In the world of electrical systems, safety and reliability are crucial. Have you ever wondered how we protect our devices from overloads or faults? Circuit breakers and disconnect switches are examples of essential components that ensure your electrical systems function safely. These devices play a vital role in preventing damage and maintaining operational efficiency.
Overview of Circuit Breakers and Disconnect Switches
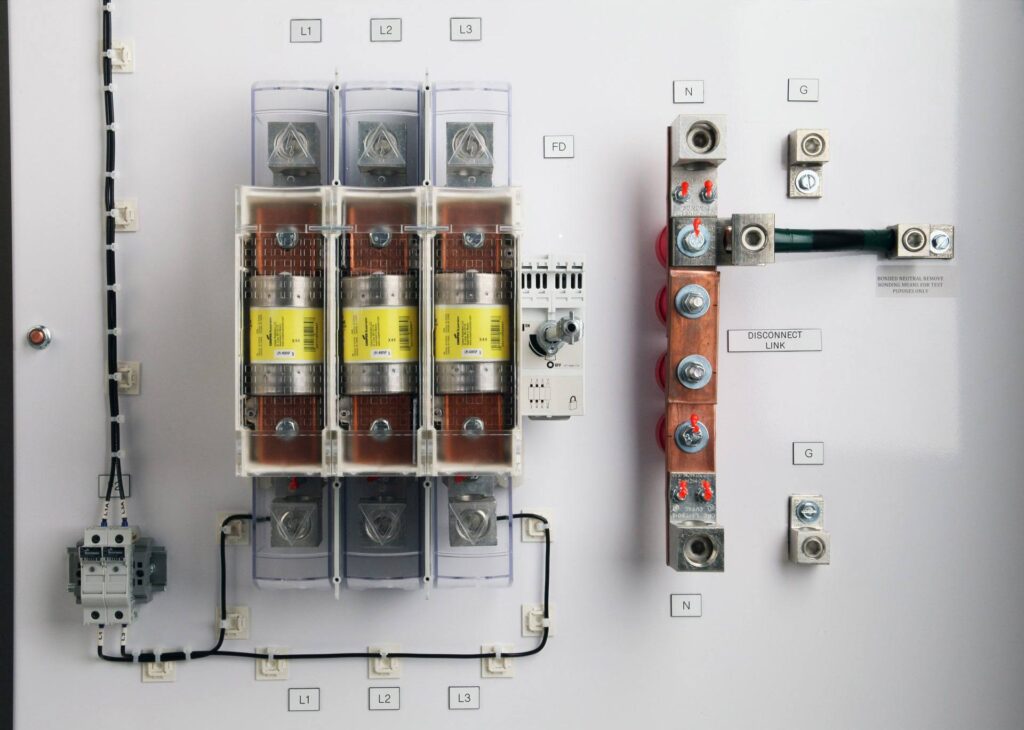
Circuit breakers and disconnect switches serve critical roles in electrical systems. Circuit breakers automatically interrupt power during overloads or short circuits, protecting equipment from damage. They sense abnormal conditions and trip the circuit, ensuring safety.
Disconnect switches, on the other hand, provide a manual means to isolate circuits for maintenance or emergencies. These devices ensure that electrical components can be safely serviced without risk of electricity flow. Both components enhance system reliability.
Examples include:
- Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCBs): Protect against overloads in residential applications.
- Residual Current Devices (RCDs): Prevent electric shock by detecting earth faults.
- Load Break Switches: Used in medium-voltage applications to safely disconnect loads.
You might notice these devices in various settings, like homes or industrial plants. Each serves its purpose while contributing to overall safety and efficiency in electrical distribution systems.
Types of Circuit Breakers
Circuit breakers come in various types, each designed for specific applications and protection needs. Understanding these types can help you choose the right one for your electrical system.
Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCB)
Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCBs) provide protection against overloads and short circuits. Commonly used in residential settings, they automatically reset after tripping. MCBs typically handle currents up to 100 amperes. They are essential for safeguarding household appliances like refrigerators and washing machines.
Molded Case Circuit Breakers (MCCB)
Molded Case Circuit Breakers (MCCBs) protect larger electrical systems. These devices accommodate currents from 100 to 2500 amperes, making them suitable for commercial and industrial applications. MCCBs feature adjustable trip settings for customized protection based on specific loads or conditions. You might find them in manufacturing plants or large office buildings.
Air Circuit Breakers (ACB)
Air Circuit Breakers (ACBs) serve high-capacity electrical systems. Often used in environments with a need for robust load management, ACBs handle current ratings over 800 amperes. Their design allows them to interrupt higher fault currents effectively. ACBs are prevalent in substations and utility companies, ensuring safe distribution of electricity across vast networks.
Understanding the different types of circuit breakers helps ensure proper selection based on your specific needs and operational requirements.
Types of Disconnect Switches
Disconnect switches come in various types, each designed for specific applications and safety requirements. Understanding these options helps you choose the right switch for your electrical system.
Open Switches
Open switches are typically found in outdoor settings and industrial environments. They allow easy access to the switch mechanism, which enhances visibility during operation. Open switches enable quick disconnection of circuits for maintenance or emergency purposes. Common examples include knife blade switches and toggle switches used in high-voltage applications.
Enclosed Switches
Enclosed switches provide enhanced protection against environmental factors like dust and moisture. These devices feature a housing that shields internal components from damage. Enclosed switches ensure reliable performance even in harsh conditions. Examples include rotary disconnects commonly used in commercial buildings and substations.
Load-Break Switches
Load-break switches can interrupt current flow while under load, making them essential for medium-voltage systems. These devices safely disconnect live circuits without causing an arc flash, enhancing safety during maintenance tasks. Load-break switches are critical for maintaining operational integrity in electrical grids. You’ll often find them utilized in utility companies and industrial plants where safe isolation is necessary.
Applications of Circuit Breakers and Disconnect Switches
Circuit breakers and disconnect switches play vital roles in various electrical applications. Their effectiveness ensures safety, reliability, and operational efficiency across different environments.
Residential Applications
In residential settings, circuit breakers are essential for protecting your home from overloads and short circuits. For example:
- Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCBs) automatically trip to prevent damage when current exceeds safe levels.
- Residual Current Devices (RCDs) cut off electricity during fault conditions to prevent electric shock.
These devices enhance safety by ensuring your household appliances operate within safe limits.
Commercial Applications
Commercial spaces require robust electrical systems that can handle diverse loads. Here are some key examples:
- Molded Case Circuit Breakers (MCCBs) protect larger installations by accommodating currents between 100 to 2500 amperes.
- Enclosed Disconnect Switches provide protection against environmental factors, making them ideal for commercial buildings.
These solutions help maintain system integrity while allowing safe maintenance procedures.
Industrial Applications
In industrial environments, the stakes are higher due to complex machinery and larger power requirements. Consider these applications:
- Air Circuit Breakers (ACBs) manage high-capacity systems with ratings over 800 amperes, commonly used in substations.
- Load-Break Switches enable safe disconnection of live circuits without causing arcs, crucial for medium-voltage operations.
Implementing these devices ensures continuous operation while safeguarding personnel and equipment.