Imagine a world where energy flows seamlessly without loss, where every component works in perfect harmony. Closed circuit examples are all around you, powering everything from your favorite gadgets to complex industrial systems. These circuits not only illustrate fundamental principles of electricity but also showcase innovative applications that drive technology forward.
Understanding Closed Circuits
Closed circuits allow electricity to flow continuously, powering devices and systems vital for everyday life. Understanding their definition and importance helps you appreciate how they function in various applications.
Definition of a Closed Circuit
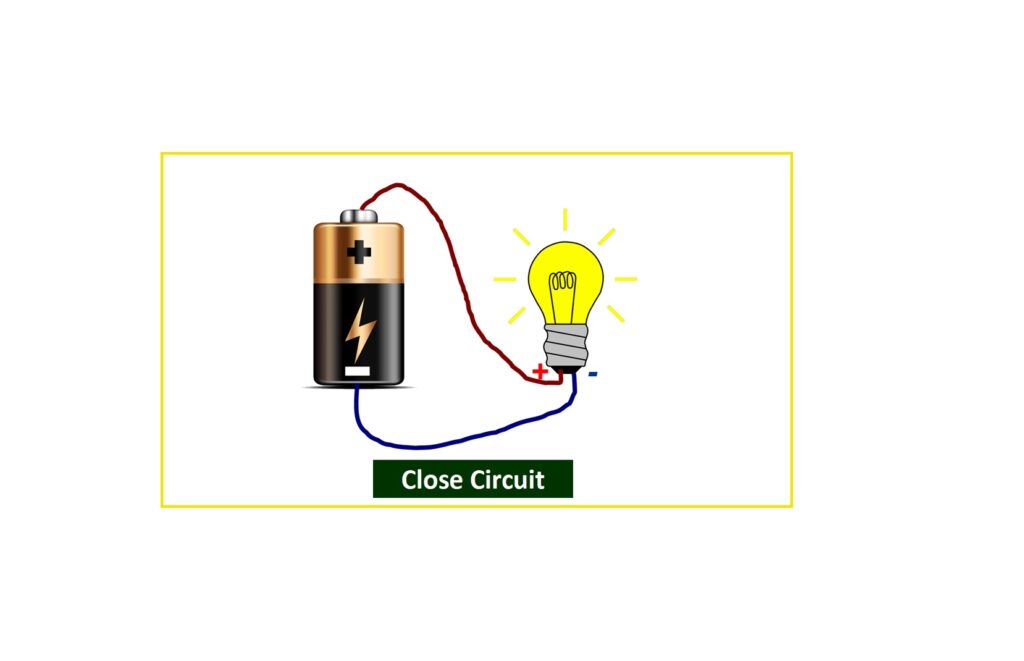
A closed circuit is a complete electrical loop that provides a path for current to flow. If any part of the circuit opens, the flow stops. This concept is fundamental in electronics. For example:
- Light bulbs turn on only when connected correctly within a closed circuit.
- Batteries supply energy through closed loops, enabling functionality in devices.
Importance of Closed Circuits
Closed circuits are crucial for reliable operation. They ensure that electrical devices receive uninterrupted power, leading to efficiency and safety. Their significance includes:
- Consistent performance: Devices operate as intended without disruptions.
- Safety mechanisms: Many systems include fail-safes that rely on closed circuits to prevent hazards.
- Versatility: Applications range from simple household items like flashlights to complex industrial machinery requiring stable power sources.
Understanding these aspects highlights the essential role closed circuits play in technology and daily functions.
Common Closed Circuit Examples
Closed circuits are all around you, powering everyday devices and educational tools. Here are some common examples that illustrate their significance in various contexts.
Everyday Household Examples
In your home, closed circuits operate numerous appliances seamlessly. Some key examples include:
- Light fixtures: When you flip a switch, it completes the circuit, allowing electricity to flow and illuminate the room.
- Televisions: A closed circuit enables your TV to receive power and function correctly when it’s plugged in.
- Refrigerators: They rely on closed circuits to maintain temperature by circulating coolant effectively.
- Washing machines: These appliances use closed circuits for consistent operation during wash cycles.
Each example showcases how essential these circuits are for daily convenience and functionality.
Educational Demonstrations
In educational settings, closed circuits serve as foundational concepts in physics and electronics. Common demonstrations include:
- Simple battery-powered circuit: Connecting a battery to a light bulb creates a basic closed circuit, illustrating how electrical energy flows.
- Circuit kits: Many kits allow students to build their own devices using batteries, wires, and bulbs, reinforcing the concept of closed circuits through hands-on experience.
- Series vs. parallel circuits: Experiments comparing these two types highlight differences in current flow and resistance within closed loops.
These demonstrations foster understanding of electrical principles while engaging learners in practical applications.
Applications of Closed Circuits
Closed circuits find extensive applications across various fields. These circuits play a crucial role in ensuring that devices operate efficiently and reliably.
Industrial Uses
In industrial settings, closed circuits are fundamental for powering heavy machinery and control systems. You might encounter them in:
- Conveyor belts: They ensure smooth operation by maintaining constant energy flow.
- Robotic arms: These rely on closed circuits to perform precise tasks.
- Motor controls: They regulate the speed and direction of machines.
Each application highlights how closed circuits support productivity and safety, making operations more efficient.
Medical Equipment
Closed circuits are vital in medical technology, where reliability is paramount. In hospitals, you’ll see them used in:
- Heart monitors: They provide continuous readings by maintaining an uninterrupted power supply.
- Infusion pumps: These devices deliver medication precisely through closed circuitry.
- Diagnostic equipment: Machines like MRI scanners depend on stable electric flow for accurate imaging.
These examples illustrate the critical role that closed circuits play in enhancing patient care and operational efficiency within healthcare facilities.
Advantages of Closed Circuits
Closed circuits provide numerous advantages across various applications. They ensure a constant flow of electricity, making them essential for both household and industrial use.
Efficiency and Reliability
Closed circuits enhance efficiency by maintaining an uninterrupted power supply. When devices operate within a closed circuit, they receive consistent voltage, which leads to reliable performance. For instance, consider how your refrigerator keeps food fresh; it relies on a closed circuit to maintain optimal cooling temperatures without interruption.
- Household appliances: Devices like microwaves and air conditioners depend on closed circuits for their functionality.
- Industrial machinery: Equipment such as conveyor belts and robotic arms operate seamlessly due to reliable power from closed circuits.
Safety Features
Safety is paramount in any electrical system, and closed circuits contribute significantly to this aspect. They incorporate safety mechanisms that protect users and equipment from potential hazards.
- Overcurrent protection: Fuses or circuit breakers interrupt the current flow when it exceeds safe levels.
- Grounding systems: These prevent electric shock by redirecting excess current safely into the ground.
In situations where devices malfunction, these safety features activate quickly, minimizing risks associated with electrical failures.