Imagine sealing a deal with just a handshake or a simple email. That’s the essence of an example of an express contract—a clear agreement where terms are explicitly stated. These contracts can take many forms, from service agreements to sales transactions, and understanding them is crucial for both parties involved.
Understanding Express Contracts
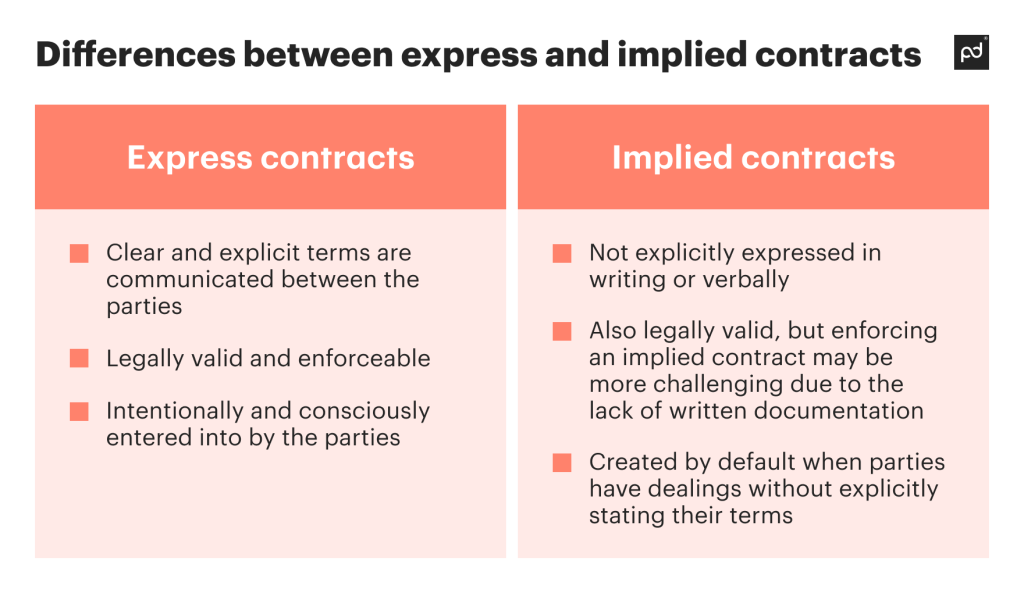
Express contracts are clear agreements with explicitly stated terms. You can form them through various means, like a handshake or an email, making them straightforward and accessible.
Definition and Key Characteristics
An express contract involves clear communication between parties about the terms of their agreement. It typically includes:
- Written or spoken terms: Both parties understand what they agreed to.
- Mutual consent: Each party accepts the conditions outlined.
- Specific obligations: Clear duties for each party exist.
These characteristics separate express contracts from implied contracts, where terms aren’t directly stated.
Importance in Business Transactions
Express contracts play a vital role in business transactions. They provide clarity and reduce misunderstandings. For example:
- Service agreements ensure that both parties know their responsibilities.
- Sales contracts outline payment details and delivery dates.
Examples of Express Contracts
Understanding express contracts requires looking at tangible examples. These agreements provide clarity in various situations, ensuring all parties are aware of their obligations.
Written Contracts in Real Estate
In real estate transactions, written contracts play a crucial role. For instance:
- Purchase Agreements: When you decide to buy a home, you sign a purchase agreement detailing the sale price and conditions.
- Lease Agreements: Renting property involves signing lease agreements that outline rent payments, duration, and responsibilities for maintenance.
- Listing Agreements: When hiring an agent to sell your property, you enter into a listing agreement specifying commission rates and marketing strategies.
These documents protect your interests and establish clear expectations.
Oral Contracts in Services
Oral contracts also serve as express contracts in service-based industries. Common examples include:
- Verbal Service Agreements: You might hire a plumber over the phone to fix your sink. The details discussed about payment and completion time form an oral contract.
- Consultation Services: If you ask for advice from a consultant without written terms but agree on fees verbally, you’ve created an enforceable contract.
While oral agreements can be binding, they often lack the clarity found in written documents. Always ensure both parties understand the terms to avoid disputes later on.
Legal Implications of Express Contracts
Express contracts carry significant legal implications that affect both parties involved. Understanding these implications ensures compliance and reduces risks associated with breaches.
Enforceability and Compliance
Enforceability hinges on clear terms. Courts uphold express contracts when the terms are explicit, whether written or spoken. For instance, a signed lease agreement clearly defines rental amounts, duration, and obligations. Additionally, mutual consent is crucial; both parties must agree to the same terms for enforceability.
Compliance requires adherence to agreed-upon conditions. If one party fails to fulfill their obligations, it can lead to legal consequences. Maintaining documentation helps establish proof of compliance in disputes.
Breach of Contract Considerations
Breach occurs when one party fails to meet contractual obligations. This can involve not delivering services or goods as promised. For example, if a contractor doesn’t complete a renovation by the deadline specified in their service contract, they breach that contract.
Consequences of a breach vary based on severity. Remedies may include monetary damages or specific performance—forcing fulfillment of the contract terms. Thus, understanding potential outcomes encourages both parties to honor their agreements and maintain positive relationships.
Common Misconceptions About Express Contracts
Many misconceptions exist regarding express contracts. Clarifying these can enhance your understanding of their nature and significance.
Myths vs. Reality
Myth: All verbal agreements lack enforceability.
Reality: While written contracts are often more straightforward, strong oral agreements can also be legally binding, provided the terms are clear and both parties consent.
Myth: Express contracts only refer to formal documents.
Reality:Express contracts encompass both spoken and written terms, such as a handshake agreement or an email exchange detailing specific obligations.
Myth: An express contract must involve a lawyer.
Reality: You don’t need legal representation to create an express contract; clear communication between parties suffices for forming valid agreements.
Clarifying Misunderstandings
Misunderstanding express contracts can lead to disputes. It’s essential you grasp the key aspects:
- Mutual Consent is Crucial: Both parties must agree on the terms for the contract to hold.
- Specific Obligations Matter: Clearly defined responsibilities prevent confusion and ensure accountability.
- Written Not Always Necessary: Oral agreements are valid, but they require clarity in communication to avoid ambiguity.
Recognizing these facts helps prevent common pitfalls associated with misunderstandings about express contracts.