Imagine a world where your every command is executed in the blink of an eye. Computing systems are at the heart of this technological marvel, powering everything from your smartphone to complex data centers. But what exactly defines a computing system? It’s more than just hardware; it’s a seamless integration of software and processes designed to perform tasks efficiently.
Overview Of Computing Systems
Computing systems play a vital role in various aspects of daily life, integrating hardware, software, and processes to perform tasks efficiently. Understanding their definition and types helps clarify their significance in technology.
Definition Of Computing Systems
A computing system refers to a combination of hardware components and software programs designed to process data. It includes devices such as computers, servers, and smartphones that execute instructions. For example, when you use your laptop to browse the internet, both the device (hardware) and the browser application (software) work together as part of a computing system.
Types Of Computing Systems
Various types of computing systems exist, each serving distinct purposes:
- Personal Computers: These are commonly used for individual tasks like word processing or gaming.
- Workstations: Designed for technical or scientific applications, they offer higher performance compared to personal computers.
- Servers: They provide resources or services over a network; for instance, web servers host websites.
- Mainframes: Used by large organizations for bulk data processing, these systems handle vast amounts of transactions.
- Supercomputers: Capable of performing complex calculations at high speeds; they’re utilized in fields such as climate research and molecular modeling.
Each type serves unique needs while contributing significantly to overall technological functionality.
Components Of A Computing System
Computing systems consist of several integral components that work together to perform tasks efficiently. Understanding these components enhances your ability to utilize technology effectively.
Hardware Components
Hardware includes the physical devices that form a computing system. Examples are:
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): This processes instructions and performs calculations.
- Random Access Memory (RAM): This temporarily stores data for quick access by the CPU.
- Storage Devices: Hard drives and solid-state drives store data long-term.
- Input Devices: Keyboards and mice allow users to interact with the system.
- Output Devices: Monitors and printers display or produce results from processing.
Each hardware component plays a crucial role in overall performance, impacting how well a computing system operates.
Software Components
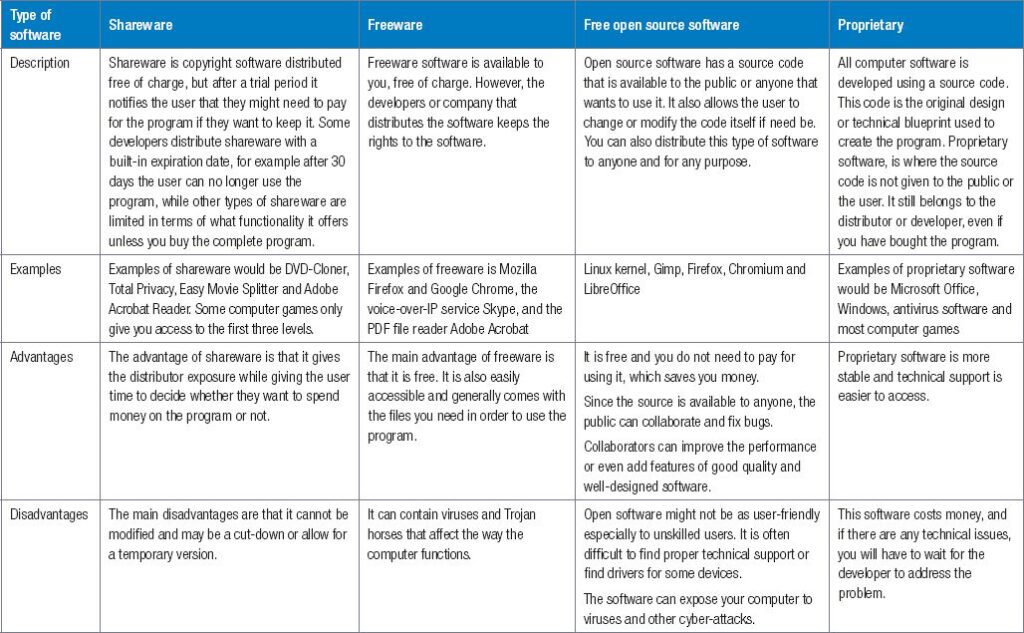
Software refers to the programs that instruct hardware on what tasks to perform. Important examples include:
- Operating Systems (OS): Windows, macOS, and Linux manage hardware resources and provide user interfaces.
- Application Software: Programs like Microsoft Office or Adobe Photoshop serve specific user needs.
- Utility Software: Tools such as antivirus programs maintain system health and security.
Without software, hardware would lack purpose. Each software type contributes uniquely to a computing system’s functionality, enabling effective operation across various applications.
Performance Metrics Of Computing Systems
Performance metrics are essential for evaluating the efficiency of computing systems. These metrics provide insights into how well a system performs its tasks and can help identify areas for improvement.
Processing Speed
Processing speed measures how quickly a computing system executes instructions. You often see this metric expressed in gigahertz (GHz) for CPUs, indicating how many cycles per second the processor can perform. For example:
- 2.5 GHz CPU: Executes 2.5 billion cycles per second, suitable for most everyday tasks.
- 3.8 GHz CPU: Handles complex applications like video editing or gaming more efficiently.
Higher processing speeds typically result in better performance, especially under heavy workloads.
Storage Capacity
Storage capacity indicates how much data a computing system can store and access. This metric is crucial as it affects overall functionality and user experience. Here are common storage options:
- HDD (Hard Disk Drive): Often found in older systems with capacities ranging from 500 GB to several terabytes, ideal for general use.
- SSD (Solid State Drive): Offers faster read/write speeds with capacities generally from 250 GB to 4 TB, enhancing system responsiveness significantly.
Understanding storage capacity helps you choose the right solutions based on your needs—be it storing large files or running multiple applications simultaneously.
Emerging Trends In Computing Systems
Emerging trends in computing systems reflect advancements that shape technology’s future. Staying informed about these trends enhances your understanding of the evolving landscape.
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing offers a flexible way to access and store data over the internet instead of relying solely on local servers. Examples include:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) provides scalable cloud solutions for businesses.
- Microsoft Azure allows organizations to build, deploy, and manage applications through Microsoft’s global network.
- Google Cloud Platform helps users leverage Google’s infrastructure for data storage and analytics.
These platforms enable you to improve efficiency while reducing costs.
Edge Computing
Edge computing processes data closer to its source rather than sending it all back to centralized servers. This trend reduces latency and bandwidth usage. Consider these examples:
- IoT devices like smart thermostats analyze data locally before sending relevant insights.
- Autonomous vehicles, which require real-time processing of vast amounts of sensor data, utilize edge computing for immediate decision-making.
- Industrial automation systems use edge computing for monitoring equipment performance in real time.
Adopting edge computing can optimize operations across various industries by enhancing speed and reliability.