Have you ever wondered how certain words can seamlessly connect your ideas? Conjunctions are essential building blocks of language, allowing you to link thoughts and create more complex sentences. From simple lists to intricate clauses, these small yet powerful words play a crucial role in effective communication.
Overview of Conjunctions
Conjunctions play a crucial role in connecting phrases, clauses, and words. They enhance the flow of sentences and help convey complex ideas clearly. Understanding conjunctions simplifies sentence construction.
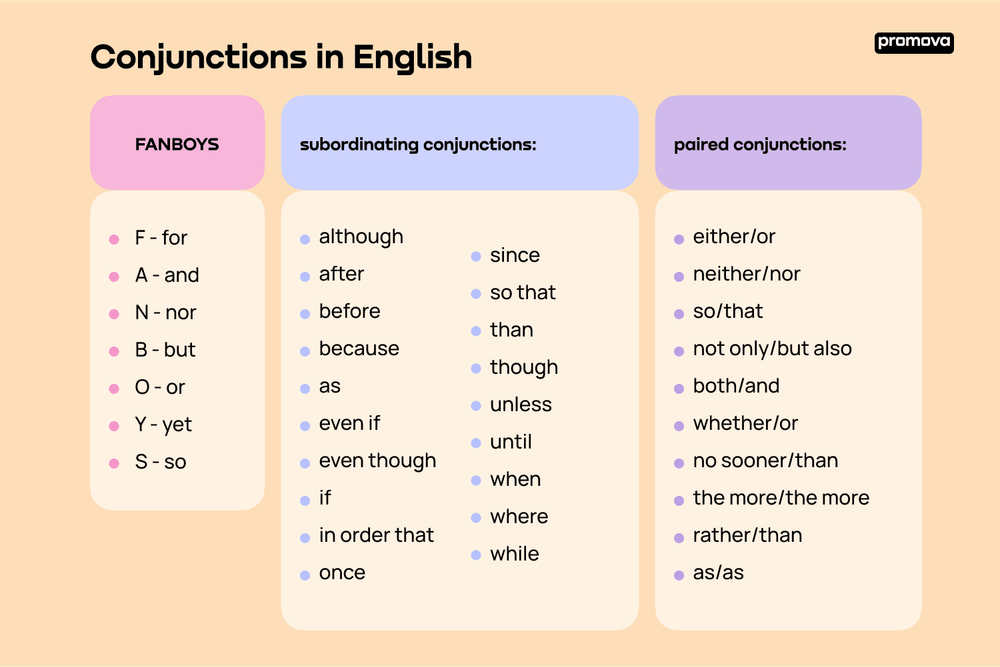
- Coordinating Conjunctions: These connect words or groups that are similar. Common examples include “and,” “but,” and “or.” For instance, you might say, “I like apples and oranges.”
- Subordinating Conjunctions: These introduce dependent clauses, establishing relationships between them and independent clauses. Examples include “because,” “although,” and “since.” An example would be, “Although it rained, we enjoyed the picnic.”
- Correlative Conjunctions: These work in pairs to connect equal elements within a sentence. Examples are “either…or,” “neither…nor,” and “not only…but also.” You can say, “Not only did she study hard, but she also passed the exam.”
Using these conjunction types effectively aids in crafting clear and engaging sentences that communicate your thoughts accurately.
Types of Conjunctions
Conjunctions play a vital role in connecting ideas and enhancing sentence structure. Understanding the three main types can improve your writing significantly.
Coordinating Conjunctions
Coordinating conjunctions connect words, phrases, or independent clauses that are similar. Common examples include “and,” “but,” and “or.” Here are some sentences illustrating their use:
- You can have tea and coffee.
- She wanted to go shopping, but it started to rain.
- Would you prefer pizza or pasta for dinner?
These conjunctions allow for smooth transitions between related thoughts.
Subordinating Conjunctions
Subordinating conjunctions introduce dependent clauses and establish relationships with independent clauses. Examples include “because,” “although,” and “since.” Here’s how they function in sentences:
- I stayed home because I was feeling unwell.
- Although it was late, I decided to finish my work.
- Since it’s your birthday, I’ll bake a cake.
These conjunctions create complex sentences that add depth to your writing.
Correlative Conjunctions
Correlative conjunctions work in pairs to connect equal elements within a sentence. Common pairs include “either…or” and “not only…but also.” Consider these examples:
- You can either stay here or come with us.
- She is not only talented but also hard-working.
- Either you finish your homework now or</string you won’t be able to play later.
Using correlative conjunctions enhances the balance of your sentences while reinforcing connections between ideas.
Common Conjunction Examples
Conjunctions play a vital role in connecting ideas within sentences. Here are some examples that illustrate their usage clearly.
Examples in Sentences
- Coordinating conjunctions:
- “I wanted to go for a walk, but it started raining.”
- “You can choose chocolate or vanilla ice cream.”
- Subordinating conjunctions:
- “Although it was late, she decided to call him.”
- “He studied hard because he wanted good grades.”
- Correlative conjunctions:
- “Not only did she finish her project, but she also helped others.”
- “Either you join us for dinner, or you stay home.”
Contextual Usage
Understanding how to use conjunctions enhances your writing’s clarity and flow. For instance, using coordinating conjunctions helps link similar ideas or contrasting thoughts effectively. Similarly, subordinating conjunctions introduce important details that add depth to your sentences. Correlative conjunctions strengthen connections between paired elements, ensuring balance in your writing.
- When creating lists: Use coordinating conjunctions like “and” or “or” to connect items smoothly.
- In complex sentences: Subordinating conjunctions clarify relationships between different clauses.
- To emphasize choices: Correlative pairs highlight options while maintaining rhythm and clarity in your writing.
Importance of Using Conjunctions
Using conjunctions significantly enhances your writing. Conjunctions help link ideas, making sentences more coherent and easier to understand. For instance, coordinating conjunctions like “and,” “but,” and “or” create smooth transitions between related thoughts. You might say, “I enjoy hiking, but I also love reading.” This construction clearly expresses contrasting interests.
Subordinating conjunctions play a crucial role in adding depth to your sentences. They introduce dependent clauses that provide important details. Consider the sentence: “I went for a run because it was sunny.” Here, the subordinating conjunction “because” explains the reason behind the action.
Correlative conjunctions maintain balance within your writing. These pairs connect equal parts of a sentence effectively. An example is: “Not only do I study hard, but I also participate in extracurricular activities.” This structure emphasizes both actions equally.
Incorporating different types of conjunctions not only improves clarity but also enriches your communication style. When you vary conjunction use, you can express complex ideas with ease. Wouldn’t you agree that effective communication relies on well-structured sentences?