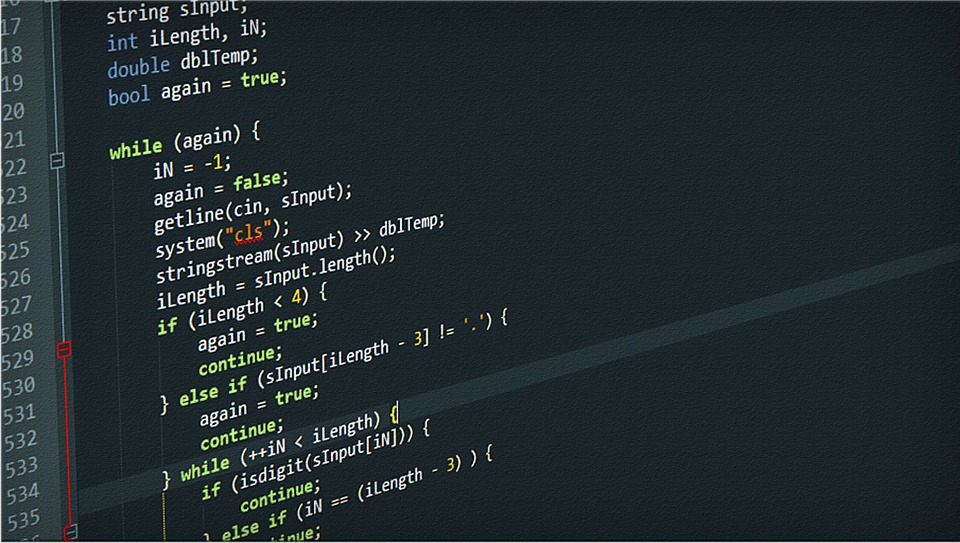
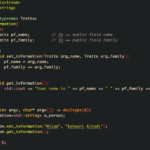
Have you ever wondered how software applications come to life? Examples of source code reveal the magic behind programming languages, showcasing how developers turn ideas into functional programs. Whether you’re a seasoned coder or just starting out, understanding these examples can deepen your appreciation for technology.
In this article, you’ll explore various examples of source code across different programming languages. From simple scripts that automate mundane tasks to complex algorithms powering modern apps, each snippet tells a story of creativity and problem-solving. By examining these real-world instances, you’ll gain insights into coding practices and techniques that can elevate your own projects.
Understanding Source Code
Source code serves as the foundation of software applications. It comprises the written instructions that computers execute to perform tasks. The clarity and organization of this code significantly impact the functionality and maintainability of a program.
Definition of Source Code
Source code refers to the set of instructions written in a programming language, which is comprehensible to humans. It’s what programmers create and modify before it’s compiled or interpreted into machine language. For instance, source code can be found in various languages like Python, Java, or C++. Each type has syntax rules that dictate how commands are structured.
Importance of Source Code
Understanding source code is crucial for several reasons:
- Troubleshooting: You can identify bugs or errors quickly by reviewing the source code.
- Customization: Modifying existing programs allows you to tailor software functionalities to meet specific needs.
- Learning: Analyzing well-written source code enhances your coding skills and reinforces best practices.
- Collaboration: Clear source code improves teamwork among developers by facilitating easier communication about project components.
By grasping these concepts, you enhance your ability to work effectively with software development projects.
Types of Source Code
Understanding the types of source code enhances your programming knowledge. Each type serves a unique purpose in software development, impacting accessibility and functionality.
Open Source Code
Open source code refers to software that anyone can inspect, modify, and enhance. It fosters collaboration among developers worldwide. Examples include:
- Linux: A widely used operating system kernel.
- Apache HTTP Server: A popular web server.
- Mozilla Firefox: An open-source web browser.
With open source projects, you benefit from community support and continuous updates. Also, you gain insight into coding practices by examining the work of others.
Proprietary Source Code
Proprietary source code is owned by an individual or company and not available for public modification. Users must adhere to licensing agreements. Common examples are:
- Microsoft Windows: The dominant operating system for PCs.
- Adobe Photoshop: Industry-standard graphic design software.
- Oracle Database: A robust database management system.
In proprietary environments, you typically rely on vendor support for troubleshooting and updates. However, this model often ensures higher levels of security due to controlled access.
Example of Source Code
Understanding examples of source code broadens your programming knowledge and enhances your skills. Here are a couple of straightforward examples to illustrate basic coding principles.
Simple Code Snippet
Here’s a simple example in Python that prints “Hello, World!” to the console:
print("Hello, World!")
This snippet showcases how easy it is to execute a command in Python. It’s often the first program written by beginners, highlighting the simplicity and accessibility of coding.
Explanation of Code Functionality
This code demonstrates fundamental concepts in programming. The print function outputs text to the console, making it essential for interaction with users. You can modify this example easily by changing the string inside the parentheses. For instance:
print("Welcome to programming!")
Now you see different output without altering any core functionality. This exemplifies how small changes can lead to varied results in software applications.
Best Practices in Writing Source Code
Writing source code involves following certain best practices that enhance clarity and maintainability. Implementing these practices leads to more robust applications and facilitates collaboration among developers.
Code Readability
Code readability is crucial for maintaining software. When you write clear and understandable code, others can easily follow your logic. Use consistent naming conventions for variables and functions, like using camelCase or snake_case throughout your project. Break down complex functions into smaller, manageable parts. For instance:
def calculate_area(radius):
return 3.14 * radius * radius
This function clearly states its purpose with a descriptive name.
Documentation and Comments
Documentation and comments improve the usability of your code. Add comments to explain why certain decisions were made or how specific sections work. This practice helps future developers (or yourself) understand the rationale behind your coding choices later on. Here’s an example of effective commenting:
// Calculate the total price including tax
function calculateTotalPrice(price, taxRate) {
return price + (price * taxRate);
}
Such documentation provides context, making it easier to grasp functionality quickly.
By prioritizing readability and thorough documentation, you set a strong foundation in writing quality source code that fosters collaboration and eases maintenance efforts over time.