Have you ever noticed how gender discrimination can seep into everyday life? Examples of gender discrimination are all around us, often manifesting in subtle yet impactful ways. From the workplace to social settings, these instances shape experiences and opportunities for countless individuals.
In this article, you’ll explore various examples that highlight the pervasive nature of gender bias. Understanding these examples is crucial for recognizing and addressing the inequalities that persist in our society. Whether it’s unequal pay for equal work or biased hiring practices, each scenario sheds light on a larger issue affecting both men and women.
By diving into real-life situations, you’ll gain insights into how deeply ingrained stereotypes influence behavior and decision-making. Get ready to uncover the reality behind gender discrimination and learn why it’s essential to challenge these norms for a more equitable future.
Overview of Gender Discrimination
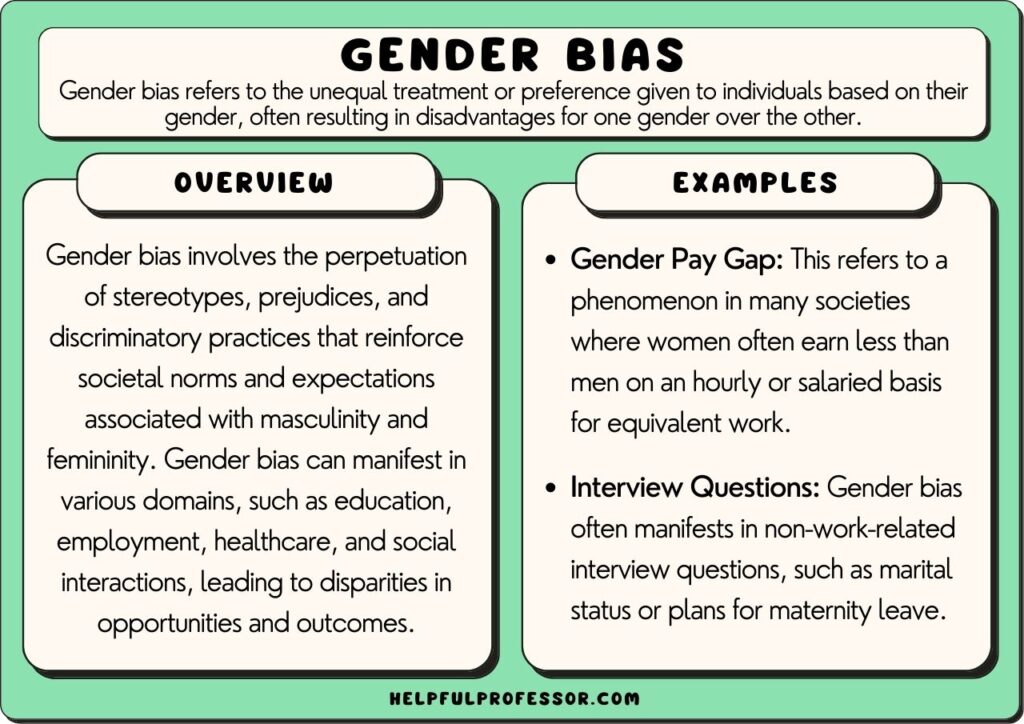
Gender discrimination occurs in many aspects of life, impacting individuals based on their gender. It’s essential to recognize some clear examples that illustrate this issue.
Workplace inequality is a significant area where gender discrimination manifests. Women often earn less than men for the same roles, leading to disparities in income and opportunities for advancement.
Hiring practices can reflect bias as well. Employers might favor male candidates over equally qualified female candidates, perpetuating a cycle of inequality.
Promotion opportunities often skew towards men as well. Studies show that women face barriers when seeking promotions, frequently encountering stereotypes regarding leadership capabilities.
Social expectations also play a role in gender discrimination. Traditional views about gender roles can limit choices and freedom, affecting personal and professional decisions.
These examples highlight the need for awareness and action to combat gender discrimination across various settings. Are you ready to challenge these norms?
Historical Context
Gender discrimination has deep roots in society, influencing behaviors and systems for centuries. Understanding its historical context reveals how entrenched biases have shaped our present.
Early Examples of Gender Discrimination
In ancient civilizations, gender roles were strictly defined. For instance, women often faced limitations regarding property ownership and voting rights. In the 19th century, the suffrage movement emerged as women demanded equal rights. Women fought tirelessly for basic legal recognition and to participate in governance. Even within families, daughters frequently received less education than sons.
