The executive branch is where the heart of government action beats. Have you ever wondered how decisions that shape your daily life are made? This branch, led by the President, plays a crucial role in enforcing laws and managing national affairs. It’s not just about the Oval Office; it includes various departments and agencies that work tirelessly behind the scenes.
Overview Of The Executive Branch
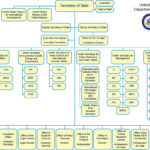
The executive branch plays a crucial role in governing and implementing laws. It is led by the President, who has significant influence over national policies. The structure includes various departments and agencies, each focusing on specific areas such as defense, education, and health.
For example, the Department of Defense oversees military operations and national security strategies. It manages resources to ensure preparedness against threats.
The Department of Education develops policies for public schooling and federal student aid programs. Its initiatives aim to improve educational access across all states.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) enforces regulations protecting air and water quality. It addresses environmental concerns through research and policy implementation.
Additionally, the executive branch handles international relations through treaties and diplomacy. For instance, it negotiates trade agreements that impact economic growth.
You might wonder how these entities collaborate. They work together under the President’s direction to address complex issues efficiently, ensuring a cohesive government response to challenges faced by citizens.
Structure Of The Executive Branch
The executive branch operates under a defined structure that includes key leadership roles and various departments. Each component plays a vital role in governing effectively.
The President
The President of the United States serves as the head of the executive branch. The President enforces federal laws, manages national affairs, and represents the U.S. on the global stage. For instance, when natural disasters occur, it’s often the President who coordinates federal responses to aid affected states. Furthermore, through executive orders, the President can direct government operations without waiting for legislative approval.
The Vice President
The Vice President assists the President in executing duties and steps in during absences or incapacities. The Vice President also presides over the Senate and breaks tie votes. An example is Kamala Harris’s role in advancing initiatives such as infrastructure improvements and healthcare reforms while supporting broader policy goals set by the administration.
Cabinet Members
Cabinet members lead specific departments within the executive branch. These leaders provide expertise and implement policies related to their respective areas. For example:
- The Secretary of Defense oversees military operations.
- The Secretary of Education develops educational standards.
- The Attorney General heads law enforcement initiatives.
Each cabinet member plays a critical role in shaping national policy by advising the President based on their department’s needs and challenges.
Functions Of The Executive Branch
The executive branch performs critical functions that shape governance and influence everyday life. This section explores key responsibilities, including law enforcement and foreign policy management.
Enforcing Laws
The executive branch ensures laws are enforced effectively. The President collaborates with various departments, such as the Department of Justice, to administer justice and uphold legal standards. For instance:
- Law Enforcement Agencies: The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) investigates federal crimes like terrorism and cybercrime.
- Regulatory Bodies: The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) enforces environmental regulations to protect public health.
These entities work together to maintain order and ensure compliance with established laws.
Conducting Foreign Policy
The executive branch plays a vital role in shaping foreign relations. Through diplomacy and treaties, the President engages with other nations on issues of trade, security, and cooperation. Key aspects include:
- Treaty Negotiation: The President can negotiate agreements that require Senate approval.
- International Relations: Ambassadors represent U.S. interests abroad while addressing global concerns.
This function is essential for maintaining national security and promoting economic growth through strategic partnerships.
The Executive Branch And Checks And Balances
The executive branch operates within a system of checks and balances, ensuring accountability and preventing abuse of power. This structure involves interactions between the three branches of government: executive, legislative, and judicial.
Legislative Oversight
Legislative oversight refers to the authority Congress has over the executive branch. It includes monitoring how laws are implemented and evaluating federal agencies’ effectiveness. For example:
- Budget Approval: Congress controls funding for various departments, influencing their operations.
- Investigations: Congressional committees can conduct investigations into executive actions, holding officials accountable.
- Confirmations: The Senate confirms presidential appointments for key positions like Cabinet members or Supreme Court justices.
These tools allow Congress to check the power of the president while ensuring transparency in governance.
Judicial Review
Judicial review empowers courts to evaluate executive actions against constitutional standards. This process ensures that no law or action violates citizens’ rights. For instance:
- Challenging Executive Orders: Courts can block orders if deemed unconstitutional or outside presidential authority.
- Reviewing Administrative Regulations: Agencies must follow proper procedures when implementing regulations; courts can invalidate those that don’t comply.
- Interpreting Treaties: Courts may interpret treaty provisions, affecting international agreements made by the president.
Through judicial review, you see a vital mechanism protecting individual liberties while maintaining balance among government branches.
Current Challenges Facing The Executive Branch
The executive branch faces numerous challenges that impact its effectiveness and public perception. One significant challenge is political polarization. As divisions between parties deepen, it becomes difficult for the President to secure bipartisan support for initiatives.
Another issue involves managing crises effectively. Events like natural disasters or pandemics require swift responses, which can strain resources and coordination among various departments. For instance, during the COVID-19 pandemic, the executive branch faced scrutiny over vaccine distribution and public health guidelines.
Economic instability presents another hurdle. Fluctuations in unemployment rates and inflation pressures demand quick action from the executive branch to stimulate growth while ensuring fiscal responsibility.
Additionally, foreign relations pose ongoing difficulties. Navigating international conflicts and trade negotiations requires diplomacy and strategy, often complicated by shifting global dynamics.
Lastly, public trust in government institutions continues to decline, affecting how policies are received. The executive branch must work diligently to rebuild this trust through transparency and accountability in decision-making processes.