Are you ready to transform your health and well-being through diet? Your daily food choices play a crucial role in how you feel, look, and even think. In this article, we’ll explore various diets that can help you reach your goals—whether it’s weight loss, increased energy, or simply feeling better.
Understanding different diet options is essential for making informed decisions. From the Mediterranean diet rich in healthy fats to the plant-based approach focusing on fruits and vegetables, each has unique benefits tailored to your needs. You might wonder which diet fits your lifestyle best.
Understanding Diet
A diet refers to the types of food and drink you consistently consume. It shapes your health and affects how you feel daily. Different diets align with various goals, such as weight management or enhancing energy levels.
Definition of Diet
A diet consists of the sum of your eating habits and choices. This can include:
- Macronutrients: Carbohydrates, proteins, and fats that provide energy.
- Micronutrients: Vitamins and minerals essential for bodily functions.
- Hydration: Water intake crucial for overall health.
Understanding your dietary patterns helps identify areas for improvement.
Importance of a Balanced Diet
A balanced diet is vital for optimal health. It ensures you receive all necessary nutrients in appropriate amounts.
A balanced diet supports physical well-being by preventing deficiencies. For example, calcium-rich foods strengthen bones while fiber aids digestion. Additionally, a variety enhances meal enjoyment and reduces dietary boredom.
Consider these benefits of maintaining balance:
- Improved immune function: Nutrients boost your body’s defenses against illness.
- Weight control: A varied intake prevents overeating specific food groups.
- Mood regulation: Certain foods influence brain chemistry positively.
Incorporating diverse food sources not only meets nutritional needs but also promotes long-term health outcomes.
Types of Diets
Diets come in various forms, each designed to achieve specific health goals or address particular needs. Understanding the different types can help you choose one that aligns with your lifestyle.
Popular Diets Explained
- Mediterranean Diet: Focuses on whole foods like fruits, vegetables, nuts, and fish. It emphasizes healthy fats from olive oil and encourages moderate wine consumption.
- Keto Diet: High in fats and low in carbohydrates. This diet aims to shift the body into a state of ketosis, where it burns fat for fuel instead of glucose.
- Paleo Diet: Centers on unprocessed foods similar to what early humans consumed. Think lean meats, fish, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds while avoiding dairy and grains.
- Plant-Based Diet: Prioritizes plant foods such as vegetables, fruits, grains, and legumes. It limits or excludes animal products entirely or focuses on them minimally.
- Intermittent Fasting: Involves cycling between periods of eating and fasting. Various methods exist; some involve skipping meals daily while others restrict eating times to certain hours.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Each Diet
Each diet has its pros and cons that vary based on individual preferences.
Mediterranean Diet
- Benefits: Supports heart health; rich in antioxidants.
- Drawbacks: Can be expensive due to fresh produce costs.
Keto Diet
- Benefits: Promotes quick weight loss; reduces hunger levels.
- Drawbacks: May lead to nutrient deficiencies; hard to maintain long-term.
Paleo Diet
- Benefits: Encourages whole food consumption; may improve metabolic health.
- Drawbacks: Excludes many food groups like dairy; can be restrictive.
Plant-Based Diet
- Benefits: Lowers risk of chronic diseases; environmental benefits.
- Drawbacks: Potential protein deficiency if not well-planned; requires careful meal prep.
- Benefits: Simplifies meal planning; may enhance metabolic health.
- Drawbacks: Some find it difficult due to hunger during fasting windows.
Nutritional Elements of a Diet
Understanding the nutritional elements of a diet is essential for making informed food choices. A balanced intake of various nutrients supports overall health and well-being.
Macronutrients: Carbs, Fats, and Proteins
Macronutrients are vital components that provide energy and support bodily functions. Each macronutrient plays a unique role in your diet:
- Carbohydrates supply energy, fueling daily activities. Sources include whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
- Fats are necessary for hormone production and nutrient absorption. Healthy fats come from avocados, nuts, and olive oil.
- Proteins help build tissues and repair muscles. Good sources are lean meats, beans, eggs, and dairy products.
