Incorporating fermented foods like kefir or kimchi into your diet introduces good bacteria while reducing sugar intake limits growth of harmful ones. Regular exercise also contributes positively by enhancing overall gut health.
Are you aware of the signs that indicate an imbalance? Symptoms such as digestive issues, fatigue, or frequent infections may suggest that bad bacteria are overpowering the good ones in your system. Keeping track of how you feel after meals can offer valuable insights into your body’s bacterial landscape.
Understanding this balance empowers you to make healthier choices daily. By focusing on foods rich in probiotics while being cautious about processed items high in sugar and fat, you promote a thriving environment for beneficial microbes within your gut.
Understanding Bacteria
Bacteria are microscopic organisms that exist everywhere, including inside your body. They can be beneficial or harmful, impacting health in various ways.
What Are Bacteria?
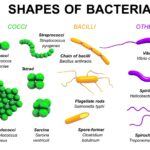
Bacteria are single-celled organisms that lack a nucleus and reproduce by dividing. They come in different shapes, such as rods (bacilli), spheres (cocci), and spirals (spirilla). You might find bacteria in soil, water, and even on your skin. Some bacteria aid digestion and boost immunity. Others cause diseases like food poisoning or infections.
Types of Bacteria
Bacteria fall into two main categories: good bacteria and bad bacteria.
- Good Bacteria: These include probiotics like Lactobacillus found in yogurt or Bifidobacterium present in fermented foods. They help maintain gut health and support the immune system.
- Bad Bacteria: Examples include Escherichia coli (certain strains) linked to foodborne illness and Staphylococcus aureus, which can cause skin infections.
You should know these examples to understand how they affect health differently. Balancing both types is crucial for overall well-being.
Good Bacteria and Their Benefits
Good bacteria, known as probiotics, provide essential support for your health. They contribute to various bodily functions that enhance well-being. Understanding their benefits helps in making informed dietary choices.
Role in Digestion
Good bacteria play a crucial role in digestion. They help break down food, making nutrients more accessible for absorption. For instance, Lactobacillus species are found in yogurt and aid lactose digestion. Additionally, Bifidobacterium strains support fiber breakdown, promoting regular bowel movements. Including fermented foods like sauerkraut or kefir can boost these beneficial bacteria.
Immune System Support
Good bacteria significantly strengthen the immune system. They enhance the production of antibodies and stimulate immune cells, which combat infections effectively. Research shows that individuals with higher levels of probiotics experience fewer colds and infections. Foods rich in good bacteria include kimchi and miso soup, both of which can improve your body’s defense mechanisms against pathogens.
Bad Bacteria and Their Impact
Bad bacteria can significantly affect your health, leading to various diseases and complications. Understanding their impact helps you make informed choices to protect your well-being.
Common Diseases Caused by Bad Bacteria
Several common diseases stem from harmful bacteria. Here are some examples:
- Foodborne Illnesses: Certain strains of E. coli and Salmonella can cause severe gastrointestinal distress.
- Staph Infections: Staphylococcus aureus may lead to skin infections, pneumonia, or bloodstream infections.
- Tuberculosis (TB): Caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, TB affects the lungs and can be fatal if untreated.
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Often caused by Escherichia coli, UTIs can result in pain and discomfort during urination.
These conditions highlight the importance of hygiene and proper food handling practices to minimize exposure to bad bacteria.
Resistance to Antibiotics
Resistance to antibiotics poses a significant challenge in treating bacterial infections. When bad bacteria evolve, they develop mechanisms that render antibiotics ineffective. This resistance occurs due to:
- Overprescribing Antibiotics: Excessive use contributes to antibiotic resistance.
- Incomplete Treatment Courses: Stopping medication early allows surviving bacteria to adapt.
- Use in Agriculture: Applying antibiotics on livestock promotes resistant strains that can transfer to humans.
As a result, infections become harder to treat, increasing healthcare costs and risks of complications. Staying informed about antibiotic use is essential for preventing resistance.
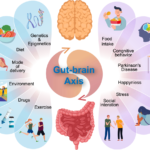
The Balance of Bacteria in Our Bodies
Bacteria play a crucial role in maintaining health, and achieving a balance between good and bad bacteria is essential. This equilibrium affects digestion, immunity, and overall well-being.
Factors Affecting Bacterial Balance
Several factors influence the balance of bacteria within your body. Understanding these can help you make informed lifestyle choices:
- Diet: A diet rich in fiber from fruits, vegetables, and whole grains promotes good bacteria. Conversely, high sugar intake can feed harmful bacteria.
- Antibiotics: While antibiotics target bad bacteria, they can also eliminate beneficial ones. It’s important to use them only when necessary.
- Stress: Chronic stress impacts gut health by altering bacterial composition. Managing stress through mindfulness or exercise supports a healthier microbiome.
- Sleep: Quality sleep helps maintain hormonal balance and supports immune function, which indirectly fosters beneficial bacteria.
By recognizing these factors, you can take proactive steps to encourage a healthy bacterial environment in your body.