Navigating the complex world of healthcare can be overwhelming, especially when it comes to understanding regulations like HIPAA. But do you know what a covered entity under HIPAA really means? This term is crucial for anyone involved in handling protected health information.
In this article, you’ll discover various examples of covered entities that play significant roles in safeguarding patient data. From hospitals and insurance companies to healthcare providers, each has specific responsibilities under HIPAA guidelines. By exploring these examples, you’ll gain insight into how they ensure compliance and protect your sensitive information.
Overview of Covered Entity HIPAA
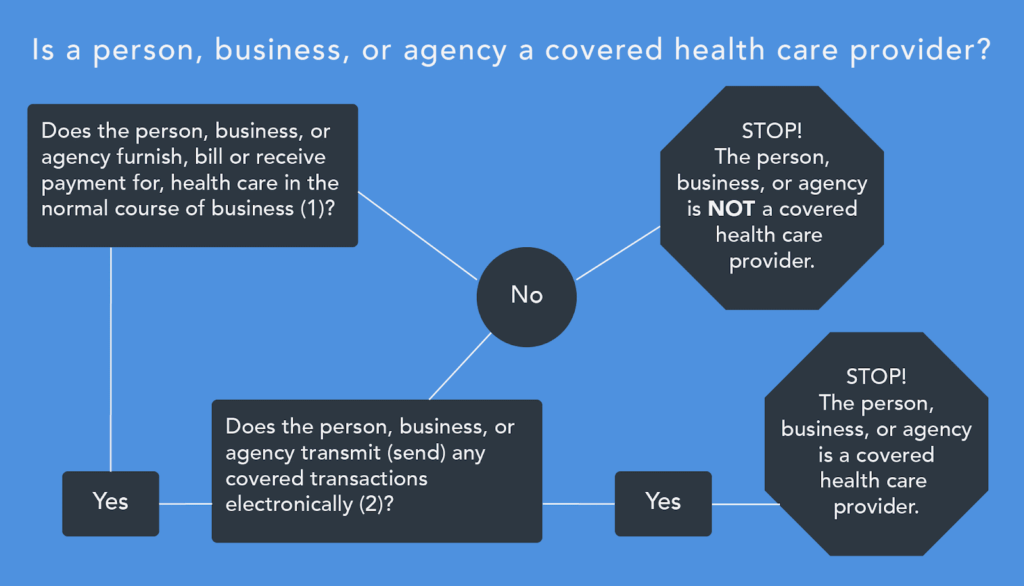
Covered entities under HIPAA include specific organizations that handle protected health information (PHI). Understanding these entities is vital for ensuring compliance with regulations. Here are the primary types:
- Healthcare Providers: Hospitals, physicians, and clinics qualify as covered entities if they transmit PHI electronically. They must follow strict guidelines to protect patient data.
- Health Plans: Insurance companies and health maintenance organizations (HMOs) are also covered entities because they manage PHI related to individuals’ coverage and claims.
- Healthcare Clearinghouses: These organizations process or facilitate the processing of nonstandard data elements into standard ones for billing purposes, making them essential in the healthcare system.
Each type of covered entity has distinct responsibilities regarding safeguarding patient information. It’s crucial for you to be aware of these roles when managing PHI within your organization.
Types of Covered Entities
Understanding the different types of covered entities under HIPAA is crucial for anyone involved in handling protected health information (PHI). Each type plays a significant role in ensuring compliance and protecting patient data.
Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers are essential covered entities. These include hospitals, doctors’ offices, and clinics that transmit PHI electronically. Examples of healthcare providers are:
- Hospitals: Facilities offering comprehensive medical services.
- Physician practices: Individual or group practices providing outpatient care.
- Nursing homes: Institutions catering to long-term care for patients.
Each provider must implement safeguards to protect patient information actively.
Health Plans
Health plans cover a variety of organizations managing healthcare costs. They include insurance companies, health maintenance organizations (HMOs), and government programs like Medicare and Medicaid. Examples of health plans are:
- Private insurance companies: Companies providing individual or employer-sponsored insurance.
- Medicare: A federal program assisting older adults with healthcare costs.
