Imagine having access to healthcare without stepping foot outside your home. Examples of telemedicine showcase how technology is revolutionizing patient care, making it more convenient and accessible than ever before. From virtual consultations to remote monitoring, telemedicine offers innovative solutions that cater to diverse health needs.
Overview Of Telemedicine
Telemedicine revolutionizes how you receive healthcare by leveraging technology to provide remote medical services. It enhances accessibility and convenience, allowing for various interactions between patients and healthcare providers.
Definition Of Telemedicine
Telemedicine refers to the delivery of medical care through digital communication technologies. This includes video conferencing, phone calls, and mobile health applications that facilitate consultations without needing in-person visits. You can access specialists or primary care physicians from your home, making it easier to manage your health.
History Of Telemedicine
The concept of telemedicine dates back to the late 20th century. Initially, it involved simple forms of communication like telephone consultations. In the 1960s, NASA employed telemedicine for astronauts’ health monitoring during missions. As technology advanced in the 1990s, internet-based platforms emerged, allowing broader access to telehealth services. Today, widespread adoption continues due to improved connectivity and a growing demand for remote healthcare solutions.
Examples Of Telemedicine Applications
Telemedicine encompasses various applications that enhance patient care and accessibility. Here are some notable examples:
Remote Patient Monitoring
Remote patient monitoring (RPM) allows healthcare providers to collect data from patients outside traditional clinical settings. This method supports chronic disease management by tracking vital signs in real-time. For instance:
- Heart Rate Monitoring: Devices send heart rate data directly to doctors, enabling timely interventions.
- Diabetes Management: Continuous glucose monitors provide insights into daily glucose levels, helping manage diabetes effectively.
This technology fosters proactive care and reduces hospital visits.
Virtual Consultations
Virtual consultations enable patients to interact with healthcare professionals via video calls or online messaging. This approach is beneficial for various scenarios, such as:
- Routine Checkups: Patients can discuss symptoms without traveling to a clinic.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Doctors can review treatment progress and adjust medications remotely.
Convenience is a key advantage, allowing you to receive medical advice from your home or workplace.
Teletherapy
Teletherapy provides mental health services through digital platforms, making therapy accessible regardless of location. It includes:
- Video Therapy Sessions: Licensed therapists conduct live sessions via secure video conferencing tools.
- Text-Based Counseling: Patients engage with therapists through chat or messaging apps for immediate support.
This flexibility enhances mental health access, especially for those facing mobility issues or stigma related to seeking help in person.
Telemedicine Technologies
Telemedicine relies on a variety of technologies that enhance patient care and accessibility. Below are key examples that illustrate how telemedicine operates effectively.
Mobile Health Apps
Mobile health apps facilitate communication between patients and healthcare providers. They allow users to track vital signs, manage medications, and schedule appointments from their smartphones. Notable examples include:
- MyFitnessPal: Helps monitor nutrition and exercise.
- HealthTap: Offers virtual consultations with doctors.
- Mayo Clinic App: Provides appointment scheduling and medical information.
These applications improve self-management for patients while ensuring they stay connected with their healthcare teams.
Video Conferencing Tools
Video conferencing tools enable real-time consultations between patients and providers. These platforms ensure high-quality interactions without the need for physical visits. Prominent options include:
- Zoom for Healthcare: Complies with HIPAA regulations, providing secure video calls.
- Doxy.me: Simple interface designed specifically for telehealth services.
- Microsoft Teams: Integrates various productivity features alongside video functionality.
Using these tools significantly reduces travel time and allows more flexible scheduling for both parties.
Wearable Devices
Wearable devices collect health data continuously, which can be shared with healthcare professionals instantaneously. Examples include:
- Fitbit: Tracks heart rate, steps, and sleep patterns.
- Apple Watch: Monitors heart health through ECG capabilities.
- Oura Ring: Provides insights into sleep quality and readiness scores.
The integration of wearables enhances remote monitoring, enabling timely interventions based on real-time data analysis.
