Have you ever wondered how functions interact in mathematics? The concept of f(g(x)) opens up a world of possibilities, showcasing the beauty of function composition. This powerful tool allows you to combine two distinct functions into one, creating new outputs based on the input from another function.
Overview of f(g(x))
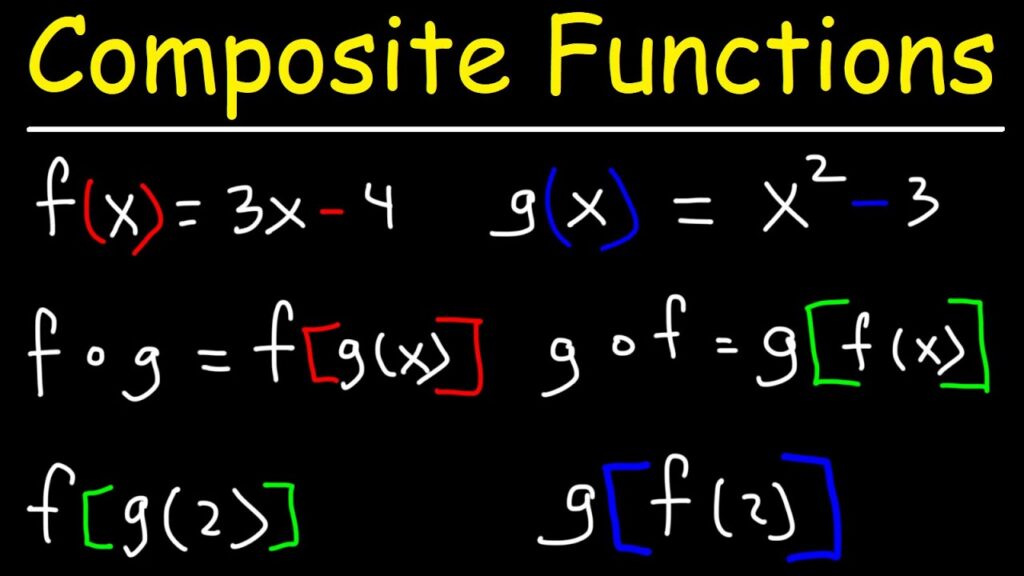
Function composition, denoted as f(g(x)), combines two functions to create a new function. This notation indicates that you apply the function g to the input x first and then apply the function f to the result of g. Understanding this concept expands your mathematical toolkit.
For example, consider these functions:
- f(x) = 2x + 3
- g(x) = x^2
In this case, f(g(x)) becomes:
- First, calculate g(x):
g(4) = 4^2 = 16
2. Then substitute into f:
f(g(4)) = f(16) = 2(16) + 3 = 35
Thus, f(g(4)) equals 35.
Another example involves different functions:
- f(x) = sin(x)
- g(x) = x/2
Now evaluate f(g(x)) for an input of π:
- Compute g(π):
g(π) = π/2
2. Substitute into f:
f(g(π)) = sin(π/2) = 1
Hence, f(g(π)) results in 1.
You can also explore how changes in one function affect the composition’s output. For instance, if you modify g to be a linear function like g(x) = x + 1 while keeping f unchanged at sin:
- Calculate:
g(pi/3) = pi/3 + 1
2. Evaluate:
f(g(pi/3))=sin(pi/3+1)
This leads to interesting variations in outputs based on functional interactions.
Function composition proves essential across various fields like calculus and computer science, offering insights into complex systems through straightforward operations. By practicing with different pairs of functions, you reinforce your understanding of their interplay and enhance problem-solving skills in mathematics.
Understanding Composite Functions
Composite functions represent a fundamental concept in mathematics, allowing you to combine two functions. This combination produces new outputs based on the input of one function into another.
Definition of Composite Functions
A composite function is formed when you apply one function to the results of another function. In mathematical notation, this is expressed as f(g(x)). Here, g(x) acts first by transforming the input x, and then f takes that output and processes it further. Essentially, the result from g becomes the input for f.
Examples of Composite Functions
To clarify how composite functions work, consider these examples:
- Quadratic and Linear Function
Let’s define two functions:
- ( f(x) = 2x + 3 )
- ( g(x) = x^2 )
To find ( f(g(4)) ):
- First calculate ( g(4) ): ( g(4) = 16 ).
- Then compute ( f(16) ): ( f(16) = 35 ).
- Trigonometric and Rational Function
Now look at these functions:
- ( f(x) = sin(x) )
- ( g(x) = x/2 )
To evaluate ( f(g(pi)) ):
- Start with ( g(pi)): This gives you pi divided by two.
- Next, find ( f(frac{pi}{2})): The result equals 1.
Applications of f(g(x))
Understanding the applications of f(g(x)) in various fields enhances your grasp of function composition. This concept finds relevance in diverse areas, including mathematics and computer science.
Real-World Examples
In real-world scenarios, you can observe function composition frequently:
- Economics: Use f(g(x)) to model supply and demand. If g(x) estimates consumer income, then f(g(x)) could predict changes in market equilibrium.
- Physics: In motion equations, if g(t) describes position over time, f(g(t)) might represent velocity based on that position.
- Biology: When studying population growth, let g(t) denote environmental factors affecting species size; then f(g(t)) can represent growth rates influenced by those factors.
These examples illustrate how this mathematical principle applies to everyday situations and complex systems alike.
Importance in Mathematics
Function composition underpins many mathematical concepts. Recognizing its importance allows for deeper insights into problem-solving:
- Calculus: In calculus, derivatives of composite functions are essential for understanding rates of change. You apply the chain rule here to find the derivative of f(g(x)).
- Algebra: Composite functions simplify expressions and solve equations efficiently. For instance, manipulating a function into a composite form often aids in finding solutions quickly.
- Graphs: Visualizing composite functions offers insights into behavior at different inputs. You can see how transformations affect outputs through graphical representations.
By grasping these applications and their significance, you enhance your mathematical skills and analytical abilities across disciplines.
Challenges in Working with f(g(x))
Working with the composition of functions, represented as f(g(x)), presents several challenges. Understanding these complexities aids in mastering function composition and its applications across mathematical disciplines.
Common Mistakes
Many encounter Common Mistakes when dealing with f(g(x)). These errors often arise from misapplying the order of operations or misunderstanding function definitions. For instance:
- Forgetting to apply g first: You might calculate f directly without considering that g must be processed before applying f.
- Incorrect domain identification: Each function has a specific domain; ignoring this can lead to invalid outputs.
- Neglecting simplification: Failing to simplify results from g before substituting into f may complicate calculations unnecessarily.
Awareness of these pitfalls allows you to navigate function compositions more effectively.
Tips for Mastery
To master the concept of f(g(x)), consider these helpful tips:
- Practice regularly: Solve various problems involving different functions, like linear and quadratic functions.
- Visualize graphs: Sketching graphs helps understand how changes in one function affect another.
- Check your work: Always substitute back to verify that your result aligns with expected values from both functions.
- Explore real-world examples: Apply composite functions in practical scenarios, such as calculating travel time based on speed and distance.
Implementing these strategies strengthens your grasp on composite functions, making complex problems easier to tackle.