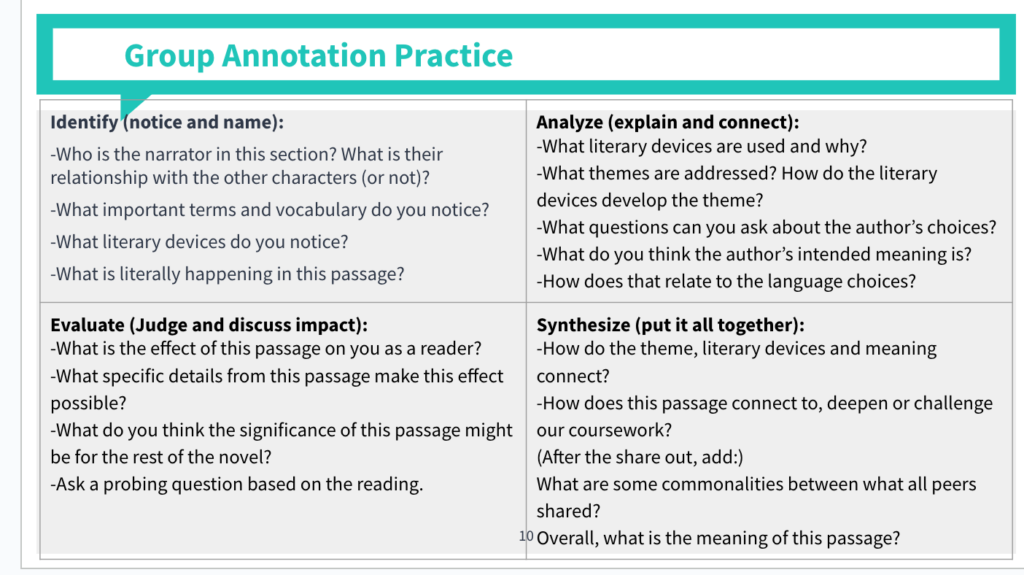
Ever wondered how annotations can transform your understanding of a text? Examples of annotation provide powerful insights that enhance learning and retention. Whether you’re diving into a complex novel or analyzing a research paper, effective annotations can highlight key themes, ideas, and connections that might otherwise go unnoticed.
Understanding Annotation
Annotations serve as essential tools for enhancing your understanding of a text. They help you engage more deeply with the material, whether you’re reading literature or academic papers.
Definition of Annotation
Annotation refers to the practice of adding notes, comments, or explanations to a text. These can include highlighting important passages, summarizing sections in your own words, or posing questions directly on the page. For example:
- Highlighting key themes in a novel.
- Summarizing complex ideas from an article.
- Questioning unclear concepts while studying.
By annotating, you create a personalized interaction with the text that aids retention and comprehension.
Importance of Annotation
Annotation is crucial for several reasons. First, it improves focus during reading sessions. When you actively engage with the material through notes and highlights, you’re less likely to zone out or miss critical information. Additionally:
- Enhances memory retention by reinforcing key points.
- Facilitates better discussions, as annotations provide reference points.
- Encourages critical thinking, prompting you to analyze rather than passively consume content.
With effective annotation strategies, you transform passive reading into an active learning experience that enriches your knowledge and insights.
Types of Annotations
Annotations come in various forms, each serving a distinct purpose. Understanding these types enhances your ability to engage with texts effectively.
Descriptive Annotations
Descriptive annotations summarize the main ideas or themes of a text. They provide readers with an overview without delving into personal opinions. For example, if you annotate a research article on climate change, your descriptive annotation might highlight key findings and methodologies used by the authors. This type of annotation aids in quickly recalling essential concepts during reviews or discussions.
Evaluative Annotations
Evaluative annotations assess the quality and relevance of a text. This involves critiquing arguments or analyzing strengths and weaknesses. If you’re reading a book on economic theory, an evaluative annotation could note how well the author supports their claims with evidence. Such annotations encourage critical thinking and help you form informed opinions about the material.
Informative Annotations
Informative annotations provide additional context or background information. These notes can clarify complex ideas or terms that may not be familiar to all readers. For instance, when annotating historical texts, you might include definitions for specific events or figures mentioned in the text. This enriches your understanding and makes connections clearer as you read along.
Example of Annotation in Literature
Annotations play a crucial role in literary analysis. They help highlight key themes and ideas within texts, enhancing your understanding. Here are some examples illustrating how annotations function within literature.
Analyzing Literary Texts
When analyzing a literary text, you can use descriptive annotations to summarize important sections. For instance:
- Highlighting key quotes: Mark passages that reveal character motivations or significant plot developments.
- Summarizing chapters: Write brief notes at the end of each chapter to encapsulate major events and themes.
- Noting stylistic devices: Identify metaphors or similes that contribute to the overall meaning of the work.
These methods clarify complex narratives and allow you to engage more deeply with the material.
Benefits for Readers and Scholars
Annotations offer numerous benefits for both casual readers and scholars. By annotating texts, you:
- Enhance comprehension: Keeping track of critical points allows for better retention.
- Facilitate discussions: Annotations serve as talking points during group studies or classroom settings.
- Encourage critical thinking: Questioning motives or implications fosters deeper analytical skills.
Overall, effective annotation transforms reading into an interactive experience that enriches your engagement with literature.
Example of Annotation in Academic Research
Annotations play a critical role in academic research, allowing you to interact with texts meaningfully. Here are some practical examples to illustrate their application.
Enhancing Research Understanding
You can enhance your understanding of complex research articles through effective annotations. For instance, when reading a study on climate change impacts:
- Highlight key findings: Identify important statistics like “30% increase in extreme weather events.”
- Summarize sections: Create short summaries that capture the essence of each section.
- Pose questions: Write down queries such as “What methodologies were used?” or “How do these findings relate to previous studies?”
These practices not only clarify information but also deepen your engagement with the material.
Best Practices for Academic Annotations
Implementing best practices improves your annotation quality. Consider these strategies:
- Be consistent: Use a uniform system for highlighting or underlining themes throughout your work.
- Use margin notes: Jot down thoughts or reactions directly beside relevant passages.
- Categorize types of annotations: Differentiate between descriptive, evaluative, and informative annotations for better organization.
By following these practices, you create a structured approach that enhances both comprehension and retention during your academic journey.
Example of Annotation in Digital Media
Annotations enhance your understanding and engagement with digital media. They can clarify concepts, highlight important information, and foster critical thinking.
Annotation Tools and Platforms
Many tools facilitate effective annotation in digital environments. Here are a few popular options:
- Hypothesis: This open-source tool allows you to annotate web pages and PDFs collaboratively.
- Kami: Ideal for educators, Kami enables annotations on documents while integrating with Google Drive.
- Mendeley: This reference manager includes features for annotating research papers and organizing citations.
These platforms support individual or collaborative efforts, making it easier to engage with content meaningfully.
Practical Applications in Digital Content
Annotations play a crucial role across various types of digital content. You can apply them in these areas:
- E-books: Highlight passages or write notes directly within the text to enhance comprehension.
- Online Articles: Add comments or summarize sections to clarify complex ideas as you read.
- Educational Videos: Use timestamps and notes to mark key points for later review.
By utilizing annotations effectively, you turn passive consumption into an interactive learning experience that deepens your understanding of digital materials.