Imagine a world powered by clean energy, where the air is fresh and the planet thrives. As concerns about climate change grow, more people are looking for sustainable solutions that not only benefit our environment but also enhance our quality of life. Clean energy isn’t just a trend; it’s a necessity for a healthier future.
Overview of Clean Energy
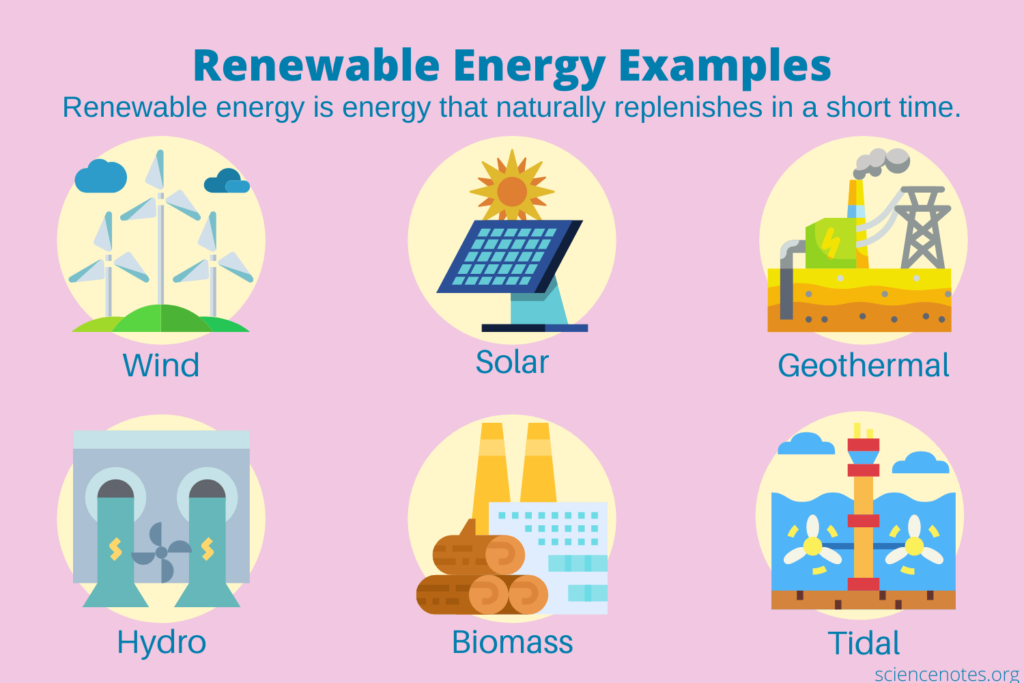
Clean energy refers to energy sources that produce minimal or no environmental impact. These sources contribute significantly to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and combating climate change.
Solar energy harnesses sunlight using solar panels. It converts sunlight into electricity, providing a sustainable power solution for homes and businesses.
Wind energy utilizes wind turbines to generate electricity. Wind farms located onshore or offshore capture wind’s kinetic energy, producing clean power without harmful emissions.
Hydropower, generated by flowing water, is another vital clean energy source. Dams and river systems convert the movement of water into electricity, supporting many communities with renewable energy.
Geothermal energy taps into the earth’s internal heat. This sustainable source provides heating and electricity generation in areas with volcanic activity.
Biomass, derived from organic materials like plants and waste, can be converted into fuel or electricity. By utilizing waste resources, biomass supports a circular economy while reducing landfill usage.
You may wonder about the benefits of these clean energy sources. They not only lower carbon footprints but also promote job creation in green technology sectors.
Types of Clean Energy Sources
Clean energy sources play a vital role in reducing environmental impact and promoting sustainability. Here’s an overview of various clean energy sources that contribute to a healthier planet.
Solar Energy
Solar energy harnesses sunlight using solar panels. You can find these panels on rooftops or in large solar farms. Solar power systems can reduce electricity bills significantly by generating your own energy. In 2025, the U.S. installed over 20 gigawatts (GW) of solar capacity, powering millions of homes and businesses.