Evolution Through the Years
Over time, gender discrimination evolved but persisted in various forms. The Industrial Revolution shifted many women into the workforce yet continued to pay them less than their male counterparts for similar work. This disparity laid foundational issues that continue today. In the late 20th century, legislation like Title IX aimed to reduce inequalities in education and sports. However, despite these advances, barriers remain evident across sectors such as leadership roles and pay equity.
The journey toward equality faces ongoing challenges. Recognizing these historical examples helps highlight persistent patterns of bias that need addressing today.
Contemporary Examples of Gender Discrimination
Gender discrimination continues to manifest in various forms across society. Recognizing these contemporary examples helps highlight the ongoing issues that many face daily.
Workplace Discrimination
In workplaces, gender discrimination appears through several practices. Women often experience lower salaries compared to male counterparts for identical roles. Research shows that women earn approximately 82 cents for every dollar earned by men in similar positions. Additionally, promotion opportunities frequently favor men despite equal qualifications among employees. This bias contributes to a lack of representation in leadership roles, reinforcing stereotypes about women’s abilities.
Educational Disparities
Educational settings also reflect gender discrimination. Girls might receive less encouragement in subjects like math and science, leading to fewer pursuing careers in STEM fields. For instance, only 28% of the workforce in computer science is female. Furthermore, schools may inadvertently reinforce traditional gender roles through activities and curriculum choices, limiting students’ aspirations based on gender rather than ability or interest.
Media Representation
Media representation plays a significant role in shaping perceptions of gender. Women are often portrayed in stereotypical roles that emphasize beauty over intelligence or competence. This portrayal can influence societal expectations and self-perception among young girls. Studies show that films with more diverse female characters tend to perform better at the box office, indicating an audience demand for varied representations beyond traditional norms.
By identifying these examples of gender discrimination, you contribute to raising awareness and advocating for change within your community and beyond.
Impact of Gender Discrimination
Gender discrimination leads to significant consequences that affect individuals and society as a whole. Understanding these impacts helps highlight the urgency for change.
Psychological Effects
Gender discrimination can cause severe psychological effects. For instance, feelings of inadequacy often arise in individuals who face bias in the workplace or educational settings. Many women experience anxiety or depression due to constant reminders of their perceived inferiority. Moreover, self-esteem issues may develop when people are not recognized for their skills and contributions, leading them to doubt their abilities. This environment discourages personal growth and professional development.
Economic Consequences
Economic consequences of gender discrimination are profound and far-reaching. Women frequently earn less than men for equivalent work; on average, they receive about 82 cents for every dollar a man earns in similar roles. This pay gap contributes to long-term financial instability, affecting retirement savings and investment opportunities.
Additionally, underrepresentation in leadership positions limits women’s career advancement options. Companies often miss out on diverse perspectives that drive innovation because they favor male candidates during promotions or hiring processes. As a result, organizations suffer from decreased productivity and creativity which ultimately affects overall economic performance.
Recognizing both the psychological effects and economic consequences of gender discrimination helps frame this issue as one that requires immediate attention across all sectors of society.
Strategies for Addressing Gender Discrimination
Addressing gender discrimination requires a collaborative approach across various sectors. Here are effective strategies that can be implemented:
- Implement Equal Pay Policies: Organizations must conduct pay audits to ensure equal compensation for equal work. This raises awareness of existing disparities and encourages fair practices.
- Promote Diversity in Hiring: Establish diverse hiring panels to reduce bias in recruitment processes. By incorporating varied perspectives, organizations enhance their decision-making effectiveness.
- Provide Training Programs: Offer training on unconscious bias and gender sensitivity for all employees. Such programs foster an inclusive culture and empower individuals to challenge discriminatory behaviors.
- Encourage Flexible Work Arrangements: Create policies that allow flexible hours or remote work options, supporting both men and women in balancing professional responsibilities with personal ones.
- Establish Mentorship Opportunities: Develop mentorship programs that connect women with leaders in their fields. These relationships provide guidance, support career development, and promote advancement.
- Support Women’s Leadership Initiatives: Encourage female participation in leadership roles through targeted initiatives like leadership workshops or networking events aimed at women.
- Foster Open Communication Channels: Create safe spaces where employees can discuss experiences of discrimination without fear of retaliation. Open dialogue leads to increased awareness and collective action against bias.
- Monitor Progress Regularly: Set measurable goals related to diversity and inclusion efforts, then evaluate progress periodically to ensure accountability within the organization.
By implementing these strategies consistently, you contribute to creating a more equitable environment that reduces gender discrimination effectively across all areas of society.