Imagine a world where diseases are treated with precision-engineered solutions. GMOs in medicine are transforming healthcare by providing innovative treatments that were once thought impossible. From genetically modified bacteria producing insulin to crops designed to combat malnutrition, the applications of GMOs extend far beyond agriculture.
You might wonder how these advancements impact your health and well-being. This article explores fascinating examples of GMOs in medicine, showcasing their role in drug production, vaccine development, and even gene therapy. Understanding the benefits and challenges of GMOs can empower you to make informed decisions about your health. Dive into this captivating topic and discover how biotechnology is shaping the future of medicine.
Overview of GMOs in Medicine
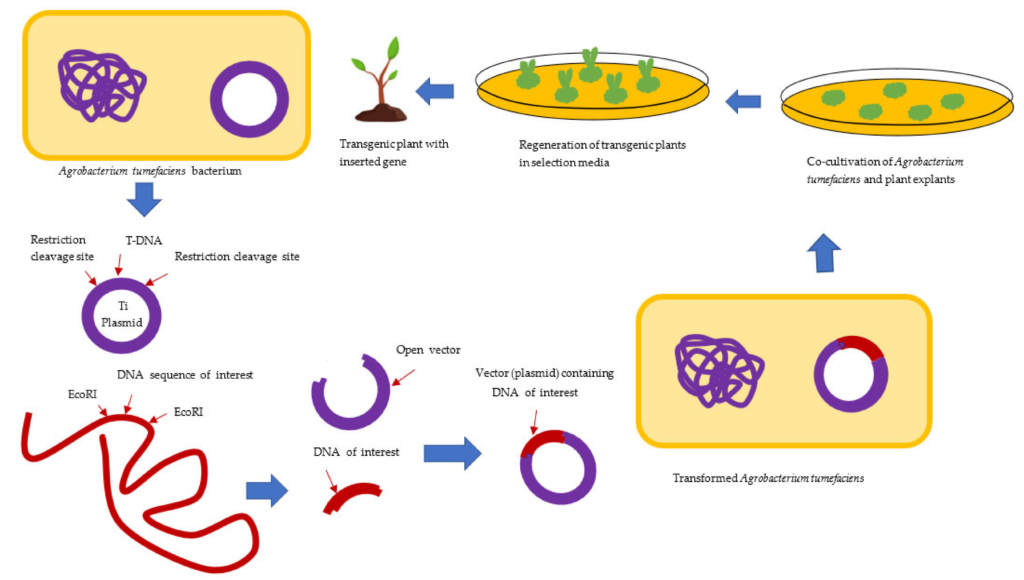
GMOs play a pivotal role in modern medicine, showcasing their potential to revolutionize healthcare. For instance, genetically modified bacteria produce insulin for diabetes management. This innovation enhances the efficiency and availability of insulin, making treatment more accessible.
Another notable example is the use of genetically engineered crops. These crops can increase nutrient content, addressing issues like malnutrition. Crops enriched with vitamins are being developed to combat deficiencies in populations where access to diverse foods is limited.
Moreover, some vaccines utilize GMOs for improved efficacy. The hepatitis B vaccine incorporates genetically modified yeast to produce the virus’s surface protein. This process leads to safer and more effective vaccination options.
In the realm of gene therapy, GMOs facilitate groundbreaking treatments for genetic disorders. Techniques such as CRISPR allow precise modifications at the DNA level, potentially curing conditions like cystic fibrosis or sickle cell anemia.
You might also consider how monoclonal antibodies produced by genetically modified cells provide targeted therapies for diseases such as cancer. These antibodies specifically attack cancer cells while sparing healthy ones.
With ongoing advancements and research into GMOs in medicine, you see opportunities for better health outcomes on the horizon. Understanding these examples helps grasp how biotechnology shapes future medical practices and patient care.
Applications of GMOs in Medical Treatments
GMOs play a crucial role in modern medicine, providing innovative solutions for various health issues. Their applications range from gene therapy to vaccine development.
Gene Therapy
Gene therapy represents a groundbreaking method for treating genetic disorders. This approach involves modifying genes to correct defects or provide new functions. For instance, CRISPR technology enables precise editing of DNA, allowing scientists to tackle conditions like cystic fibrosis and sickle cell anemia. In addition, clinical trials have shown promise with therapies that replace faulty genes or deliver healthy copies into cells. You might wonder about the future impact; experts believe these advancements could lead to cures for previously untreatable diseases.
