Equilateral triangles are more than just a geometric shape—they’re everywhere in our world! Have you ever noticed how often this perfect triangle pops up in architecture, art, and nature? With all sides equal and angles measuring 60 degrees, equilateral triangles offer unique examples that showcase their beauty and symmetry.
In this article, you’ll discover fascinating equilateral triangle examples across various fields. From the iconic pyramids of Egypt to modern design elements, these triangles play a vital role in aesthetics and functionality. You might be surprised to learn how frequently they appear in everyday objects or even in the natural world around you.
Equilateral Triangle Examples in Nature
Equilateral triangles appear frequently in nature, showcasing their unique symmetry and balance. These shapes often help organisms thrive or adapt to their environments.
Plant Structures
Plants exhibit equilateral triangles in various structures. For example:
- Leaves: Some leaves form equilateral triangle shapes, optimizing light exposure for photosynthesis.
- Flower Petals: Certain flowers, like lilies, have petals arranged in an equilateral triangle pattern, promoting efficient pollination.
- Seed Arrangements: The arrangement of seeds in fruits like sunflowers often follows a triangular pattern, maximizing space and resource use.
These examples illustrate how plants utilize the stability of equilateral triangles for growth and reproduction.
Animal Anatomy
Animals also display equilateral triangle characteristics in their anatomy. Notable instances include:
- Shells: Some shells, like those of certain mollusks, follow triangular designs that enhance structural integrity.
- Fins: Fish fins may exhibit triangular shapes that improve swimming efficiency by reducing drag.
- Body Shapes: Insects such as bees show triangular body segments which contribute to aerodynamic movement.
Such anatomical features highlight the importance of equilateral triangles in evolution and functionality among species.
Equilateral Triangle Examples in Art
Equilateral triangles appear frequently in art, enhancing both aesthetics and meaning. Their symmetrical properties provide balance and harmony, making them a popular choice among artists.
Famous Paintings
Several famous paintings incorporate equilateral triangles to create visual interest. For instance:
- The Last Supper by Leonardo da Vinci showcases triangular compositions with figures strategically placed to form an equilateral triangle around Christ.
- The Holy Family by Michelangelo features Mary, Joseph, and baby Jesus arranged within a triangular framework that emphasizes stability and unity.
- Composition VII by Wassily Kandinsky displays abstract shapes, including equilateral triangles, contributing to the dynamic movement of the piece.
These examples illustrate how triangles guide the viewer’s eye while conveying deeper meanings.
Architecture
Architecture often uses equilateral triangles for structural integrity and aesthetic appeal. Notable examples include:
- The Louvre Pyramid in Paris presents a striking glass structure designed as an equilateral triangle that harmonizes with its surroundings.
- St. Peter’s Basilica features triangular elements throughout its façade, symbolizing the Holy Trinity while ensuring architectural strength.
- The Sydney Opera House employs sail-like structures resembling equilateral triangles to create a unique silhouette against the skyline.
These designs highlight how artists and architects utilize geometric shapes for beauty and functionality.
Equilateral Triangle Examples in Mathematics
Equilateral triangles appear frequently in mathematics, showcasing unique properties and applications. Their equal sides and angles contribute to various mathematical concepts.
Geometric Properties
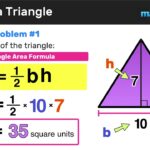
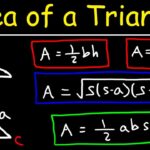
In geometry, an equilateral triangle has three equal sides and three equal angles, each measuring 60 degrees. This symmetry leads to interesting calculations:
- The perimeter is calculated by multiplying one side’s length by three.
- The area can be determined using the formula: ( frac{sqrt{3}}{4} times a^2 ), where ( a ) is the length of a side.
These properties make equilateral triangles essential for understanding other geometric principles and shapes.
Real-World Applications
You can find equilateral triangles in numerous real-world applications, especially in design and engineering. They provide strength and stability due to their shape. Here are some examples:
- Bridges often use triangular supports for better weight distribution.
- Roof structures frequently incorporate triangular designs for enhanced durability during extreme weather.
- Tiling patterns utilize equilateral triangles to create aesthetically pleasing visuals while maintaining structural integrity.
These practical uses highlight how understanding equilateral triangles benefits various fields, from architecture to everyday items.
Equilateral Triangle Examples in Design
Equilateral triangles frequently appear in design, enhancing both aesthetics and functionality. Their symmetrical nature provides balance, making them visually appealing and structurally sound. Here are some notable examples.
Graphic Design
In graphic design, equilateral triangles serve various purposes. Designers often use them to create logos and branding materials that convey stability and unity. For instance:
- Adobe’s Logo: The iconic triangle shape emphasizes creativity.
- Delta Airlines: The triangular symbol represents flight and direction.
- Triangular Layouts: Many websites utilize triangular grids for an organized look.
Such designs capture attention while maintaining visual harmony.
- Tetra Paks: These containers use triangular shapes for efficient storage.
- Kettle Designs: Some kettles feature a triangular base for better