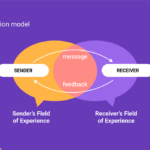
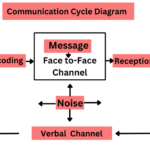
Have you ever wondered why some conversations flow effortlessly while others feel like pulling teeth? Understanding communication styles can be the key to unlocking more meaningful interactions in both your personal and professional life. Each person has a unique way of expressing thoughts and emotions, which influences how messages are received.
Overview of Communication Styles
Communication styles vary widely among individuals, impacting how messages are delivered and received. Understanding these styles enhances your interactions in both personal and professional environments. Here are some common communication styles:
- Assertive: This style involves expressing thoughts and feelings openly while respecting others. You might use “I” statements, such as “I feel…” or “I think…”.
- Aggressive: An aggressive communicator tends to dominate conversations. They may interrupt frequently, raise their voice, or use hostile language.
- Passive: Passive communicators avoid expressing their opinions and often agree with others to maintain peace. You may notice them using phrases like “Whatever you think is best.”
- Passive-Aggressive: This style masks true feelings behind indirect communication. For example, someone could say they’re fine but then act sulky or give the silent treatment.
Recognizing these styles helps tailor your approach when interacting with different individuals. Additionally, adapting your communication can lead to more effective exchanges and improved relationships.
Types of Communication Styles
Understanding the different types of communication styles enhances your ability to interact effectively. Here are four primary communication styles, each with unique characteristics.
Assertive Communication
Assertive communication involves expressing thoughts and feelings clearly while respecting others. For example, you might say, “I feel overwhelmed when meetings run late; can we stick to the agenda?” This approach fosters open dialogue and encourages collaboration. Assertive communicators often use “I” statements to express their needs without sounding confrontational.
Aggressive Communication
Aggressive communication is characterized by dominating conversations and disregarding others’ opinions. An aggressive communicator might state, “You always mess things up!” This style creates conflict and can alienate others. The goal seems more about winning an argument than fostering understanding or cooperation.
Passive Communication
Passive communication includes avoiding direct expression of thoughts or feelings. A passive communicator may agree to everything even if they disagree internally, saying something like, “Sure, whatever works for you.” This style leads to misunderstandings as important viewpoints remain unexpressed. Often, passive individuals suppress their emotions to avoid conflict.
Passive-Aggressive Communication
Passive-aggressive communication involves indirect expression of negative feelings. Instead of addressing issues directly, someone might make sarcastic comments or give silent treatment. For instance, saying “Fine! I’ll just do it myself,” conveys frustration without confrontation. This style complicates relationships as underlying issues are rarely resolved openly.
Influence of Communication Styles
Understanding the influence of communication styles enhances interactions in various aspects of life. Your ability to perceive and adapt to different styles can significantly impact personal relationships, professional settings, and cultural exchanges.
Personal Relationships
In personal relationships, communication styles shape the dynamics between individuals. For example, an assertive partner expresses feelings directly while respecting boundaries, leading to healthier conversations. Conversely, a passive individual might avoid conflicts by not sharing their opinions, which can create resentment over time. Recognizing these differences helps you navigate discussions more effectively.
Professional Settings
Communication styles also play a crucial role in professional environments. An assertive communicator often leads teams with clarity and confidence, fostering collaboration among colleagues. On the other hand, aggressive communication, such as yelling or dismissing others’ ideas during meetings, creates a hostile workspace that hinders productivity. Adapting your style according to workplace culture promotes better teamwork and reduces misunderstandings.
Cultural Variations
Cultural backgrounds heavily influence communication preferences. For instance, in collectivist cultures, indirect forms of communication are common; people may prioritize harmony over directness. In contrast, individualistic cultures often encourage straightforward expressions of ideas and feelings. Understanding these variations enables you to interact respectfully across diverse cultural contexts and prevents misinterpretations that could damage relationships.
Improving Communication Styles
Improving your communication style can significantly enhance interactions in both personal and professional settings. By implementing specific strategies, you can foster clearer understanding and stronger relationships.
Self-Assessment Techniques
Self-assessment helps identify your communication strengths and weaknesses. Start by reflecting on past conversations. Ask yourself questions like:
- How did others react to my messages?
- Was I clear in expressing my thoughts?
- Did I listen actively to others?
You might also consider using surveys or quizzes designed for self-evaluation. These tools provide insights into whether you lean toward assertive, passive, or aggressive styles.
Developing Effective Communication Skills
Developing effective communication skills involves practice and commitment. Here are some strategies:
- Practice active listening: Focus on understanding before responding.
- Use “I” statements: Express feelings without blaming others, such as “I feel frustrated when…”
- Seek feedback: Encourage honest input from friends or colleagues about your communication approach.
- Engage in role-playing: Simulate conversations to explore different styles safely.
By incorporating these methods into daily interactions, you can refine your ability to communicate effectively across various contexts.