Eukaryotic cells are the building blocks of complex life, but do you know just how diverse they really are? From the tiniest yeast to towering redwoods, examples of eukaryotic cells showcase a remarkable variety of forms and functions. Understanding these examples not only highlights the complexity of life but also reveals how these cells contribute to ecosystems and human health.
In this article, you’ll explore fascinating eukaryotic cell examples across different kingdoms. You’ll discover how plants, animals, fungi, and protists each represent unique adaptations, showcasing their roles in our world. Get ready to dive into the intricate cellular structures that make life as we know it possible. Whether you’re a student or simply curious about biology, this journey through eukaryotic diversity will inspire your understanding of life’s complexity.
Overview Of Eukaryotic Cells
Eukaryotic cells are complex and diverse, forming the foundation of all multicellular organisms. These cells contain a nucleus enclosed within membranes, setting them apart from prokaryotic cells. You can find eukaryotic cells in various life forms, including plants, animals, fungi, and protists.
Plant cells demonstrate unique characteristics like cell walls made of cellulose and chloroplasts for photosynthesis. Examples include:
- Moss: A simple land plant that thrives in moist environments.
- Oak tree: A large tree known for its longevity and robust structure.
Animal cells lack cell walls but possess flexible membranes enabling mobility and communication. Common examples include:
- Human red blood cells: Essential for transporting oxygen through the bloodstream.
- Muscle cells: Specialized for contraction and movement.
Fungal cells exhibit distinct traits such as chitin-rich cell walls. Notable examples are:
- Yeast: Used in baking and brewing due to its fermentation capabilities.
- Mushrooms: The fruiting bodies of certain fungi that play vital roles in decomposition.
Protist cells, often single-celled organisms, showcase incredible diversity. Key examples include:
- Amoeba: Known for its ability to change shape while moving or engulfing food.
- Paramecium: Covered in cilia that aid in locomotion and feeding.
Each eukaryotic cell type contributes significantly to ecosystems and human industries alike. Understanding these variations enhances your knowledge of biological systems.
Types Of Eukaryotic Cells
Eukaryotic cells come in various forms, each with unique characteristics. Understanding these types enhances your knowledge of biological diversity.
Animal Cells
Animal cells lack a rigid cell wall, making them flexible and adaptable. You can find different types of animal cells throughout the body, including:
- Muscle Cells: Essential for movement, they contract and relax.
- Nerve Cells (Neurons): Transmit signals for communication within the body.
- Red Blood Cells: Carry oxygen from the lungs to tissues.
These examples illustrate how animal cells contribute to vital bodily functions.
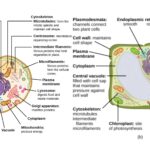
Plant Cells
Plant cells possess distinct features that support their role in photosynthesis and structural integrity. Their key components include:
- Cell Walls: Made of cellulose, providing strength.
- Chloroplasts: Organelles where photosynthesis occurs.
- Central Vacuoles: Store nutrients and maintain turgor pressure.
Examples like oak trees or sunflowers highlight how plant cells enable growth and energy production.
Fungal Cells
Fungal cells are quite different from plants and animals but play crucial roles in ecosystems. Notable aspects include:
- Chitin-rich Cell Walls: Offer protection while remaining flexible.
- Hyphae Structures: Allow fungi to absorb nutrients efficiently.
Examples Of Eukaryotic Cells
Eukaryotic cells are diverse and play vital roles in various life forms. Here are some notable examples:
Human Cells
Human cells encompass a wide range of types, each with specific functions. For instance, muscle cells enable movement, while nerve cells facilitate communication within the body. Moreover, red blood cells transport oxygen to tissues. Each cell type has unique adaptations that contribute to overall health and function.
Yeast Cells
Yeast cells represent a crucial group of eukaryotic organisms commonly used in baking and brewing. These single-celled fungi include species like Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which ferments sugars to produce carbon dioxide and alcohol. Their ability to thrive in various conditions makes them valuable for food production and scientific research.
Protist Cells
Protist cells showcase incredible diversity among unicellular and multicellular organisms. Examples include amoebas, known for their flexible shapes, and paramecia, which possess cilia for movement. Both protists play essential roles in aquatic ecosystems as primary producers or consumers, influencing nutrient cycles.
Significance Of Eukaryotic Cells
Eukaryotic cells play a pivotal role in the complexity of life. Their structure allows for specialization, enabling organisms to perform diverse functions efficiently. Here are key points that highlight their significance:
- Cellular Organization: Eukaryotic cells contain organelles like the nucleus and mitochondria, which manage cellular processes effectively.
- Genetic Diversity: These cells support genetic variation through sexual reproduction, promoting adaptability in changing environments.
- Ecosystem Roles: Eukaryotic organisms contribute to nutrient cycles. Plants produce oxygen and food through photosynthesis, while fungi decompose organic matter.
- Human Health: Understanding eukaryotic cells aids in medical advancements. For instance, knowledge of human cells leads to treatments for diseases.
You might wonder why eukaryotes are essential in biotechnology. They serve as model organisms for research and can be engineered for applications like drug production. This versatility underscores their importance across various fields.
In agriculture, they enable crop improvement through genetically modified plants that resist pests or tolerate harsh conditions. This aspect highlights how eukaryotic cells impact food security directly.
Consider protists as well; they maintain aquatic ecosystems by serving as primary producers or decomposers. Their roles demonstrate the interdependence among different life forms.
Ultimately, understanding eukaryotic cell functions enriches your insight into biology’s complexity and its relevance to everyday life.