Balancing these macronutrients promotes optimal energy levels and supports metabolic health.
Micronutrients: Vitamins and Minerals
Micronutrients consist of vitamins and minerals that support various bodily processes. While needed in smaller amounts than macronutrients, they play crucial roles:
- Vitamins, like vitamin C found in citrus fruits or vitamin D from sunlight exposure, boost immune function.
- Minerals, such as calcium from dairy products or iron from leafy greens, support bone health and oxygen transport.
Incorporating a variety of foods ensures adequate intake of these essential micronutrients for overall wellness.
Dietary Guidelines
Dietary guidelines provide a framework for making healthy food choices. They emphasize the importance of balance, variety, and moderation in your daily diet. Following these guidelines can lead to improved health outcomes and overall well-being.
Recommended Daily Intakes
Recommended daily intakes help you understand how much of each nutrient you should consume. For adults, the following values are suggested:
| Nutrient | Recommended Daily Intake |
|---|---|
| Carbohydrates | 225-325 grams |
| Protein | 46-56 grams |
| Fats | 70-100 grams |
| Fiber | 25-38 grams |
| Water | About 2.7 liters (for women) / 3.7 liters (for men) |
These recommendations vary based on age, sex, and activity level. Are you meeting your nutritional needs? Adjusting portion sizes and food choices can help align with these guidelines.
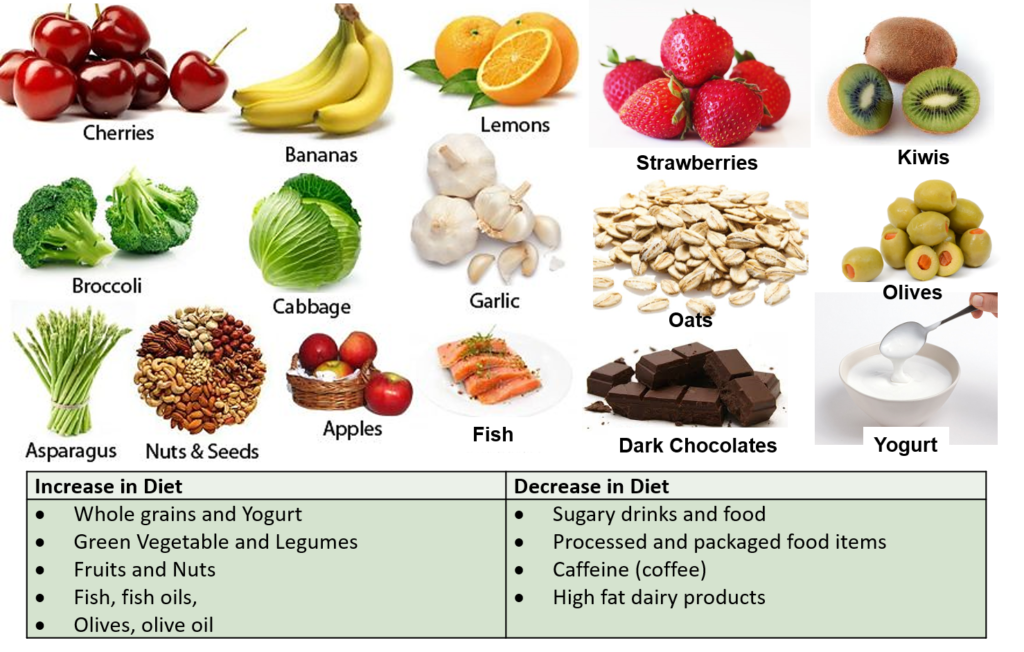
Tips for Healthy Eating
Healthy eating involves simple yet effective strategies that make a significant difference over time. Consider implementing these tips into your routine:
- Plan meals ahead to avoid impulsive choices.
- Incorporate fruits and vegetables into every meal for essential nutrients.
- Choose whole grains instead of refined grains for added fiber.
- Limit added sugars by reading labels and opting for natural sweeteners when possible.
- Stay hydrated by drinking water throughout the day instead of sugary drinks.