Imagine walking into a doctor’s office where everything runs smoothly, patient records are instantly accessible, and your healthcare provider has all the information they need at their fingertips. This is the power of EMR systems. These electronic medical record systems revolutionize how healthcare providers manage patient data, making processes faster and more efficient.
Overview of EMR Systems
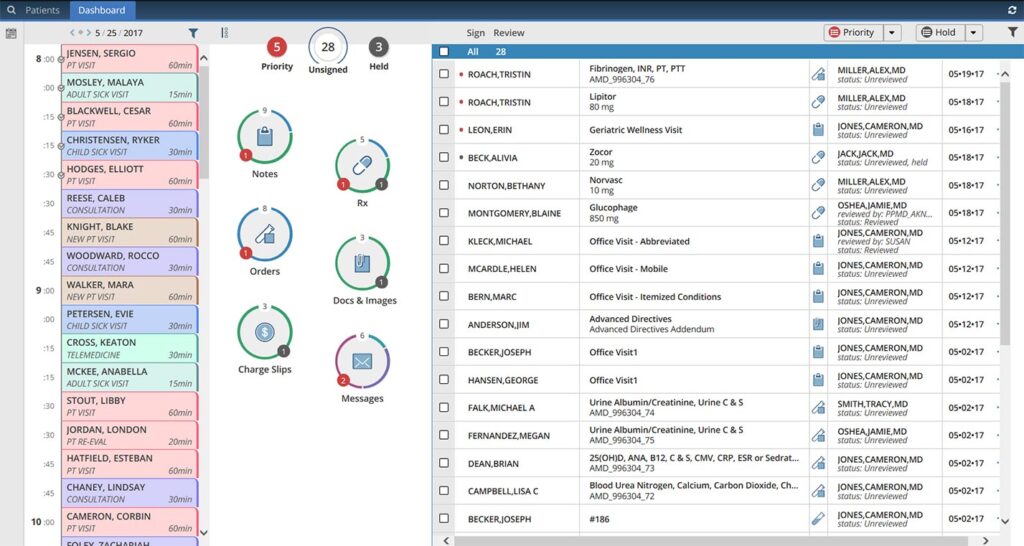
EMR systems revolutionize how healthcare providers manage patient information. They streamline access to records, enabling quicker decision-making and improved patient care.
Definition of EMR Systems
Electronic Medical Record (EMR) systems are digital versions of patients’ paper charts. These systems encompass a variety of functionalities, including documentation of medical histories, treatment plans, and diagnostic results. EMRs facilitate the collection and storage of patient data in a centralized location, accessible to authorized personnel. This transition from paper to digital significantly enhances the efficiency and accuracy of record-keeping.
Importance in Healthcare
EMR systems play a crucial role in modern healthcare settings. Their importance manifests in several ways:
- Improved Patient Care: Quick access to comprehensive patient records allows for informed clinical decisions.
- Enhanced Coordination: Data sharing among different providers ensures continuity in treatment.
- Increased Efficiency: Administrative tasks become streamlined, reducing time spent on paperwork.
- Data Security: Robust security measures protect sensitive health information from unauthorized access.
With these advantages, it’s clear that EMR systems contribute significantly to better healthcare outcomes.
Key Features of EMR Systems
EMR systems offer various essential features that enhance healthcare delivery and patient management. Understanding these functionalities helps you appreciate their significance in improving efficiency and accuracy within medical practices.
Patient Data Management
Patient data management is a core feature of EMR systems. These systems allow for the comprehensive documentation of patient histories, treatments, and outcomes. For instance, when a new patient visits a clinic, their information can be entered directly into the system. This eliminates the need for paper records and ensures that all relevant details are readily accessible to healthcare providers at any time.
Reporting and Analytics
Reporting and analytics tools in EMR systems provide valuable insights. These features enable healthcare providers to track trends in patient care and treatment effectiveness. For example, an EMR system might generate reports on common diagnoses over a specific period or evaluate medication adherence rates among patients. Such data-driven insights help improve clinical decision-making processes.
Interoperability
Interoperability is crucial for effective communication between different healthcare entities. EMR systems facilitate seamless sharing of information across various platforms. If a patient sees multiple specialists, each provider can access shared data through interoperable EMRs. This capability enhances coordinated care efforts and reduces the risk of medical errors due to incomplete information sharing among providers.
Benefits of EMR Systems
EMR systems offer numerous advantages that transform the healthcare landscape. Their implementation leads to significant improvements in patient care, operational efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
Improved Patient Care
EMR systems enhance patient care through streamlined access to health records. With instant retrieval of patient histories and treatment plans, providers make faster decisions. For example, a clinician can quickly check medication allergies before prescribing new treatments. Moreover, reminders for preventive care or follow-up appointments improve adherence to treatment protocols.
Increased Efficiency
Efficiency skyrockets with the use of EMR systems in daily operations. Automated tasks like appointment scheduling reduce administrative burdens on staff. Additionally, electronic prescriptions minimize errors associated with handwritten notes, ensuring patients receive correct medications promptly. Tasks such as billing and coding also become more straightforward through integrated systems, allowing healthcare professionals to focus more on patient interactions than paperwork.
Cost-Effectiveness
The adoption of EMR systems proves financially beneficial over time. By reducing paper usage and storage costs, practices save money while improving workflow. For instance, fewer resources spent on physical record maintenance lead to lower overhead expenses. Furthermore, enhanced efficiency often results in increased patient throughput—more patients treated equates to greater revenue without compromising service quality.
Challenges in Implementing EMR Systems
Implementing Electronic Medical Record (EMR) systems presents several challenges that can affect healthcare providers. Understanding these issues is crucial for successful integration.
Data Security Concerns
Data security remains a significant challenge when adopting EMR systems. Healthcare organizations face threats from cyberattacks, which can compromise sensitive patient information. For instance, the 2025 data breach at Universal Health Services exposed records of over 600,000 patients. Ensuring compliance with regulations like HIPAA requires robust security measures and ongoing training to protect against unauthorized access.
User Training and Adoption
User training and adoption often prove difficult during implementation. Staff members may resist transitioning from paper-based records to digital systems, leading to inefficiencies. For example, if nurses aren’t trained properly on new software features, they might struggle with documentation processes. Effective training programs are essential to enhance user confidence and ensure smooth daily operations within the healthcare setting.
High Initial Costs
High initial costs represent another hurdle in implementing EMR systems. The expenses associated with purchasing software, hardware upgrades, and training can be substantial. A study by the Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society indicates that average upfront costs range from $15,000 to $70,000 per provider for comprehensive systems. These financial barriers can deter smaller practices from making the switch despite long-term savings potential through improved efficiency.