Vaccine Development
Vaccine development has significantly benefited from GMOs, enhancing both safety and effectiveness. One notable example is the hepatitis B vaccine, which utilizes genetically modified yeast to produce the hepatitis B surface antigen. This process results in a safer vaccine with fewer side effects compared to traditional methods. Moreover, researchers are exploring mRNA vaccines like those developed for COVID-19; these vaccines instruct cells to produce viral proteins that trigger immune responses without using live virus particles. Such innovations demonstrate how GMOs contribute substantially to public health initiatives and disease prevention efforts.
By understanding these applications of GMOs in medical treatments, you can appreciate their transformative impact on healthcare today and into the future.
Benefits of GMOs in Medicine
GMOs provide significant advantages in the medical field, enhancing treatment options and patient outcomes. Here are some key benefits:
Improved Efficacy
GMOs increase the effectiveness of treatments across various conditions. For example, genetically modified bacteria produce insulin that’s purer and more effective for diabetes management. Additionally, monoclonal antibodies derived from genetically engineered cells target specific cancer cells with higher precision. This targeted approach minimizes damage to healthy cells while maximizing therapeutic effects.
Other examples include vaccines like the hepatitis B vaccine, which utilizes genetically modified yeast for safer production. These innovations lead to better health outcomes by ensuring that medications are both potent and reliable.
Cost-Effectiveness
Utilizing GMOs can lower healthcare costs significantly. Genetically engineered crops, such as biofortified varieties, improve nutritional content without increasing food prices. Moreover, producing drugs through GMOs often reduces manufacturing costs due to streamlined processes.
For instance:
- Insulin Production: Recombinant DNA technology allows for large-scale insulin production at a fraction of traditional methods’ cost.
- Vaccines: mRNA vaccines developed from GMOs have demonstrated rapid development timelines and reduced expenses compared to conventional vaccine production methods.
This cost savings translates into affordable treatments for patients worldwide, making essential therapies accessible to those who need them most.
Challenges and Concerns
GMOs in medicine present various challenges and concerns that require careful consideration. These issues primarily relate to ethical considerations and public perception.
Ethical Considerations
Ethical dilemmas arise when modifying organisms for medical purposes. For instance, gene editing techniques like CRISPR raise questions about consent, especially regarding inheritable changes. You might wonder if future generations should bear the consequences of today’s genetic modifications. Furthermore, the use of GMOs in therapies often involves animals or human trials, prompting debates about animal rights and the moral implications of experimenting on living beings.
Public Perception
Public perception significantly influences the acceptance of GMOs in medicine. Many people express skepticism towards genetically modified products due to safety concerns or misinformation. Surveys indicate that a considerable percentage of individuals associate GMOs with potential health risks. This perception affects regulatory policies and can hinder research funding. Additionally, media coverage often highlights negative aspects while neglecting positive outcomes, contributing to distrust in GMO innovations within healthcare settings.
By addressing these challenges head-on, stakeholders can foster informed discussions around GMOs’ role in medicine.
Future Prospects of GMOs in Medicine
Genetically modified organisms (GMOs) hold significant potential for the future of medicine. Their applications continue to expand, offering innovative solutions for various health challenges. Here are some promising examples:
- Gene therapy advancements: Techniques like CRISPR enable precise edits to DNA, targeting disorders such as muscular dystrophy and hemophilia. These innovations could transform how genetic conditions are treated.
- Personalized medicine: GMOs can facilitate tailored treatments based on individual genetic profiles. This approach enhances treatment efficacy and reduces adverse effects by aligning therapies with specific patient needs.
- Vaccine development: The use of GMOs in vaccine production is evolving rapidly. For instance, mRNA vaccines demonstrate a swift response to emerging infectious diseases, showcasing adaptability in global health crises.
- Enhanced diagnostics: Genetically engineered microbes can serve as biosensors for detecting diseases early. Such tools improve disease management through timely interventions.
- Production of biopharmaceuticals: GMOs streamline the manufacturing process for critical medications like monoclonal antibodies, making them more accessible and affordable.
As you consider these advancements, it’s clear that the future prospects of GMOs in medicine promise not only enhanced treatments but also improved patient outcomes across diverse healthcare fields.