- Medicaid: A state and federal partnership aiding low-income individuals.
These plans handle sensitive PHI related to coverage decisions, premiums, and claims processing.
Healthcare Clearinghouses
Healthcare clearinghouses act as intermediaries for processing nonstandard data elements into standard formats. They play a vital role in billing and claims submission by converting data from providers before it reaches insurers. Examples include:
- Billing services: Firms specializing in medical billing for healthcare providers.
- Data processing centers: Organizations that aggregate PHI for reporting purposes.
Clearinghouses help streamline transactions between providers and payers while maintaining confidentiality standards set by HIPAA.
Responsibilities of Covered Entities
Covered entities must adhere to various regulations under HIPAA to protect patient information. Understanding these responsibilities is crucial for compliance and safeguarding protected health information (PHI).
Privacy Rule
The Privacy Rule mandates that covered entities ensure the confidentiality of PHI. They must:
- Limit access: Access to PHI should only be granted to authorized personnel.
- Obtain consent: Patients must provide consent before their information can be shared.
- Implement safeguards: Covered entities need to create policies that prevent unauthorized disclosures.
Security Rule
The Security Rule focuses on protecting electronic PHI (ePHI). Covered entities are required to:
- Conduct risk assessments: Regular evaluations help identify vulnerabilities in ePHI management.
- Utilize encryption: Encrypting data protects it from unauthorized access during transmission and storage.
- Train staff members: Ongoing education ensures all employees understand security protocols.
Breach Notification Rule
In case of a data breach, covered entities must follow specific notification procedures. They need to:
- Notify affected individuals: Inform patients about breaches affecting their PHI within 60 days.
- Report breaches to HHS: Report breaches involving 500 or more individuals immediately.
- Document incidents: Maintain records detailing the nature and response actions taken regarding each breach.
By understanding these responsibilities, you can better ensure compliance with HIPAA regulations while protecting patient privacy effectively.
Compliance Challenges for Covered Entities
Covered entities face significant compliance challenges under HIPAA. Understanding these hurdles is essential for effectively managing protected health information (PHI).
Understanding Scope
The scope of HIPAA regulations can be complex. Covered entities must identify all relevant areas affected by the Privacy Rule and Security Rule, including:
- Patient records: Maintaining confidentiality in storage and access.
- Data transmission: Securing electronic PHI during transfer.
- Third-party vendors: Ensuring business associates comply with HIPAA standards.
Recognizing these elements helps you establish a comprehensive compliance strategy.
Training and Implementation
Training staff on HIPAA compliance remains a critical challenge. It’s crucial that all employees understand their responsibilities regarding PHI. Effective training programs should include:
- Regular updates: Keeping staff informed about changes in regulations.
- Practical exercises: Engaging scenarios to reinforce learning.
- Clear policies: Providing accessible documentation on protocols.
Implementation of these training initiatives fosters a culture of privacy within your organization, enabling better protection of patient data.
Future Considerations for Covered Entities
Covered entities face evolving challenges in maintaining HIPAA compliance. For instance, technology advancements necessitate regular updates to security protocols. As organizations adopt new electronic health record (EHR) systems, they must ensure these platforms meet stringent data protection standards.
Regulatory changes also impact covered entities significantly. For example, the introduction of new privacy regulations may require adjustments in data handling practices. Staying informed about potential legislative shifts is vital for continuous compliance.
Additionally, covered entities should prioritize staff training to enhance awareness of HIPAA requirements. Regular workshops can reinforce the importance of safeguarding protected health information (PHI). Moreover, investing in ongoing education fosters a culture of privacy and accountability within the organization.
You might consider conducting risk assessments periodically. These evaluations help identify vulnerabilities related to ePHI management and allow for timely remediation efforts. Furthermore, establishing clear communication channels with third-party vendors ensures they adhere to HIPAA standards as well.
Finally, you can’t overlook the significance of patient engagement in future considerations. Encouraging patients to understand their rights under HIPAA promotes transparency and strengthens trust between healthcare providers and patients. Thus, empowering individuals through educational resources enhances overall compliance efforts.