Understanding the difference between concrete and abstract nouns can transform your grasp of language. Have you ever wondered why some words evoke tangible images while others stir emotions or ideas? Concrete nouns refer to things you can touch, see, or measure—like “apple” or “dog.” In contrast, abstract nouns represent concepts or feelings that aren’t physically present, such as “happiness” or “freedom.”
Understanding Nouns
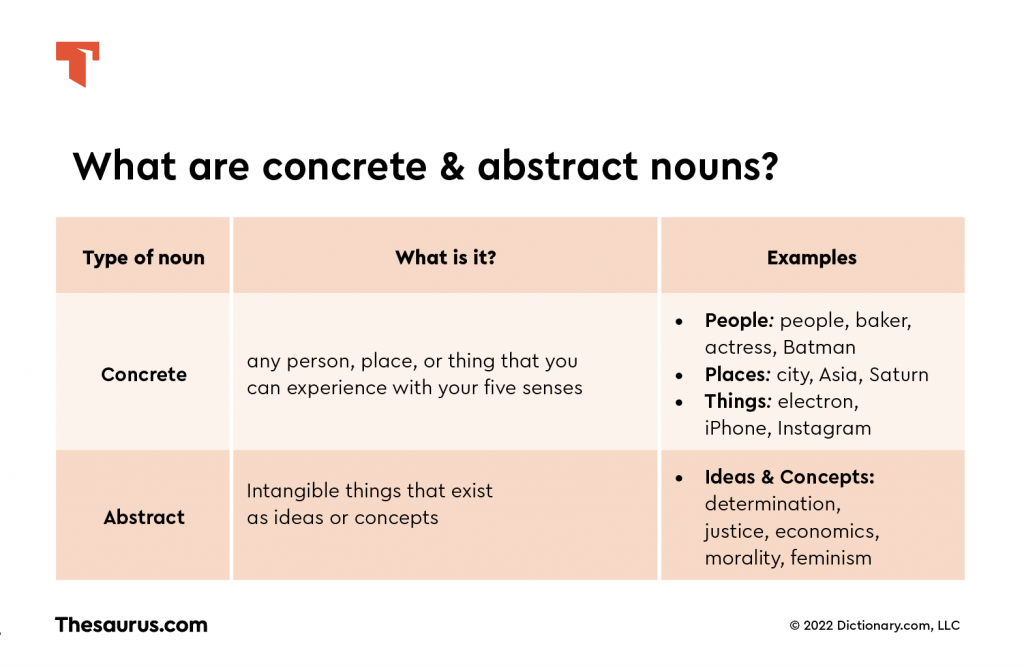
Concrete nouns are tangible items you can see, touch, smell, taste, or hear. Examples include strong words like “car,” “tree,” and “coffee.” Each of these can be experienced through your senses. You might find a car parked outside or enjoy the aroma of freshly brewed coffee in the morning.
On the other hand, abstract nouns represent ideas or feelings that can’t be sensed physically. Consider strong examples such as “love,” “freedom,” and “justice.” These concepts exist in thought but lack physical form. How often do you ponder on the meaning of freedom?
When identifying concrete and abstract nouns, context plays a crucial role. For instance, while “dream” refers to an experience during sleep (concrete), it also describes aspirations (abstract). This duality shows how one word can function differently based on its usage.
Additionally, some nouns can shift between being concrete and abstract depending on their application. Think about “light.” It denotes physical light when discussing illumination (concrete) but can also symbolize hope or clarity (abstract). Isn’t it fascinating how language works this way?
Concrete Nouns
Concrete nouns represent tangible items you can perceive through your senses. These include things you can see, touch, smell, taste, or hear. Understanding concrete nouns enhances your language competency.
Definition and Examples
Concrete nouns are objects or entities that exist physically. For example:
- Apple: You can see its color and feel its texture.
- Dog: Its barking and presence are easily perceived.
- Car: You can hear its engine running and feel the metal.
Other examples include chair, tree, and coffee. Each of these words represents something real, making them easy to identify in everyday situations.
Usage in Sentences
Using concrete nouns effectively clarifies communication. Here are some examples:
- “The apple on the table is ripe.”
- “I heard a dog barking outside my window.”
- “She parked her car in the driveway.”
These sentences illustrate how concrete nouns enrich descriptions by providing clear imagery. By focusing on specifics like location or action, you create vivid scenes for your readers.
Abstract Nouns
Abstract nouns represent ideas, qualities, and concepts that aren’t tangible. They express feelings or states of being rather than physical objects. Understanding abstract nouns enriches your vocabulary and enhances your expression in writing.
Definition and Examples
Abstract nouns refer to things you can’t see, touch, or measure directly. For example:
- Happiness captures a feeling of joy.
- Freedom expresses the state of being free.
- Justice signifies fairness or moral rightness.
Each of these words conveys an idea that exists in thought rather than as a physical entity.
Common Mistakes
Many confuse abstract nouns with adjectives or verbs. Remember:
- “Bravery” is an abstract noun, while “brave” is an adjective.
- “Excite” is a verb; its corresponding abstract noun is “excitement.”
When using these nouns, clarity matters. Ensure you’re expressing thoughts accurately without mixing parts of speech.
Differences Between Concrete and Abstract Nouns
Concrete nouns and abstract nouns serve distinct roles in language. Concrete nouns refer to items you can perceive through your senses, while abstract nouns represent ideas, feelings, or qualities that lack physical form.
Visualizing the Concepts
Visualizing these concepts can help clarify their differences. For example:
- Concrete Nouns:
- “Table”
- “Book”
- “Dog”
You see, hear, or touch these items. They create a clear image in your mind.
- Abstract Nouns:
- “Love”
- “Freedom”
- “Justice”
These words evoke emotions or thoughts but don’t have a tangible presence. Can you visualize what love feels like? It’s complex because it exists only as an idea.
Importance in Language
Understanding concrete and abstract nouns enhances communication skills. With concrete nouns, you provide specific details that paint vivid images for your audience. For instance:
- “The cat sat on the soft rug.”
Here, readers imagine a cozy scene thanks to the noun choices.
In contrast, with abstract nouns, you express deeper meanings and emotions. Consider:
- “Her happiness was contagious.”
This sentence conveys more than just joy; it captures an emotional state that resonates universally.
Recognizing these categories aids clarity and expression in writing. By choosing the right type of noun, you strengthen your message and connect better with others.