Every day, you encounter various stimuli that prompt responses, often without even realizing it. Understanding the concept of a response to stimuli not only illuminates how living organisms interact with their environment but also reveals fascinating insights into behavior and adaptation. From the quick reflexes of a person dodging an object to plants bending toward sunlight, these examples showcase nature’s remarkable ability to react.
Understanding Response to Stimuli
Responses to stimuli represent how organisms react to changes in their environment. These reactions play a crucial role in survival and adaptation. Examples of these responses illustrate the diverse strategies that living beings employ.
Definition of Stimuli
Stimuli refer to any changes or signals in the environment that provoke a response from an organism. These can be physical, chemical, or biological factors. For instance, temperature changes act as stimuli prompting animals to seek shelter or migrate. Recognizing stimuli is essential for understanding how organisms interact with their surroundings.
Types of Stimuli
Several types of stimuli influence responses across different organisms:
- Physical Stimuli: Light, sound, and temperature are common examples. An animal may flee from loud noises.
- Chemical Stimuli: The presence of toxins or food sources triggers specific reactions. Plants respond by releasing chemicals when attacked by pests.
- Biological Stimuli: Interactions within species also serve as stimuli. Mating calls attract potential partners among various animal species.
These categories demonstrate the varied ways living organisms perceive and react to their environments.
Examples of Response to Stimuli in Nature
Living organisms exhibit fascinating responses to stimuli in their environments. These reactions are crucial for survival and adaptation.
Plant Responses
Plants respond to various stimuli, demonstrating their ability to adapt. For example, phototropism occurs when plants bend toward light sources. This response helps maximize photosynthesis. Another notable response is thigmotropism; vines wrap around objects when they encounter them, which supports growth and stability. Additionally, some plants release chemicals as a defense mechanism against herbivores or pathogens, illustrating a reactive strategy essential for survival.
Animal Responses
Animals also showcase remarkable responses to environmental stimuli. For instance, when startled by loud noises, many animals display flight responses, quickly fleeing the danger. Predatory animals often use chemical cues from potential prey; this olfactory response aids in hunting. Furthermore, social animals communicate through vocalizations and body language in reaction to each other’s behaviors—these interactions enhance group cohesion and survival strategies among species.
Human Responses to Stimuli
Humans exhibit various responses to stimuli, showcasing the complexity of our interactions with the environment. These responses can be immediate or reflective, depending on the nature of the stimulus and the context.
Reflex Actions
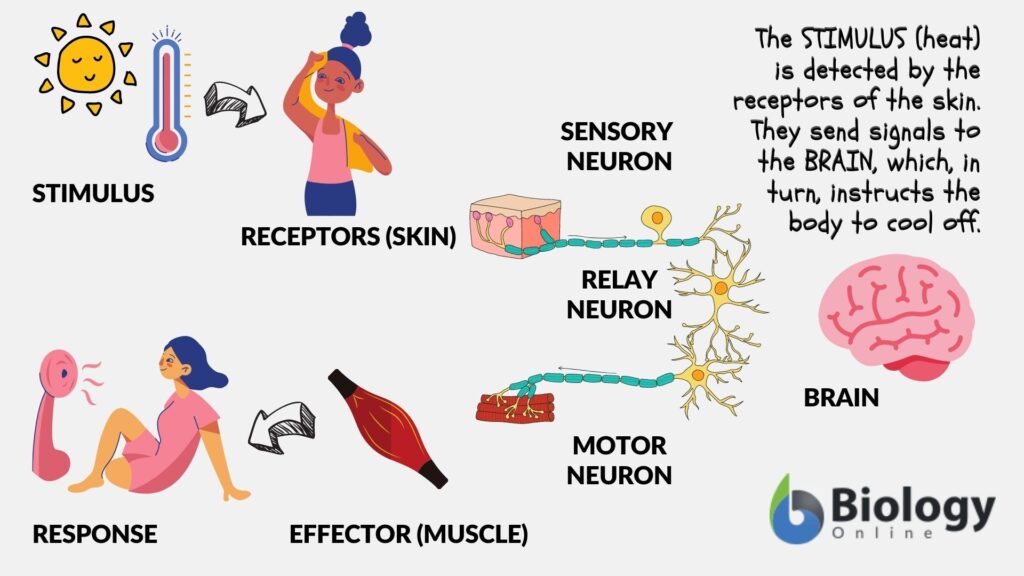
Reflex actions are involuntary responses to specific stimuli. They occur quickly without conscious thought. For example:
- Knee-jerk reflex: When a doctor taps your knee, it triggers an automatic kick.
- Withdrawal reflex: Touching something hot causes you to pull your hand back instantly.
- Blink reflex: Bright lights or sudden movements prompt an immediate blink for protection.
These actions play a crucial role in protecting you from harm by enabling rapid reactions.
Cognitive Responses
Cognitive responses involve thinking and decision-making processes when faced with stimuli. You analyze situations before reacting. For instance:
- Problem-solving: Encountering a challenge at work prompts you to devise solutions.
- Emotional response: Seeing a loved one may evoke feelings of joy or comfort.
- Decision-making: Choosing between two job offers requires evaluating each opportunity’s pros and cons.
These cognitive processes illustrate how humans assess their surroundings, allowing for more informed and deliberate reactions.
Applications of Response to Stimuli
Responses to stimuli play a vital role across various fields. Understanding these responses provides insights into behavior and adaptation, with significant implications in medicine and psychology.
In Medicine
In medicine, responses to stimuli are crucial for diagnosis and treatment. For instance:
- Reflex testing: Doctors assess reflex actions, like the knee-jerk response, to gauge neurological function.
- Pain response: Pain receptors react to harmful stimuli, signaling injury or illness.
- Drug reactions: Medications provoke specific physiological responses, determining their effectiveness.
Recognizing these responses helps healthcare professionals tailor treatments and improve patient outcomes.
In Psychology
In psychology, understanding how you respond to stimuli reveals much about behavior. Key examples include:
- Conditioned responses: These occur when an external stimulus triggers a learned reaction (like salivating at the sound of a bell).
- Emotional reactions: Certain situations elicit feelings based on past experiences or memories.
- Social interactions: Non-verbal cues prompt immediate responses that influence communication.