Nouns are the building blocks of language, and understanding their various forms can transform your communication skills. Whether you’re describing a person, place, thing, or idea, examples of nouns help clarify your thoughts and make your writing more vivid. Have you ever wondered how many types of nouns exist and how they function in everyday conversation?
Understanding Nouns
Nouns serve as essential building blocks in language. They name people, places, things, and ideas, helping you convey thoughts clearly and effectively.
Definition of Nouns
A noun is a word that identifies a person, place, thing, or concept. For example, “dog,” “city,” and “happiness” are all nouns. By naming these entities, nouns provide clarity in communication. You often find them as subjects or objects in sentences.
Types of Nouns
Nouns can be categorized into several distinct types:
- Common Nouns: General names for items like “car,” “teacher,” or “fruit.”
- Proper Nouns: Specific names such as “Sarah,” “New York,” or “Monday.”
- Collective Nouns: Words representing groups like “team,” “flock,” or “bunch.”
- Abstract Nouns: Names for concepts such as “freedom,” “love,” or “beauty.”
Understanding these types enhances your writing by allowing you to choose the most precise words for your message.
Common Examples of Nouns
Nouns play a crucial role in language, and understanding their types helps improve communication. Here are some common examples to illustrate different categories.
Proper Nouns
Proper nouns refer to specific names of people, places, or organizations. They always begin with a capital letter. For instance:
- People: Michael Jordan, Angela Merkel
- Places: Paris, Mount Everest
- Organizations: NASA, United Nations
These nouns identify unique entities and help provide clarity in conversation.
Common Nouns
Common nouns represent general items or concepts, not specific ones. These do not require capitalization unless starting a sentence. Some examples include:
- Objects: book, car
- Animals: dog, cat
- Concepts: happiness, freedom
Using common nouns allows for broader discussions without pinpointing exact references.
Abstract and Concrete Nouns
Nouns fall into two primary categories: abstract nouns and concrete nouns. Understanding these types helps clarify your writing.
Examples of Abstract Nouns
Abstract nouns represent ideas, emotions, or concepts that you can’t physically touch. They convey feelings or qualities rather than tangible objects. Here are some common examples:
- Happiness: A state of well-being.
- Freedom: The power to act or speak freely.
- Courage: The ability to confront fear.
- Justice: Fair treatment in accordance with the law.
When discussing abstract nouns, think about how they influence interactions and expressions.
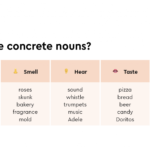
Examples of Concrete Nouns
Concrete nouns refer to things you can see, touch, smell, hear, or taste. They provide a sense of reality and specificity in your writing. Consider these examples:
- Apple: A fruit that’s crisp and sweet.
- Dog: A loyal animal often kept as a pet.
- Car: A vehicle used for transportation.
- House: A building where people live.
Concrete nouns anchor your thoughts in reality, making descriptions more vivid.
Collective Nouns
Collective nouns refer to words that represent groups of people, animals, or things. These nouns simplify language by allowing you to describe several entities with a single term. For example, when discussing a group of animals, instead of listing each one individually, you can use collective nouns for clarity.
Here are some common examples:
- Team: A group of players working together in sports.
- Flock: A collection of birds, often flying together.
- Class: A group of students learning in the same setting.
- Herd: A large group of animals grazing or moving together.
- Crew: The team working on a ship or aircraft.
Using collective nouns streamlines communication and enhances your writing. They help convey your message more efficiently while maintaining engagement. Do you find it easier to remember collective terms than individual names? It often simplifies discussions about larger groups.
When using collective nouns, consider whether you’re referring to the group as a single unit or as individuals. For instance, “The team is winning” treats the team as one entity, while “The team are arguing among themselves” emphasizes individual actions within the group. This distinction affects how you structure your sentences.
By incorporating these terms into your vocabulary, you enrich your language skills and improve clarity. Recognizing and utilizing collective nouns effectively allows for more vivid descriptions in both spoken and written communication.
Possessive Nouns
Possessive nouns show ownership or a relationship between things. They help clarify who owns what, which is essential for effective communication. Here are some examples:
- Singular possessive nouns: Add an apostrophe and “s” to the end of a singular noun.
- Example: the cat’s toy indicates that the toy belongs to one cat.
- Plural possessive nouns: For plural nouns ending in “s,” add just an apostrophe after the “s.”
- Example: the dogs’ owner shows that multiple dogs share one owner.
- Irregular plural possessive nouns: For irregular plurals, add an apostrophe and “s.”
- Example: the children’s playground signifies that the playground belongs to children.
Understanding how to use possessive nouns enhances your writing by providing clarity about relationships. You’ll find these forms in everyday language, from casual conversations to professional documents.
In summary:
- Singular: cat’s
- Plural (ending in s): dogs’
- Irregular plural: children’s
Using possessive nouns correctly can significantly improve your ability to express relationships clearly and concisely.