Have you ever wondered why some people have strikingly similar features or behaviors? Dominant traits in humans play a fascinating role in shaping our identities and characteristics. These traits, which often overshadow their recessive counterparts, influence everything from physical appearance to certain personality aspects.
Overview of Dominant Traits in Humans
Dominant traits play a crucial role in defining human characteristics. These traits manifest more prominently than recessive ones, influencing both physical features and behaviors.
Strong examples of dominant traits include:
- Brown eyes: Brown eye color is a common dominant trait; it often overshadows blue or green eyes.
- Curly hair: Individuals with curly hair frequently inherit this trait over straight hair due to its dominant nature.
- Widow’s peak: The presence of a widow’s peak hairline demonstrates dominance over a straight hairline.
Moreover, some personality traits display dominance as well. For instance:
- Extroversion: Extroverted individuals tend to engage easily with others, showcasing this trait more than introverted counterparts.
- Risk-taking behavior: Many people exhibit risk-taking tendencies that overshadow cautious approaches.
In genetics, understanding these dominant traits helps explain inheritance patterns. You can trace these traits through family lineage, revealing how they shape individual identities across generations.
Common Dominant Traits
Dominant traits in humans manifest in various forms, impacting both physical attributes and behaviors. Understanding these traits provides insight into genetics and individual characteristics.
Physical Traits
Several physical traits often appear as dominant within the human population. For instance:
- Brown eyes: This eye color dominates over blue and green, affecting a large percentage of the global population.
- Curly hair: Curly hair strands typically overshadow straight ones, showcasing dominance in many families.
- Widow’s peak: This hairline shape presents itself more frequently than its straight counterpart.
These examples illustrate how dominant traits play a significant role in defining your appearance.
Behavioral Traits
Behavioral traits also exhibit dominance among individuals. Some common examples include:
- Extroversion: Extroverted personalities tend to thrive in social settings, often leading group activities or engaging others easily.
- Risk-taking behavior: Individuals displaying boldness frequently seek out new experiences and challenges over cautiousness.
Recognizing these behavioral patterns helps you understand interpersonal dynamics better.
Genetic Basis of Dominance
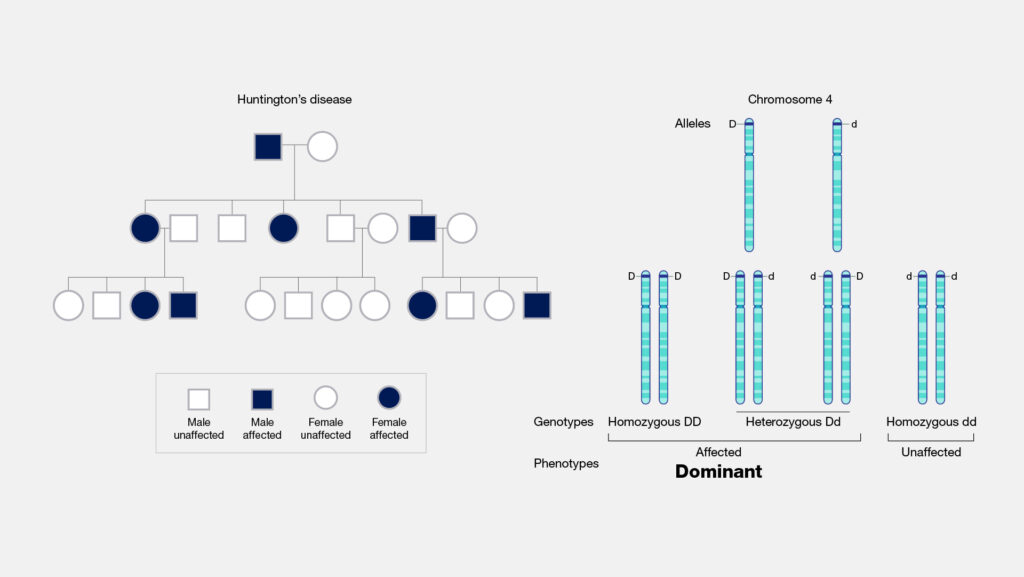
Understanding the genetic basis of dominant traits reveals how specific genes influence human characteristics. Dominant traits arise from alleles, which are variations of a gene. These alleles can determine physical appearance and certain behaviors.
Dominant Alleles Explained
Dominant alleles express their effects even when paired with recessive alleles. For example, if you inherit a brown eye allele from one parent and a blue eye allele from another, your eyes will be brown due to the dominance of the brown eye allele. Another strong example is curly hair; one curly hair allele can produce curls, while straight hair requires two straight hair alleles.
Inheritance Patterns
Inheritance patterns illustrate how dominant traits pass through generations. You might notice that if one parent has a dominant trait, such as a widow’s peak, there’s a high chance their children will also display this trait. This pattern is predictable:
- If both parents carry dominant and recessive alleles, about 75% of their offspring may exhibit the dominant trait.
- When one parent carries only recessive traits, none of the children will show the dominant characteristic.
Understanding these patterns helps clarify why certain traits appear more prominently in families or populations over time.
Implications of Dominant Traits
Understanding the implications of dominant traits reveals their far-reaching effects on health and personality. These traits shape not only individual identities but also influence social dynamics and well-being.
Impact on Health
Dominant traits often correlate with specific health conditions. For instance, individuals with brown eyes might have a genetic predisposition to certain eye diseases. Similarly, those possessing curly hair can experience different skin sensitivities due to genetic factors.
Some common examples include:
- High cholesterol: This trait can run in families, influenced by dominant genes.
- Certain cancers: Genetic markers for breast or colon cancer may display dominance, increasing risk.
- Lactose tolerance: A dominant trait that affects dietary choices and digestive health.
These examples show how understanding dominant traits can guide preventive measures and personalized healthcare strategies.
Influence on Personality
Personality is significantly affected by dominant traits too. Traits like extroversion tend to dominate social settings, influencing interactions and relationships. People who exhibit this trait often thrive in group environments and lead conversations spontaneously.
Key examples include:
- Leadership tendencies: Individuals with extroverted traits often assume leadership roles naturally.
- Social adaptability: Extroverts typically navigate social situations with ease, making connections quickly.
- Risk-taking behavior: Those displaying dominance in this area may embrace challenges more readily than others.
Recognizing these influences helps you understand your behavioral patterns and improve interpersonal relationships effectively.