Fungi and bacteria are examples of organisms that play crucial roles in our ecosystems. Have you ever wondered how these tiny life forms impact everything from soil health to human medicine? Both fungi and bacteria are essential for nutrient cycling, decomposition, and even food production.
Fungi and Bacteria Are Examples Of Microorganisms
Fungi and bacteria are crucial components of the microbial world. They play significant roles in various processes that sustain life on Earth.
Fungi include organisms like molds, yeast, and mushrooms. These fungi decompose organic matter, returning nutrients to the soil. For instance:
- Mushrooms break down wood and other plant materials.
- Yeast aids in fermentation, producing bread and alcoholic beverages.
Bacteria encompass a vast range of single-celled organisms. They exist in diverse environments, from soil to human intestines. Key examples include:
- Lactobacillus, found in yogurt, supports digestive health.
- Nitrogen-fixing bacteria enhance soil fertility by converting atmospheric nitrogen into usable forms.
Both fungi and bacteria contribute to nutrient cycling within ecosystems. Without them, organic matter would accumulate, disrupting ecological balance. Their ability to break down complex substances is vital for sustaining life.
You may wonder about their impact on human health too. Certain fungi produce antibiotics like penicillin, which revolutionized medicine. Similarly, beneficial bacteria help maintain gut flora balance.
Fungi and bacteria are more than just microorganisms; they’re essential for ecosystem functionality and human health maintenance.
Characteristics of Fungi
Fungi display unique characteristics that set them apart from other organisms. Understanding these traits provides insight into their vital roles in ecosystems and human applications.
Structure and Composition
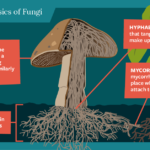
Fungi consist of a network of filaments called hyphae, which form a mass known as mycelium. This structure allows fungi to efficiently absorb nutrients from the environment. The cell walls contain chitin, making them distinct from plant cells that have cellulose. Additionally, fungi can exist as single-celled organisms like yeasts or multicellular forms such as molds and mushrooms.
Reproductive Methods
Fungi reproduce through various methods, ensuring their survival and adaptation. They primarily use spores for reproduction, which can be dispersed by wind or water. Some fungi engage in sexual reproduction, combining genetic material to create diverse offspring. Others reproduce asexually by budding or fragmentation, allowing quick population growth under favorable conditions. Such versatility enables fungi to thrive in numerous environments.
Characteristics of Bacteria
Bacteria exhibit unique features that distinguish them from other microorganisms. Understanding these characteristics is essential for recognizing their roles in ecosystems and human health.
Structure and Composition
Bacteria possess a simple structure that enables rapid reproduction and adaptability. Their cell wall, primarily made of peptidoglycan, provides shape and protection. Additionally, bacteria can be classified based on their shapes:
- Cocci: Spherical-shaped bacteria, such as Staphylococcus aureus.
- Bacilli: Rod-shaped bacteria, like Escherichia coli.
- Spirilla: Spiral-shaped bacteria, such as Spirillum minus.
Moreover, some bacteria are surrounded by a capsule that enhances their ability to evade the immune system.
Reproductive Methods
Bacteria reproduce mainly through binary fission. In this process, one bacterium divides into two identical cells, allowing for rapid population growth under favorable conditions. Some notable points about bacterial reproduction include:
- Asexual reproduction: This method maintains genetic consistency within populations.
- Conjugation: Bacteria can exchange genetic material through direct contact.
- Transformation and transduction: These methods allow for genetic variation by incorporating DNA from the environment or via viruses.
These reproductive strategies contribute significantly to bacterial diversity and adaptability in various environments.
