In today’s digital world, encryption and decryption technology are examples of essential tools for safeguarding information. With cyber threats constantly evolving, understanding how these technologies work can make all the difference in protecting your sensitive data. Have you ever wondered how your online transactions remain secure or how private messages stay confidential?
What Is Encryption And Decryption Technology?
Encryption and decryption technology plays a crucial role in securing sensitive data. These processes protect information from unauthorized access, ensuring that only intended recipients can read it.
Definition Of Encryption
Encryption transforms readable data into an unreadable format using algorithms. This process secures sensitive information like passwords, credit card numbers, and personal messages. For example:
- AES (Advanced Encryption Standard): Commonly used by governments to secure classified data.
- RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman): Often employed for secure data transmission over the internet.
You might encounter encryption when shopping online or communicating via messaging apps. In these scenarios, your personal details remain confidential through strong encryption methods.
Definition Of Decryption
Decryption is the reverse process of encryption. It converts encrypted data back into its original format so authorized users can access it. For instance:
- Symmetric Key Decryption: Uses the same key for both encryption and decryption.
- Asymmetric Key Decryption: Utilizes a pair of keys—one public and one private—for secure communications.
When you receive an encrypted email, your device uses decryption to display the message properly. Without this essential step, sensitive content remains inaccessible to anyone lacking the appropriate permissions.
Importance Of Encryption And Decryption Technology
Encryption and decryption technologies play a vital role in safeguarding sensitive information. They ensure that your data remains confidential and secure, even amidst increasing cyber threats.
Data Privacy And Security
Data privacy hinges on robust encryption practices. When you share personal details online, encryption transforms that data into an unreadable format. For instance:
- AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) protects files on your devices.
- RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) secures emails by encrypting the content before transmission.
These technologies help you maintain control over your information, preventing unauthorized access or breaches.
Compliance With Regulations
Compliance with regulations necessitates effective encryption methods. Laws like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) mandate strict data protection measures. By employing encryption:
- You fulfill legal obligations while processing personal data.
- You mitigate risks of heavy fines associated with non-compliance.
Using strong encryption helps ensure that your organization meets these standards while enhancing trust among customers.
Common Types Of Encryption And Decryption Methods
Encryption and decryption methods play a crucial role in safeguarding digital information. Understanding the different types can help you choose the right approach for your security needs. Below are two main categories of encryption: symmetric and asymmetric.
Symmetric Encryption
Symmetric encryption uses the same key for both encryption and decryption. This method ensures that only those who possess the key can access the original data. Popular examples include:
- AES (Advanced Encryption Standard): Widely used for securing sensitive data, especially in government and financial sectors.
- DES (Data Encryption Standard): An older standard, now considered less secure but historically significant.
- 3DES (Triple DES): Enhances DES by applying it three times, offering increased security.
Are you aware that symmetric encryption is generally faster than asymmetric? This speed makes it ideal for encrypting large amounts of data quickly.
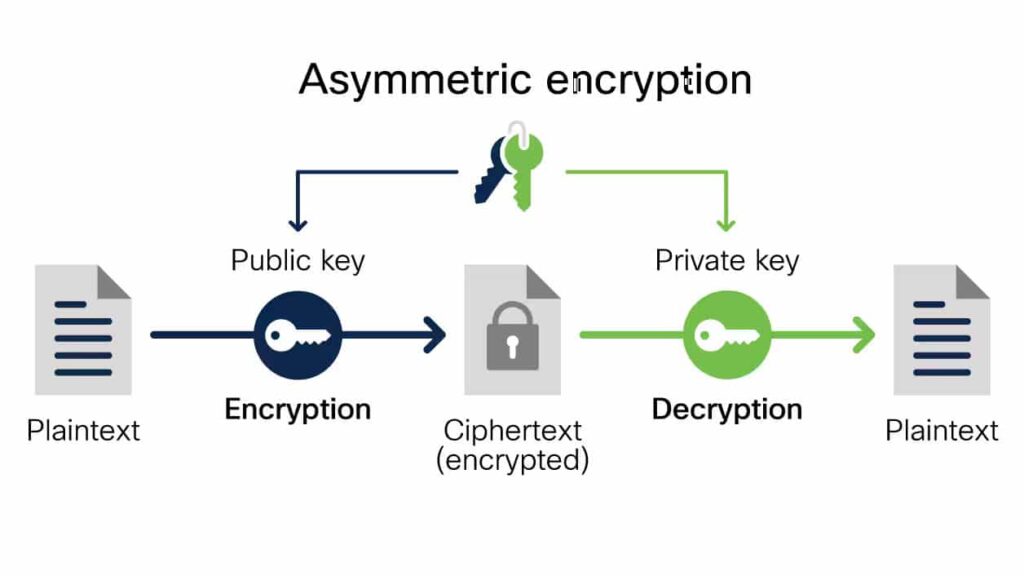
Asymmetric Encryption
Asymmetric encryption employs a pair of keys—one public and one private—for its operations. The public key encrypts data while only the corresponding private key can decrypt it. Key examples include:
- RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman): A widely used algorithm that secures online communications such as SSL/TLS.
- ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography): Offers similar security to RSA but with smaller key sizes, making it efficient for mobile devices.
Isn’t it fascinating how asymmetric encryption enhances security? By separating keys, it allows for safer transactions over unsecured channels.
Real-World Applications Of Encryption And Decryption Technology
Encryption and decryption technologies play vital roles across various sectors, ensuring data security and privacy. These applications are critical in safeguarding sensitive information from unauthorized access.
Secure Communication
Secure communication relies heavily on encryption techniques. Messaging apps like WhatsApp use end-to-end encryption, meaning only you and the recipient can read the messages. Email services often implement Transport Layer Security (TLS) to protect email content during transmission. Additionally, video conferencing platforms employ encryption to ensure private meetings remain confidential. These methods prevent eavesdropping and maintain trust among users.
Data Protection In Cloud Services
Data protection in cloud services is paramount for businesses today. Providers such as Google Drive and Dropbox utilize encryption to secure user files both at rest and in transit. This means that even if someone intercepts your data, they can’t access it without the proper keys. Companies also comply with regulations like GDPR by applying strong encryption measures for personal data stored in cloud environments. This approach minimizes risks associated with data breaches and enhances customer confidence in their services.
Challenges And Future Trends In Encryption And Decryption Technology
Encryption and decryption technologies face significant challenges as cyber threats evolve. As you navigate this landscape, it’s crucial to recognize the impact of these changes on security measures.
Evolving Threat Landscape
Cybercriminals continuously develop sophisticated techniques to breach encryption. For instance, attacks like man-in-the-middle (MITM) can intercept data during transmission. Additionally, ransomware has become prevalent, targeting organizations worldwide and demanding payment for data release.
Consider these common threats:
- Phishing attacks: Deceptive emails aimed at acquiring sensitive information.
- Data breaches: Unauthorized access to databases containing personal data.
- Malware: Software designed to disrupt or gain unauthorized access.
This evolving threat landscape necessitates constant adaptations in encryption practices to ensure ongoing protection against potential vulnerabilities.
Advances In Quantum Computing
Quantum computing poses a unique challenge for traditional encryption methods. Unlike classical computers, quantum systems can process vast amounts of data simultaneously. This capability might render current algorithms like RSA ineffective against future attacks.
You might wonder about the implications:
- Increased speed of decryption: Quantum computers could break existing encryption within hours or minutes.
- Need for post-quantum cryptography: New algorithms must be developed to withstand quantum capabilities and protect sensitive data.
By understanding these advancements, you can prepare your security strategies accordingly and stay ahead in protecting your digital assets.