Imagine a world where your actions lead to immediate responses, shaping your next steps. Feedback loops are essential mechanisms that drive improvement and adaptation in various systems. From personal growth to business strategies, understanding how feedback loops function can transform the way you approach challenges.
In this article, you’ll explore compelling examples of feedback loops across different contexts. Whether it’s in technology, education, or even nature itself, these cycles of action and reaction illustrate the power of continuous learning. Have you ever wondered how successful companies refine their products based on customer input? Or how ecosystems maintain balance through natural processes?
Join us as we dive deeper into these fascinating examples of feedback loops and discover how they can enhance your decision-making and problem-solving skills.
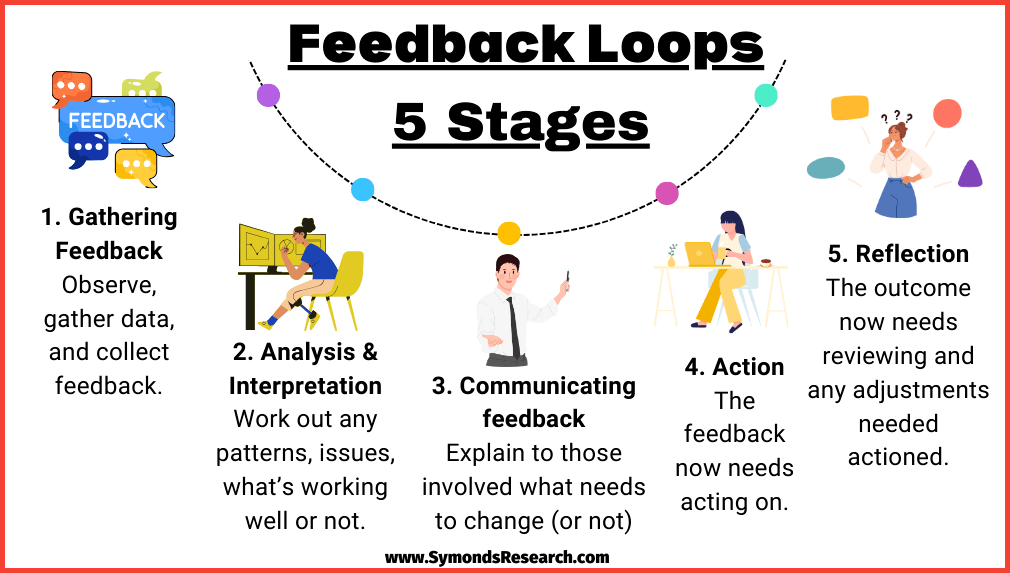
Understanding Feedback Loops
Feedback loops play a crucial role in various systems, promoting growth and adaptation. Grasping their mechanics can enhance your understanding of how changes influence outcomes.
Definition of Feedback Loop
A feedback loop refers to a process where the output of a system influences its own input. In simple terms, it’s a cycle where results are fed back into the system for evaluation and adjustment. For instance, in business, customer feedback directly impacts product development strategies. Understanding this concept helps identify areas for improvement.
Importance in Various Systems
Feedback loops are essential across different domains:
- Technology: Software updates often rely on user feedback to enhance functionality.
- Education: Teachers adjust teaching methods based on student performance assessments.
- Nature: Ecosystems utilize self-regulating mechanisms to maintain balance.
Recognizing these applications demonstrates the versatility of feedback loops. Each example illustrates how continuous input shapes development and effectiveness within systems.
Example of Feedback Loop in Nature
Feedback loops play a crucial role in maintaining balance within natural systems. Understanding these mechanisms helps illustrate the interconnectedness of life on Earth.
Homeostasis in Biological Systems
In biological systems, feedback loops regulate internal conditions. For instance, when your body temperature rises, sensors detect this change and trigger sweating to cool you down. This process exemplifies a negative feedback loop, where the output (cooling) counters the initial stimulus (heat). Similarly, if your blood sugar drops, your pancreas releases glucagon to raise it back to normal levels. These processes ensure stability despite external fluctuations.
Predator-Prey Dynamics
Predator-prey relationships demonstrate another form of feedback loop. When prey populations increase, predators find more food and reproduce more successfully. Consequently, as predator numbers rise, they reduce prey populations. This decline leads to food scarcity for predators, slowing their reproduction rates and allowing prey numbers to recover. Therefore, both species influence each other’s population dynamics through this cyclical interaction, showcasing nature’s intricate balance.
Example of Feedback Loop in Technology
Feedback loops play a crucial role in technology, enhancing systems through continuous evaluation and adaptation. They allow developers and companies to refine their products based on real-user input.
Feedback Loops in Software Development
In software development, feedback loops are vital for improving applications. You may notice regular updates in your apps; those often stem from user reports and testing results. For instance, Agile methodology incorporates short cycles called sprints. During these sprints:
- Developers gather feedback from users.
- Teams analyze the data to identify issues.
- Adjustments are made before the next iteration.
This process leads to more functional software that meets user needs effectively.
User Experience Feedback
User experience (UX) feedback significantly influences design decisions. Companies actively solicit input through surveys or usability tests. This information shapes future designs by highlighting areas of improvement. Consider how tech giants like Apple or Google implement UX feedback:
- Regularly conduct usability studies with diverse groups.
- Implement changes based on collected insights, such as navigation adjustments or feature enhancements.
- Measure success post-launch using analytics tools to monitor user behavior.
By closely monitoring user interactions, businesses can create intuitive interfaces that keep customers engaged and satisfied.
Example of Feedback Loop in Business
Feedback loops play a critical role in business, driving innovation and improvement. Understanding these processes can enhance your strategies and lead to better outcomes.
Customer Feedback and Product Improvement
Customer feedback serves as a vital component for product enhancement. Companies gather insights through surveys, reviews, and direct communication. For instance, online retailers like Amazon use customer ratings to identify product issues. When customers report problems with a specific item, the company adjusts its offerings or improves quality based on that input. This continuous process ensures products meet market demands effectively.
Performance Metrics and Organizational Growth
Performance metrics are essential for tracking organizational success. Businesses often implement key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure effectiveness. For example, sales teams review conversion rates regularly. If results fall short, management analyzes data to pinpoint weaknesses in their strategy. Then adjustments occur—whether it’s refining marketing tactics or enhancing training programs—to foster growth and improve overall performance continuously.
By leveraging customer insights and performance metrics effectively, businesses create robust feedback loops that drive positive change.