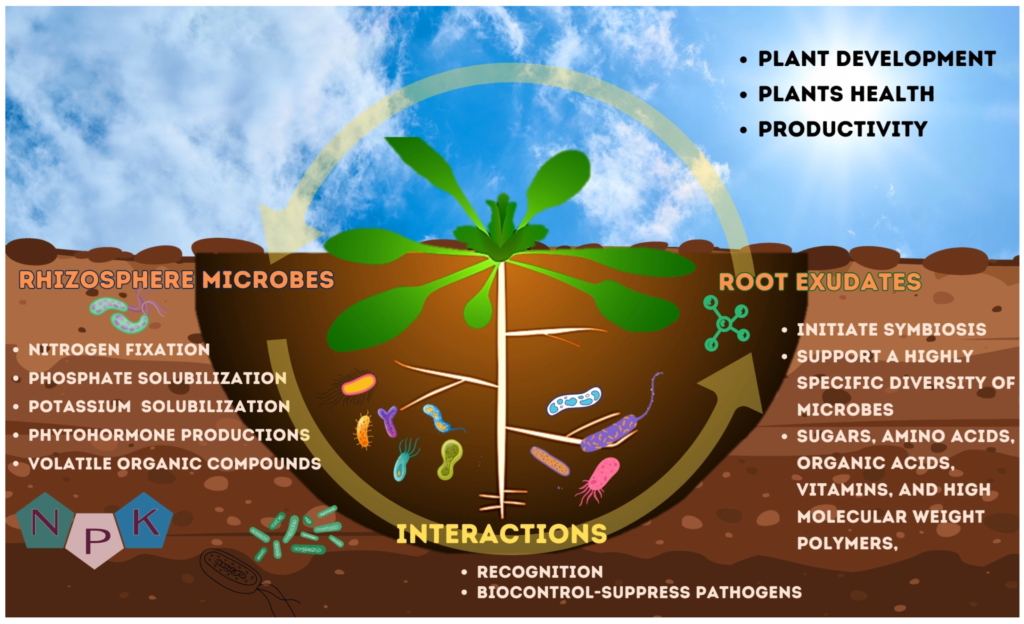
The Role of Fungi and Bacteria in Ecosystems
Fungi and bacteria play crucial roles in maintaining ecosystem health. Their interactions contribute significantly to nutrient cycling, decomposition, and symbiotic relationships within various environments.
Decomposition and Nutrient Cycling
Fungi break down complex organic materials. They decompose dead plants and animals, returning vital nutrients to the soil. For instance, mushrooms release enzymes that digest cellulose in wood. This process enriches soil fertility, promoting plant growth.
Bacteria also enhance nutrient cycling. Certain species convert nitrogen from the atmosphere into forms usable by plants. Nitrogen-fixing bacteria like Rhizobium form nodules on legume roots, facilitating this process. As a result, these microorganisms prevent nutrient depletion and support diverse ecosystems.
Symbiotic Relationships
Many fungi and bacteria engage in mutually beneficial partnerships with other organisms. Mycorrhizal fungi connect with plant roots, enhancing water and nutrient absorption while receiving carbohydrates in return. This relationship boosts plant resilience against drought.
Bacteria frequently collaborate with fungi as well. Some species produce antibiotics that protect plants from pathogens while benefiting from the host’s resources. These interactions foster healthy ecosystems by boosting biodiversity and stability across different habitats.
Understanding the essential roles of fungi and bacteria highlights their impact on environmental balance and resource sustainability.
Applications of Fungi and Bacteria
Fungi and bacteria play vital roles across various fields, influencing medicine, industry, and agriculture. Their applications are diverse, showcasing their importance in everyday life.
Medical Uses
Fungi significantly contribute to modern medicine. For instance, penicillin, derived from the Penicillium mold, revolutionized antibiotic treatment for bacterial infections. Additionally, fungi such as Aspergillus oryzae produce enzymes used in fermentation processes for medications. Moreover, some fungal compounds exhibit anticancer properties, providing new avenues for cancer therapy.
Bacteria also have crucial medical applications. Lactobacillus species are essential probiotics that promote gut health and enhance digestion. Furthermore, genetically engineered bacteria can produce insulin for diabetes management. Another example is using Streptomyces bacteria to develop antibiotics like streptomycin that treat tuberculosis.
Industrial Applications
In industry, fungi serve multiple purposes. Yeasts, particularly Saccharomyces cerevisiae, are key players in baking and brewing industries due to their fermentation capabilities that produce carbon dioxide and alcohol. Additionally, certain fungi help break down waste products during bioremediation processes.
Bacteria also find extensive use in industrial applications. Bioreactors utilize microorganisms to produce biofuels sustainably through fermentation processes, creating an eco-friendly energy source. Besides this, bacteria like Pseudomonas can degrade environmental pollutants in wastewater treatment facilities.
By understanding these examples of how fungi and bacteria impact various sectors significantly enhances your appreciation of their roles in both human health and industrial advancements.