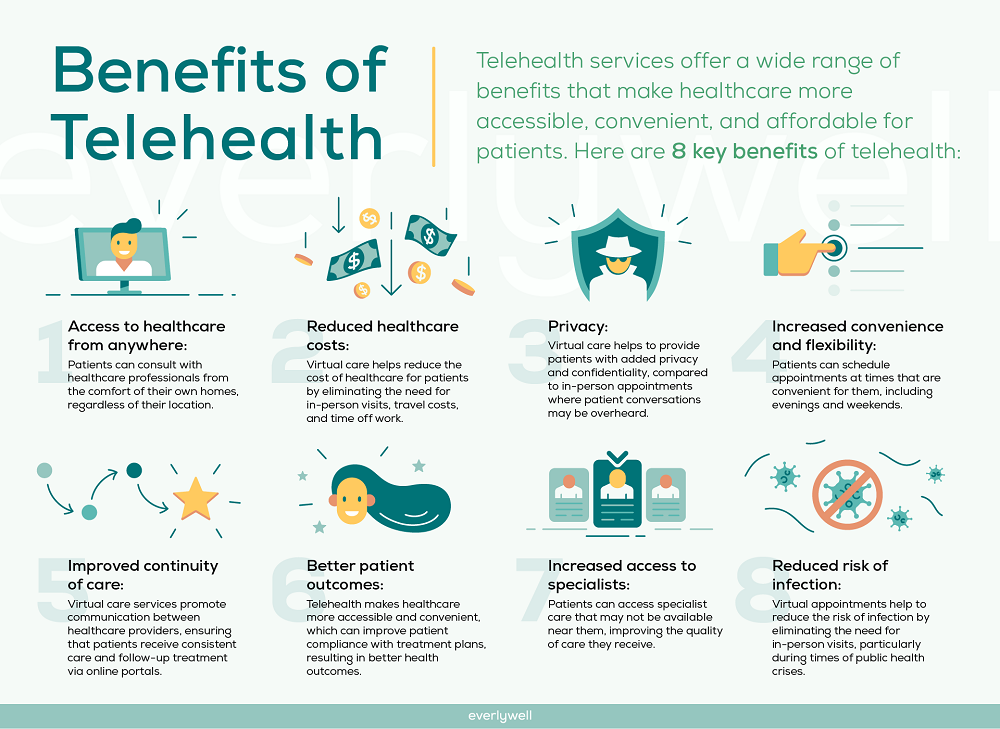
Benefits Of Telemedicine
Telemedicine provides numerous advantages that enhance healthcare delivery. These benefits significantly improve patient experiences and outcomes.
Increased Access To Care
Telemedicine increases access to healthcare services, especially for individuals in remote areas. Patients can consult with specialists without traveling long distances. For instance, rural residents can connect with urban healthcare providers through video calls. Additionally, those with mobility issues benefit from virtual appointments, ensuring they receive necessary care from the comfort of their homes.
Cost-Effectiveness
Telemedicine is often more cost-effective compared to traditional in-person visits. It reduces travel costs and time associated with visiting a clinic or hospital. Moreover, patients save on expenses related to childcare or taking time off work for appointments. Health systems also experience lower operating costs due to decreased overhead for physical office spaces and resources.
Improved Patient Outcomes
Telemedicine contributes to improved patient outcomes by facilitating timely interventions. Regular monitoring via remote tools allows healthcare providers to track vital signs continuously, leading to faster response times for potential health issues. Furthermore, patients engaged in teletherapy report higher satisfaction rates as they have easier access to mental health support tailored to their needs. This proactive approach ultimately enhances overall health management and well-being.
Challenges In Telemedicine
Telemedicine faces several challenges that can impact its effectiveness and accessibility. Understanding these issues is crucial for improving remote healthcare services.
Technical Limitations
Technical limitations hinder the full potential of telemedicine. Connectivity issues, such as slow internet speeds or unreliable networks, disrupt consultations. Additionally, not all patients have access to the necessary technology, like smartphones or computers. Some platforms may also lack user-friendliness, making it hard for older adults to navigate digital interfaces. These factors contribute to lower adoption rates among certain populations.
Regulatory Issues
Regulatory issues complicate telemedicine practices. Different states have varying laws regarding licensure and reimbursement for services. This inconsistency creates confusion for both providers and patients about what’s covered under insurance plans. Moreover, temporary waivers during emergencies may not be permanent, leading to uncertainty in future care delivery options. Navigating these regulations often demands significant administrative effort.
Patient Privacy Concerns
Patient privacy concerns pose a significant barrier in telemedicine. The transmission of sensitive health information over digital platforms raises fears about data breaches and unauthorized access. Many patients worry about their confidentiality during virtual appointments, especially if third-party applications are used. Ensuring compliance with regulations like HIPAA is critical for protecting patient information and building trust in telehealth solutions.