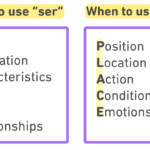
Mastering the conjugation of ser is essential for anyone looking to speak Spanish fluently. This irregular verb serves as a cornerstone in the language, helping you describe identity, characteristics, and origin. Have you ever wondered how to use “ser” correctly in different contexts?
Overview of Ser
Understanding the verb “ser” is essential for anyone learning Spanish. This irregular verb serves multiple functions in sentences, primarily involving identity, characteristics, and origin.
- Identity: Use “ser” to express who someone is.
- Example: Yo soy estudiante (I am a student).
- Characteristics: Describe inherent traits or qualities.
- Example: Ella es alta (She is tall).
- Origin: Indicate where someone or something comes from.
- Example: Nosotros somos de México (We are from Mexico).
- Time and Date: “Ser” also helps tell time and dates.
- Example: Son las tres (It’s three o’clock).
- Occupation: You can state someone’s job or profession using “ser”.
- Example: Él es médico (He is a doctor).
These examples illustrate the foundational role “ser” plays in Spanish grammar. By mastering its conjugation, you enhance your ability to communicate clearly and accurately in various contexts.
Importance of Conjugation
Mastering the conjugation of “ser” is essential for effective communication in Spanish. This verb serves as a building block, enabling you to express identity, characteristics, and origin accurately.
Regular vs. Irregular Verbs
Understanding the difference between regular and irregular verbs helps with conjugation. While regular verbs follow predictable patterns, “ser” is an irregular verb that does not conform to these rules. For example:
- Present tense: yo soy (I am), tú eres (you are)
- Preterite tense: fui (I was), fuiste (you were)
Recognizing these irregular forms enhances your ability to use “ser” correctly across different tenses.
Context in Spanish Language
Context determines how you use “ser” effectively. This verb appears in various situations like:
- Describing identity: “Yo soy médico” (I am a doctor).
- Stating characteristics: “Ella es inteligente” (She is smart).
- Indicating origin: “Nosotros somos de España” (We are from Spain).
Conjugation of Ser in Different Tenses
Understanding the conjugation of “ser” across various tenses is crucial for effective communication in Spanish. Here’s a breakdown to help you grasp these important forms.
Present Tense Conjugation
In the present tense, “ser” reflects current states or identities. The forms are:
- Yo soy (I am)
- Tú eres (You are – informal)
- Él/Ella/Usted es (He/She is, You are – formal)
- Nosotros/as somos (We are)
- Ellos/Ellas/Ustedes son (They/You all are)
Using “ser” in sentences like “Yo soy estudiante” illustrates identity.
Past Tense Conjugation
The past tense indicates completed actions or states. In the preterite tense, the conjugations include:
- Yo fui (I was)
- Tú fuiste (You were – informal)
- Él/Ella/Usted fue (He/She was, You were – formal)
- Nosotros/as fuimos (We were)
- Ellos/Ellas/Ustedes fueron (They/You all were)
For example, saying “Ella fue médica” shows a temporary state in the past.
Future Tense Conjugation
While Spanish often expresses future intentions with verbs like “ir,” you can also use “ser.” The future tense includes:
- Yo seré (I will be)
- Tú serás (You will be – informal)
- Él/Ella/Usted será (He/She will be, You will be – formal)
- Nosotros/as seremos (We will be)
- Ellos/Ellas/Ustedes serán (They/You all will be)
Common Mistakes in Conjugation
Understanding the conjugation of “ser” is crucial, yet many learners make common mistakes. One frequent error involves confusing the present tense forms. For example, using “yo eres” instead of “yo soy” leads to misunderstandings.
Another mistake occurs with past tense usage. Some might say “ella es médica” when they mean “ella fue médica.” This confusion can change the meaning significantly, as one indicates a current state while the other refers to a completed action.
Future tense errors also arise frequently. You might hear someone say “tú serás” incorrectly when referring to multiple people; it should be “ustedes serán.” Ensuring you use the appropriate form based on number and context helps maintain clarity.
Additionally, mixing up formal and informal contexts presents challenges. Using “usted es” in casual settings may sound overly formal, while “tú eres” could appear too familiar in professional situations. Recognizing these nuances aids effective communication.
Lastly, don’t forget about regional variations! In some Spanish-speaking countries, forms like “vos sos” are used instead of “tú eres.” Being aware of these differences enriches your understanding and fluency in conversations.
By paying attention to these common mistakes and practicing regularly, you’ll improve your command over “ser,” enhancing both your written and spoken Spanish skills.
Tips for Mastering Conjugation of Ser
Understanding how to use ser in various contexts enhances your Spanish fluency. Focus on these tips:
- Practice Regularly: Frequent practice helps cement the different forms of ser in your mind. Use flashcards or apps to quiz yourself.
- Contextual Learning: Learn sentences that incorporate ser in real-life scenarios, like introducing yourself or describing someone.
- Engage with Native Speakers: Speaking with native speakers provides practical experience and immediate feedback on your usage of ser.
- Utilize Online Resources: Websites and videos can provide interactive exercises focused on conjugating ser, making learning more engaging.
- Write Daily Sentences: Incorporate daily journaling into your routine, focusing on using different tenses of ser, such as “Yo soy feliz” (I am happy) or “Ella fue maestra” (She was a teacher).
- Group Study Sessions: Collaborate with peers to practice conjugations together; teaching others reinforces your own understanding.
- Identify Mistakes: Review common errors you make when using ser. For instance, remember not to confuse “tú eres” with “yo soy”.
By implementing these strategies, you’ll gain confidence in using the verb ser correctly across various tenses and contexts, ultimately improving your Spanish communication skills significantly.