Imagine navigating the complex world of finance without a solid understanding of accounting. It’s the backbone of every business, providing clarity and insight into financial health. In this article, you’ll discover examples of accounting that illustrate its vital role in decision-making and strategic planning.
Overview of Accounting
Accounting serves as a backbone for any business, enabling clear financial tracking and reporting. It encompasses various processes that help you understand the financial position of your organization. Here are some key examples illustrating its significance:
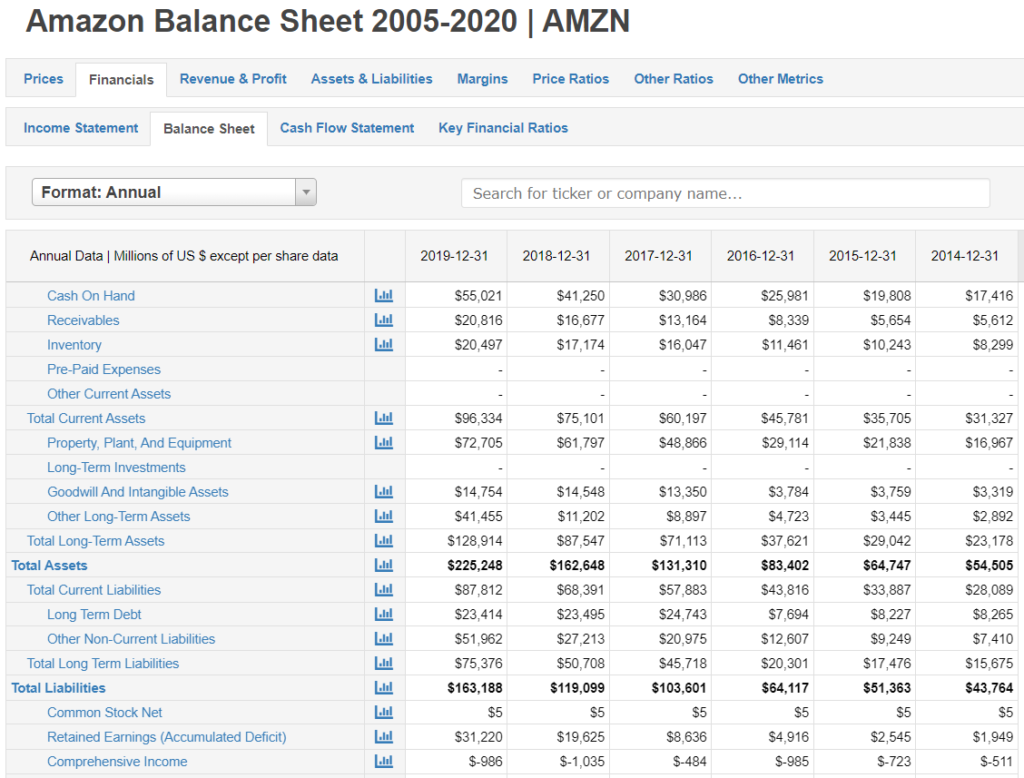
- Financial Statements: These documents summarize your company’s performance over a specific period. They include the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement.
- Budgeting: This process involves planning future finances based on past performance. You can allocate resources effectively by creating budgets.
- Tax Compliance: Accurate accounting ensures you meet tax obligations on time. Proper records prevent costly penalties and audits from tax authorities.
- Cost Analysis: Understanding costs helps in pricing products or services competitively. Analyzing direct and indirect costs aids decision-making regarding production levels.
- Auditing: Regular audits verify the accuracy of financial information. These assessments build trust with stakeholders like investors and creditors.
Each of these elements emphasizes how accounting assists in strategic planning and management decisions within a business context.
Importance of Accounting
Accounting plays a significant role in every business, providing essential insights into financial health. Understanding its importance can enhance decision-making and strategic planning.
Financial Decision-Making
Accounting data drives informed financial decisions. Businesses use accounting to analyze revenue, expenses, and profitability. For example:
- Profitability analysis: Identifying which products or services generate the most profit helps allocate resources effectively.
- Cash flow management: Regular tracking of cash inflows and outflows ensures you maintain sufficient liquidity for operations.
Without accurate accounting records, businesses risk making poor decisions that could impact their bottom line.
