Imagine a healthcare system where every aspect of your well-being is interconnected. Integrated health services are transforming the way we approach medical care, making it more holistic and efficient. By combining various health services, these models aim to improve patient outcomes while streamlining processes.
Overview of Integrated Health Services
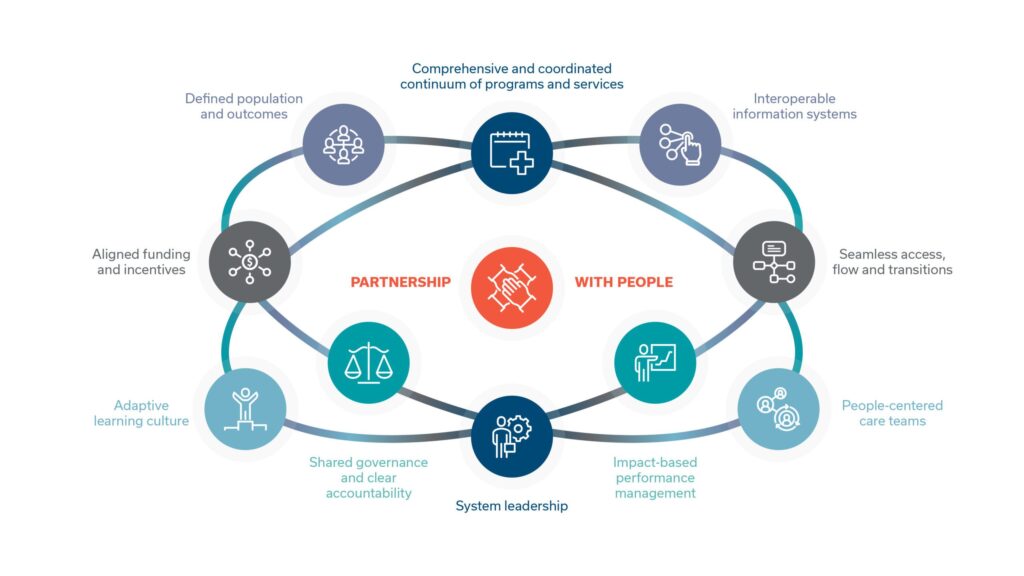
Integrated health services encompass a variety of approaches designed to coordinate and enhance healthcare delivery. These services combine multiple aspects of care, focusing on the patient’s overall well-being rather than isolated treatments.
Examples include:
- Patient-Centered Medical Homes (PCMH): These models emphasize continuous and comprehensive care through a team-based approach, ensuring that all patient needs are met.
- Integrated Behavioral Health Services: This model combines mental health and primary care, allowing for holistic treatment plans that address both physical and psychological issues simultaneously.
- Community Health Teams: These teams consist of various healthcare professionals who collaborate to provide coordinated services within the community, addressing social determinants of health.
- Telehealth Integration: By incorporating telemedicine into traditional healthcare settings, patients gain access to specialists without the need for travel, improving convenience and continuity of care.
You may notice how these examples illustrate the shift towards more interconnected systems in healthcare. They not only improve patient outcomes but also streamline processes across different service areas.
Benefits of Integrated Health Services
Integrated health services provide numerous advantages, enhancing the healthcare experience for patients and providers alike. These benefits manifest in multiple areas, from improved patient care to greater cost efficiency.
Improved Patient Outcomes
Integrated health services lead to better patient outcomes. Coordinated care ensures that all healthcare providers are on the same page regarding a patient’s needs. For instance:
- Patient-Centered Medical Homes (PCMH) promote continuous engagement with primary care providers.
- Integrated Behavioral Health Services allow mental health specialists to collaborate closely with primary care doctors.
- Community Health Teams address social determinants affecting patients’ overall well-being.
These collaborative approaches result in reduced hospital readmissions and enhanced management of chronic conditions.
Cost Efficiency
Cost efficiency is a significant benefit of integrated health services. By combining various services under one umbrella, organizations can reduce operational costs. Consider these examples:
- Telehealth Integration lowers transportation expenses for patients needing specialist consultations.
- Shared Resources among community health teams cut down administrative costs.
- Preventive Care Programs reduce the need for expensive emergency interventions.
Such strategies not only save money but also allocate resources more effectively across healthcare systems.
Examples of Integrated Health Services
Integrated health services come in various forms, each designed to improve patient care and streamline healthcare delivery. Here are some notable examples:
Community Health Programs
Community health programs focus on addressing local health needs through collaborative approaches. They often include:
- Mobile clinics that provide essential medical services in underserved areas.
- Health education initiatives aimed at promoting healthy lifestyles and preventing diseases.
- Support groups for managing chronic conditions like diabetes or hypertension.
These programs enhance access to care while fostering community engagement.
Telehealth Services
Telehealth services expand access to healthcare by providing virtual consultations and follow-ups. These services include:
- Video calls with primary care providers for routine check-ups.
- Remote monitoring tools that track patients’ vital signs from home.
- Online therapy sessions, enabling mental health support without geographical constraints.
Telehealth improves convenience, as you can receive care from the comfort of your home.
Patient-Centered Medical Homes
Patient-Centered Medical Homes (PCMH) emphasize coordinated, comprehensive care tailored to individual needs. Key features of PCMHs include:
- Care teams, consisting of doctors, nurses, and specialists working together.
- Personalized treatment plans developed through shared decision-making with patients.
- Continuous access, ensuring timely appointments and follow-up care.
This model prioritizes your overall well-being, enhancing communication among all healthcare providers involved in your care.
Challenges in Implementing Integrated Health Services
Implementing integrated health services presents several challenges that can impact effectiveness and sustainability. These barriers often hinder the seamless delivery of care.
Funding and Resource Allocation
Funding plays a crucial role in the success of integrated health services. Many organizations struggle to secure adequate financing for collaborative initiatives. Limited budgets can restrict access to essential resources, impacting patient care quality. Moreover, uneven distribution of funds across various sectors complicates resource allocation. Here are some common funding-related issues:
- Inconsistent governmental support.
- Fragmented insurance reimbursement policies.
- Insufficient investment in technology and training.
Such factors create obstacles for developing comprehensive programs that address diverse healthcare needs.
Interprofessional Collaboration
Interprofessional collaboration is vital for integrated health services, yet it faces significant hurdles. Teams often include professionals from different disciplines, which can lead to misunderstandings or conflicting priorities. Without clear communication channels, effective teamwork suffers. Additionally, varying professional cultures may result in resistance to change among team members. Consider these collaboration challenges:
- Different communication styles across professions.
- Varied levels of commitment to integration goals.
- Lack of shared decision-making processes.
Addressing these issues requires ongoing training and fostering an environment that values collective input and cooperation among all providers involved.