Imagine a world where healthcare providers have instant access to patient records, treatment histories, and real-time data at their fingertips. This is the power of clinical information systems. These innovative tools are transforming how medical professionals deliver care by streamlining processes and enhancing communication within healthcare settings.
In this article, you’ll explore various examples of clinical information systems that are making waves in the industry. From electronic health records (EHRs) to decision support systems, each plays a crucial role in improving patient outcomes and operational efficiency. Ever wondered how these systems can reduce errors and save time? You’re about to find out! Dive into the fascinating world of clinical information systems and discover how they’re reshaping the future of healthcare delivery.
Overview Of Clinical Information Systems
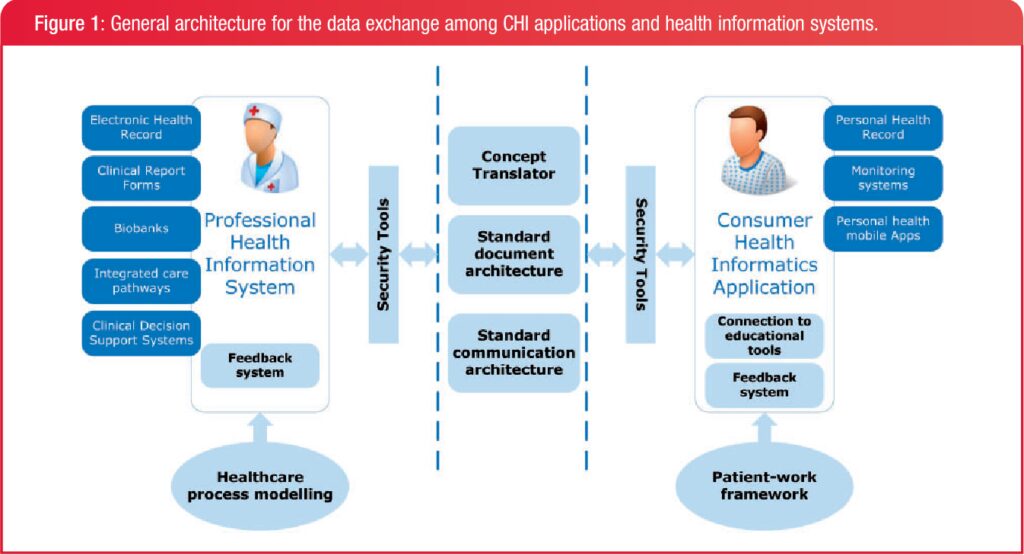
Clinical information systems play a crucial role in modern healthcare. They enhance patient care by providing timely access to essential data, thereby improving decision-making and operational efficiency.
Definition And Purpose
A clinical information system refers to any system that manages healthcare data. These systems include electronic health records (EHRs), computerized physician order entry (CPOE), and clinical decision support systems (CDSS). The primary purpose of these systems is to improve the quality of care through accurate, accessible information. For instance, EHRs allow providers to track patient history seamlessly, which leads to better treatment outcomes.
Key Components
Key components of clinical information systems contribute significantly to their effectiveness:
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs): Store comprehensive patient data digitally.
- Computerized Physician Order Entry (CPOE): Enables providers to place orders for medications or tests electronically.
- Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS): Offers alerts and reminders based on patient-specific data.
- Data Analytics Tools: Analyze trends in patient populations for improved public health strategies.
These components work together to ensure healthcare professionals have immediate access to vital information at the point of care.
Types Of Clinical Information Systems
Clinical information systems encompass various types designed to enhance healthcare delivery. Each system plays a distinct role in improving patient care, streamlining processes, and reducing errors.
Electronic Health Records (EHR)
Electronic health records (EHRs) are digital versions of patients’ paper charts. They provide real-time access to patient data, aiding in decision-making and coordination among healthcare providers. EHRs improve the accuracy of information and reduce the chances of miscommunication. Some notable examples include:
- Epic Systems: Widely used across hospitals for comprehensive patient data management.
- Cerner: Offers robust interoperability features that connect multiple healthcare facilities.
- Allscripts: Focuses on integrated solutions for small to mid-sized practices.
Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS)
Clinical decision support systems (CDSS) assist healthcare professionals by providing evidence-based recommendations. These systems analyze patient data and suggest optimal treatment options, enhancing clinical outcomes. Examples of CDSS include:
- UpToDate: Provides clinicians with instant access to clinical guidelines and research articles.
- IBM Watson Health: Utilizes artificial intelligence to support oncologists in personalized cancer treatment plans.
- Meditech: Integrates clinical decision support tools directly into EHRs for seamless use during patient visits.
By implementing these systems effectively, you can significantly improve the quality of care delivered in medical settings.
Benefits Of Clinical Information Systems
Clinical information systems provide numerous advantages that significantly enhance healthcare delivery. These systems improve efficiency, accuracy, and patient outcomes by offering real-time access to vital information.
Improved Patient Care
One major benefit of clinical information systems is the improvement in patient care. For instance, electronic health records (EHRs) allow providers to quickly view a patient’s medical history, medication lists, and allergies. This immediate access helps clinicians make informed decisions during consultations. Additionally, computerized physician order entry (CPOE) minimizes prescription errors by ensuring that orders are legible and correctly entered into the system.
Enhanced Data Management
Another critical advantage is Enhanced Data Management. Clinical information systems streamline data collection and storage processes. You can easily retrieve patient data when needed, reducing time spent on paperwork. Moreover, these systems often include built-in analytics tools that allow for tracking trends in patient populations or treatment effectiveness over time.
Some key features include:
- Centralized databases: Consolidate various types of healthcare data.
- Interoperability: Enable different healthcare facilities to share patient information efficiently.
- Secure access: Protect sensitive health data while allowing authorized users easy retrieval.
By implementing these technologies, you foster a more organized approach to managing patient care and ensure better operational workflows across your practice or hospital setting.
Challenges In Implementing Clinical Information Systems
Implementing clinical information systems presents several challenges that healthcare organizations must navigate. These obstacles can hinder the effectiveness of these systems despite their potential benefits.
Technical Barriers
Technical barriers often arise during the integration of clinical information systems. Issues include:
- Interoperability: Different systems may not communicate effectively, creating data silos.
- Infrastructure: Insufficient IT infrastructure can lead to slow system performance or downtime.
- Data Migration: Transferring existing patient data to new platforms poses risks of data loss or inaccuracies.
These technical challenges require careful planning and investment in technology to ensure smooth implementation.
User Training And Adaptation
User training and adaptation pose significant hurdles as well. Without proper training, staff may struggle to utilize the new systems effectively. Key aspects include:
- Understanding Features: Users need to familiarize themselves with all functionalities for optimal use.
- Resistance to Change: Some staff members might resist adopting new technologies due to comfort with old processes.
- Ongoing Support: Continuous support and resources are essential for user confidence and competence.
Addressing these issues through structured training programs enhances user experience and improves overall system utilization.
Future Trends In Clinical Information Systems
Clinical information systems continue evolving, shaping the future of healthcare. Emerging technologies and methodologies promise to enhance patient care significantly while streamlining workflows.
Integration With Telehealth
Integration with telehealth is becoming essential in clinical information systems. By combining these platforms, healthcare providers can offer seamless remote consultations. For example:
- Epic Systems provides integrated telehealth solutions, allowing clinicians to access patient records during virtual visits.
- Cerner incorporates telemedicine features within its EHR platform, enhancing documentation and communication.
- Doxy.me integrates with existing clinical information systems for straightforward video conferencing.
Such integrations enable better continuity of care and improve accessibility for patients.
Role Of Artificial Intelligence
The role of artificial intelligence (AI) in clinical information systems is expanding rapidly. AI enhances decision-making and operational efficiency through advanced data analytics. Notable examples include:
- IBM Watson Health, which analyzes vast amounts of medical literature to provide evidence-based recommendations.
- Google Health’s AI algorithms, which assist in diagnosing conditions by analyzing medical images more accurately than traditional methods.
- Zebra Medical Vision employs machine learning to interpret radiological images, highlighting potential health issues early.
These innovations not only streamline processes but also empower clinicians with actionable insights that lead to improved outcomes.