Legal Compliance
Compliance with laws relies heavily on accurate accounting. Businesses must adhere to various regulations regarding financial reporting and tax obligations. Consider these examples:
- Tax filings: Timely and accurate tax returns prevent penalties from the IRS or state authorities.
- Financial statements: Preparing GAAP-compliant statements ensures transparency for investors and stakeholders.
By maintaining proper accounting practices, you can avoid legal issues while fostering trust with clients and partners.
Types of Accounting
Accounting encompasses various types, each serving distinct purposes within a business. Understanding these types enhances your ability to make informed financial decisions.
Managerial Accounting
Managerial accounting focuses on providing information for internal decision-making. It equips managers with the data necessary to plan budgets, control operations, and evaluate performance. Examples include:
- Budget forecasts help anticipate future revenues and expenses.
- Cost analysis reports offer insights into production costs.
- Variance analysis compares budgeted figures to actual results, identifying discrepancies.
These tools enable better strategic planning and operational efficiency.
Financial Accounting
Financial accounting deals with preparing external financial statements that reflect a company’s overall performance. This type is crucial for stakeholders like investors and creditors. Key examples include:
- Balance sheets show assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific time.
- Income statements summarize revenues and expenses over a period.
- Cash flow statements track cash inflows and outflows, indicating liquidity status.
These documents ensure transparency in reporting financial health.
Tax Accounting
Tax accounting focuses specifically on tax-related matters. It ensures compliance with applicable tax laws while optimizing tax liabilities. Some key aspects are:
- Preparation of tax returns, ensuring all income and deductions are accurately reported.
- Tax planning strategies, which aim to minimize taxable income through legitimate means.
- Advisory services, helping businesses navigate complex regulations effectively.
This area is essential for maintaining legal compliance and maximizing financial efficiency.
Example of Accounting
Accounting examples illustrate its impact on businesses. By examining real-world scenarios, you can see how accounting principles apply in practice.
Real-World Case Studies
- Company A’s Profitability Analysis: Company A used profitability analysis to identify its most lucrative products. This process allowed them to allocate resources effectively, boosting overall revenue by 15% within a year.
- Startup B’s Cash Flow Management: Startup B faced cash flow issues during its first quarter. By implementing strict monitoring and forecasting techniques, they ensured sufficient liquidity for operations, reducing overhead costs by 20%.
- Nonprofit C’s Budgeting Process: Nonprofit C created an annual budget based on previous financial statements and projected donations. This budgeting process enabled them to plan programs more efficiently, resulting in a 30% increase in community outreach initiatives.
Common Practices in Businesses
Effective accounting practices enhance business performance. Here are some common methods:
- Regular Financial Reporting: Businesses prepare monthly or quarterly financial statements to assess their economic health accurately.
- Budget Forecasting: Companies use historical data to predict future expenses and revenues, guiding strategic planning.
- Cost Analysis Techniques: Organizations analyze fixed and variable costs to optimize pricing strategies and improve profitability.
- Auditing Procedures: Regular audits verify the accuracy of financial information, ensuring compliance with regulations.
Implementing these practices fosters better decision-making and nurtures trust among stakeholders. Strong accounting foundations lead to informed choices that drive business success.
Challenges in Accounting
Accounting presents various challenges that can impact financial accuracy and business operations. Understanding these challenges helps you navigate the complexities of accounting effectively.
Technology Integration
Implementing technology in accounting streamlines processes, but it also brings difficulties. You may face issues such as data security risks or software compatibility problems. Additionally, employees might require training to adapt to new systems, which can delay implementation. Examples of technology integration challenges include:
- Data Migration: Transferring existing data into new systems without loss.
- User Adoption: Ensuring all team members are comfortable with new tools.
- System Updates: Keeping software current while minimizing disruptions.
Addressing these challenges is crucial for maintaining accurate financial records.
Regulatory Changes
Regulatory changes pose significant hurdles for accountants. You must stay updated on evolving laws and standards to ensure compliance. Non-compliance can lead to severe penalties or legal consequences. Common regulatory challenges include:
- Tax Law Updates: Adapting accounting practices to reflect new tax regulations.
- Financial Reporting Standards: Complying with changing GAAP or IFRS requirements.
- Audit Regulations: Meeting stricter audit guidelines imposed by governing bodies.
Staying informed about these changes ensures your accounting practices remain compliant and reliable.