Wind Energy
Wind energy is generated through wind turbines that convert wind movement into electricity. This source can produce large amounts of power efficiently without emissions. The U.S. added approximately 14 GW of wind power capacity in 2025 alone, making it one of the fastest-growing renewable resources available today.
Hydropower
Hydropower uses flowing water to generate electricity, typically from dams or river systems. It’s one of the oldest and most reliable forms of clean energy, providing about 17% of the total electricity supply in the U.S. Furthermore, hydropower facilities are capable of adjusting output quickly to meet demand fluctuations.
Biomass
Biomass comes from organic materials like wood, agricultural crops, and waste products converted into fuel or electricity. This source reduces landfill waste while producing usable energy—it accounted for around 5% of total U.S. energy consumption in recent years. It’s often used for heating and transportation fuels as well.
Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy taps into heat stored beneath the Earth’s surface to generate electricity or provide direct heating solutions. In regions with volcanic activity, geothermal plants operate efficiently, supplying a consistent power source regardless of weather conditions. As per estimates, geothermal could provide up to 10% of global electricity needs by tapping existing resources effectively.
These clean energy sources not only combat climate change but also foster economic growth and job creation within their respective industries.
Benefits of Clean Energy
Clean energy offers numerous advantages that significantly enhance environmental sustainability and economic growth. By utilizing renewable sources, you contribute to a healthier planet while enjoying various benefits.
Environmental Impact
Clean energy sources reduce greenhouse gas emissions. For instance, solar panels generate electricity without air pollutants. Wind turbines harness wind power, offering a sustainable alternative with minimal land disruption. Additionally, hydropower relies on flowing water for energy production, which conserves natural resources and protects ecosystems.
Economic Advantages
Investing in clean energy creates jobs and stimulates local economies. For example, the solar industry employs over 250,000 people in the U.S., promoting job growth in various sectors. Wind farms also spur economic development by providing new opportunities for maintenance and operation roles. Furthermore, these industries often lead to lower energy costs for consumers over time.
Energy Security
Clean energy enhances national security by reducing dependence on fossil fuels. By diversifying your energy sources through renewables like geothermal or biomass, you stabilize supply lines and mitigate risks associated with price volatility. Moreover, increased use of domestic clean energy ensures reliable access to power during crises or disruptions from foreign suppliers.
Challenges in Clean Energy Adoption
Clean energy adoption faces several significant challenges that hinder its widespread implementation. Understanding these obstacles is crucial for overcoming them and advancing towards a sustainable future.
Technological Barriers
Technological barriers present major hurdles in clean energy. Many renewable technologies require advanced infrastructure and high initial investments, which can deter potential adopters. For instance:
- Storage Solutions: Efficient battery technology is still developing, limiting the ability to store energy from intermittent sources like solar and wind.
- Grid Integration: Upgrading existing grid systems to accommodate distributed energy resources often entails substantial costs.
- Innovation Gaps: Lack of research funding may slow advancements in emerging technologies, affecting scalability.
Policy and Regulation
Policy and regulation significantly influence clean energy adoption. Inconsistent policies across regions create uncertainty for investors and consumers. Key issues include:
- Subsidies: Varying levels of government support can impact market competitiveness between fossil fuels and renewables.
- Regulatory Frameworks: Complex regulatory processes can delay project approvals, discouraging investment.
- Incentives: Lack of clear incentives for adopting clean technologies leads to slower growth in the sector.
Public Awareness
Public awareness plays a critical role in clean energy adoption. Misunderstandings or lack of knowledge can impede acceptance among consumers. Consider these factors:
- Education Campaigns: Limited outreach programs fail to inform the public about the benefits of clean energy options.
- Misinformation: Social media can spread misinformation about renewable technologies, creating skepticism.
- Community Engagement: Local initiatives that promote participation often lead to greater acceptance but are frequently underfunded.
Addressing these challenges requires collaborative efforts among governments, industries, and communities to foster an environment conducive to clean energy growth.