The simple present tense is a fundamental aspect of English that you encounter daily. Understanding its usage can transform your communication skills and help you express routines, facts, and general truths effortlessly. Have you ever wondered how to describe your everyday activities or share timeless information?
Understanding Simple Present Tense
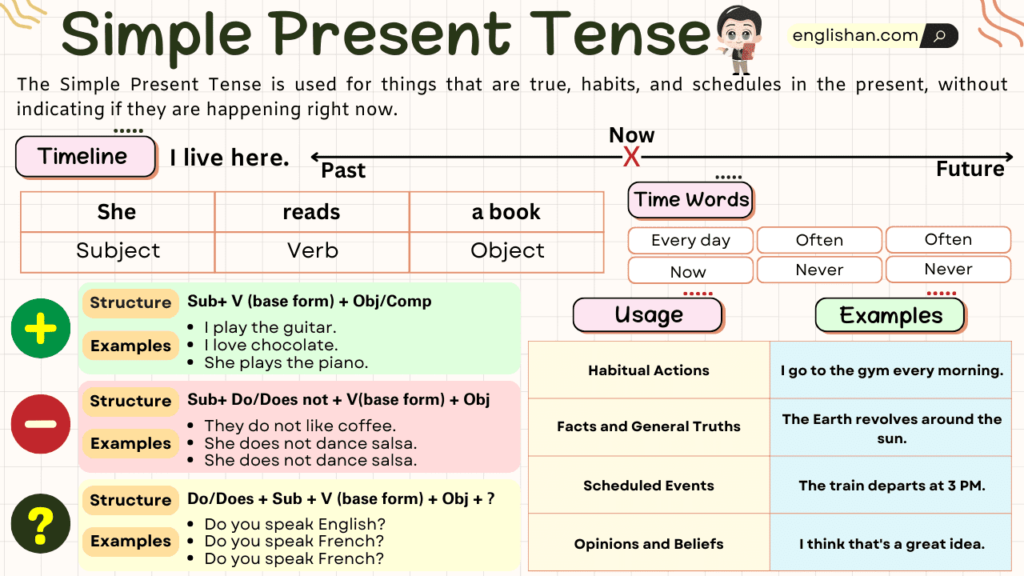
The simple present tense describes actions that are habitual, factual, or generally true. It plays a significant role in everyday communication by allowing you to convey information clearly and directly.
Definition of Simple Present Tense
The simple present tense indicates actions happening regularly or facts that remain constant. For example:
- I read books every day.
- She works at a bank.
In these sentences, the verbs “read” and “works” illustrate routine activities. This tense often uses the base form of verbs for all subjects except the third person singular, where you add an “-s” or “-es.”
Importance of Simple Present Tense
Mastering the simple present tense enhances your ability to communicate effectively in English. It helps you express:
- Daily routines:He jogs in the morning.
- Universal truths:Water freezes at 32 degrees Fahrenheit.
- Scheduled events:The train departs at 6 PM.
Understanding this tense improves clarity when describing regular occurrences or timeless facts. You’ll find it essential for conversations about your life and experiences.
Common Uses of Simple Present Tense
The simple present tense serves multiple functions in daily communication. It conveys actions that occur regularly or facts that remain unchanged.
Describing Habits and Routines
You use the simple present tense to describe habits and routines. For example, “I exercise every morning” illustrates a regular activity. Other examples include:
- “She drinks coffee before work.”
- “They play soccer on weekends.”
These sentences clearly communicate consistent behaviors.
Stating General Facts
General facts are expressed using the simple present tense. For instance, “Water freezes at 32 degrees Fahrenheit” is an undeniable truth. Additional examples are:
- “The Earth revolves around the Sun.”
- “Cats are mammals.”
Each statement denotes a fact that holds true universally.
Expressing Scheduled Events
Scheduled events also utilize the simple present tense. For instance, “The train departs at 6 PM” indicates a specific timetable. More examples include:
- “School starts at 8 AM.”
- “The meeting begins next Tuesday.”
These phrases effectively convey fixed arrangements or plans.
Examples of Simple Present Tense in Sentences
The simple present tense conveys routines, facts, and general truths. Here are examples that illustrate how this tense functions in different types of sentences.
Affirmative Sentences
Affirmative sentences state facts or habitual actions. You might say:
- I read books every day.
- She plays basketball on weekends.
- They visit their grandparents each month.
These examples highlight regular activities, showing how you can use the simple present to express what you do routinely.
Negative Sentences
Negative sentences indicate actions that do not occur or facts that aren’t true. For instance:
- I don’t like spicy food.
- He doesn’t work on Fridays.
- We don’t watch television often.
In these cases, the negative form clearly communicates what isn’t happening or what someone prefers to avoid.
Interrogative Sentences
Interrogative sentences ask questions about habits or facts. You could ask:
- Do you exercise regularly?
- Does she enjoy reading novels?
- What time does the train arrive?
These examples show how the simple present tense forms questions effectively, helping you gather information about routines and schedules.
Tips for Using Simple Present Tense
Using the simple present tense effectively enhances communication clarity. Here are some tips to keep in mind.
Recognizing Time Expressions
Time expressions often accompany the simple present tense. Phrases like “every day,” “usually,” and “always” indicate habitual actions. For example:
- I read books every day.
- She usually goes to the gym on weekends.
These expressions help convey frequency and routine, making your sentences more precise.
Subject-Verb Agreement
Subject-verb agreement is essential in the simple present tense. Ensure that singular subjects pair with singular verbs, while plural subjects match with plural verbs. For instance:
- He plays soccer every Saturday (singular).
- They play soccer every Saturday (plural).
Remember, when using “he,” “she,” or “it,” add an -s or -es to the verb form as needed, such as in “She studies biology.” This rule ensures grammatical accuracy in your sentences.