Ever wondered what an effective audit report looks like? Examples of audit reports can provide a clear roadmap for understanding financial health and compliance. Whether you’re a business owner, accountant, or just curious about the auditing process, knowing how to interpret these documents is crucial.
Overview Of Audit Reports
Audit reports provide critical insights into an organization’s financial health and compliance with regulations. These documents summarize the findings from an audit, offering a clear view of strengths and weaknesses. Here are some key components typically found in audit reports:
- Executive Summary: This section highlights essential findings and recommendations for stakeholders.
- Scope of Audit: It defines the boundaries of the audit, detailing what was examined.
- Findings: Clear identification of discrepancies or issues discovered during the audit process.
- Recommendations: Actionable advice aimed at addressing identified issues.
Understanding these components enhances your ability to interpret audit reports effectively. Each part plays a role in conveying important information to various audiences, including business owners and financial analysts. When looking at examples of audit reports, you’ll notice how structured they are—this structure aids clarity.
For example, consider a report that reveals significant inconsistencies in inventory management practices. Such findings could lead to recommendations about improving internal controls over stock levels.
You might also encounter compliance-focused audits where adherence to regulatory standards is evaluated thoroughly. In these cases, highlighted deficiencies can prompt immediate corrective actions.
Overall, effective audit reports serve as tools for transparency and accountability within organizations. They guide decision-making processes while fostering trust among stakeholders.
Key Components Of An Audit Report
An audit report comprises several key components that convey crucial information. Understanding these elements helps you interpret the findings effectively.
Executive Summary
The executive summary provides a concise overview of the audit process and its outcomes. It highlights the main objectives, scope, and significant findings. For example, an executive summary may state: “This audit assessed compliance with financial regulations for fiscal year 2025.” This section allows stakeholders to grasp essential insights quickly.
Scope Of Audit
The scope of the audit defines the boundaries and focus areas examined during the process. It includes the timeframe, specific departments, and relevant financial statements. For instance, a report might specify: “The audit covered transactions from January 1 to December 31, 2025.” Clearly outlining this information sets expectations for what was included in the examination.
Findings And Recommendations
Findings detail issues discovered during the audit along with their implications. Recommendations offer actionable steps to address these issues. A well-structured report might present findings like:
- Finding 1: Inadequate documentation for expenses.
- Recommendation: Implement a standardized expense reporting system.
By presenting both findings and recommendations clearly, you facilitate informed decision-making among stakeholders.
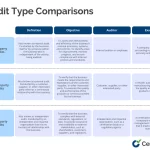
Types Of Audit Reports
Audit reports come in various forms, each serving distinct purposes within organizations. Understanding these types enhances your ability to interpret and utilize them effectively.
Internal Audit Report
An Internal Audit Report evaluates an organization’s internal controls and processes. It identifies areas for improvement and ensures compliance with policies. Typically, it includes:
- Purpose: Clarifies the objectives of the audit.
- Scope: Defines what was reviewed during the audit.
- Findings: Details issues discovered within internal processes.
- Recommendations: Offers actionable steps for improvement.
These reports are crucial for maintaining operational efficiency. They help you assess risks and ensure alignment with organizational goals.
External Audit Report
An External Audit Report is conducted by independent auditors to assess financial statements’ accuracy and fairness. This type of report includes:
- Opinion Statement: The auditor’s conclusion on whether the financial statements present a true picture.
- Basis for Opinion: Explains how the opinion was formed, detailing methods used.
- Key Audit Matters (KAM): Highlights significant areas that required more attention during the audit.
External audits build trust among stakeholders by providing transparency regarding financial health. You can rely on these reports when making informed decisions about investments or partnerships.
Real-World Example Of Audit Report
Audit reports serve as critical documents that reflect an organization’s financial and operational integrity. Here’s a practical example to illustrate the structure and content of an effective audit report.
Analysis Of The Example
Consider a fictional company, ABC Corp, which underwent an external audit. The audit report included key components such as:
- Executive Summary: This brief overview highlighted the main findings, stating that ABC Corp’s financial statements presented a true and fair view.
- Scope of the Audit: The audit focused on fiscal year 2025, examining revenue recognition practices and compliance with accounting standards.
- Findings: Significant issues were noted regarding inventory valuation methods, impacting cost of goods sold calculations.
- Recommendations: It suggested revising inventory tracking systems to enhance accuracy and reliability.
This structured format allows stakeholders to quickly grasp the essential information.
Lessons Learned
Several lessons emerge from analyzing this audit report example:
- Clarity is Key: A well-organized report ensures important findings are easily understood.
- Specificity Matters: Clearly defining the scope helps set expectations for stakeholders about what was examined.
- Actionable Recommendations Enhance Value: Providing specific steps for improvement fosters trust in the auditing process.
By focusing on these aspects, you can ensure your own audit reports convey crucial insights effectively.