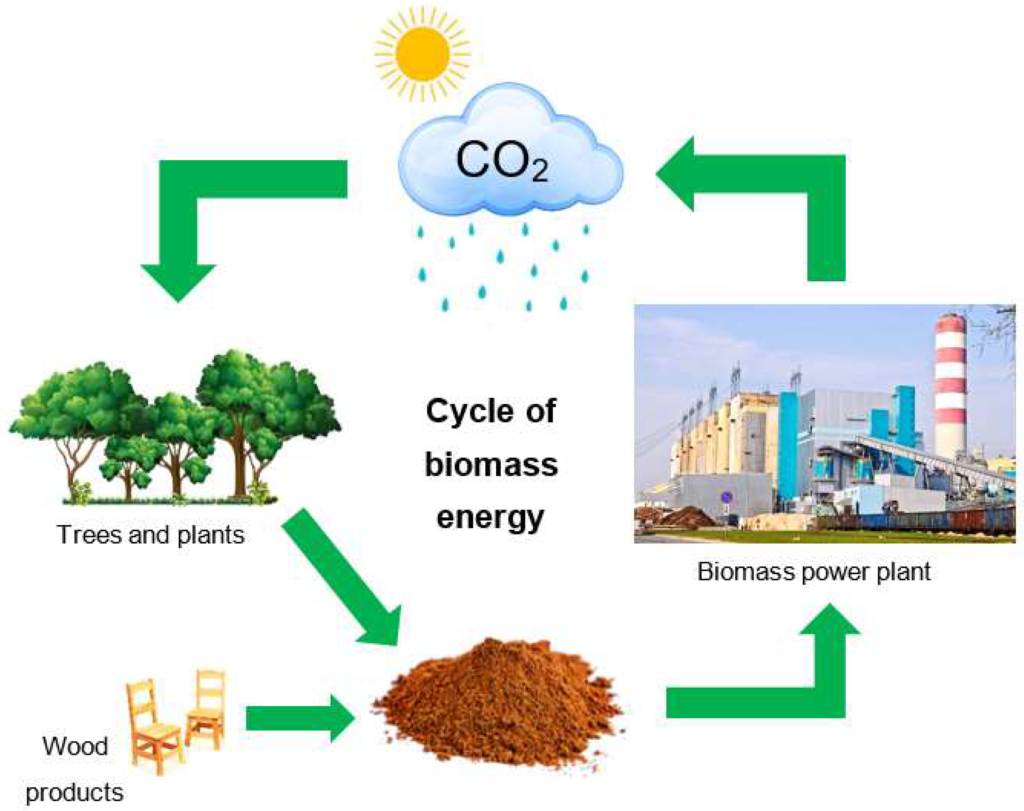
Imagine harnessing the power of nature to fuel your home and reduce your carbon footprint. Biomass energy offers a sustainable solution by converting organic materials into renewable energy sources. From agricultural waste to wood chips, this eco-friendly alternative is gaining traction as a viable way to meet our growing energy demands.
Overview Of Biomass Energy
Biomass energy comes from organic materials, offering a renewable source of power. It uses waste products from various industries and natural processes. For example, agricultural residues like corn stalks or sugarcane bagasse can be transformed into energy through combustion or conversion into biofuels.
Another common example includes wood chips and sawdust, often sourced from lumber mills, which can generate heat or electricity. These resources provide a sustainable way to utilize what would otherwise be waste.
Additionally, you might find biomass derived from dedicated crops such as switchgrass or miscanthus. These plants grow quickly and require less water than traditional crops while yielding significant energy outputs.
Landfill gas is another interesting option; it captures methane produced by decomposing waste in landfills for use in heating or electricity generation. This process not only generates power but also reduces greenhouse gas emissions.
Biomass energy utilizes diverse sources including agricultural waste, wood products, dedicated energy crops, and landfill gas to create sustainable and renewable energy solutions that help reduce carbon footprints effectively.
Types Of Biomass Energy
Biomass energy comes from various organic materials. Understanding these types can help you choose the most suitable sources for renewable energy.
Organic Materials
Organic materials play a crucial role in biomass energy production. These include:
- Agricultural residues: Corn stalks and wheat straw serve as effective feedstocks.
- Wood byproducts: Sawdust, wood chips, and bark from lumber mills are abundant resources.
- Food waste: Leftover food and agricultural products can create energy through anaerobic digestion.
You might find it surprising how much potential lies in these everyday items. The conversion of these materials into energy not only reduces landfill waste but also provides valuable alternatives to fossil fuels.
Energy Crops
Dedicated energy crops represent another significant category within biomass. These crops are specifically grown for their biomass yield. Examples include:
- Switchgrass: A perennial grass known for its high energy density.
- Miscanthus: Another perennial that thrives on marginal land with minimal inputs.
- Giant reed: This fast-growing plant offers great potential due to its high biomass production.
These crops contribute significantly to sustainable biomass energy systems. They provide consistent yields and require fewer resources compared to conventional crops, making them an attractive option for farmers looking to diversify their income streams while promoting sustainability.
Advantages Of Biomass Energy
Biomass energy offers numerous benefits that enhance its appeal as a sustainable energy source. Key advantages include its renewable nature and contribution to carbon neutrality.
Renewable Resource
Biomass energy derives from organic materials, making it a Renewable Resource. Examples of these materials include:
- Agricultural residues: Corn stalks, wheat straw, and rice husks can be used for energy production.
- Wood byproducts: Sawdust and wood chips from lumber mills provide valuable resources for biomass conversion.
- Dedicated energy crops: Switchgrass and miscanthus are specifically cultivated for their high biomass yield.
These examples demonstrate how readily available organic materials can generate consistent energy while supporting local economies.
Carbon Neutrality
Biomass is often considered carbon neutral, which means it doesn’t significantly increase atmospheric carbon dioxide levels when managed sustainably. For instance:
- When plants grow, they absorb CO2 from the atmosphere.
- Burning these plants releases CO2 back into the air but keeps the cycle balanced if new plants are replanted.
This balance helps mitigate climate change impacts compared to fossil fuels. Moreover, utilizing waste products reduces methane emissions from landfills, contributing further to environmental benefits.
Challenges Of Biomass Energy
Biomass energy presents several challenges that impact its viability and effectiveness. Understanding these obstacles helps in evaluating its overall potential as a renewable energy source.
Sustainability Concerns
Sustainability concerns arise from the land-use changes associated with biomass production. Converting forests or agricultural land to grow dedicated energy crops can lead to habitat loss. Moreover, intensive farming practices may degrade soil health, impacting biodiversity.
Another issue is the carbon neutrality debate. While biomass energy is often deemed carbon neutral due to CO2 absorption by plants, emissions from processing and transportation can offset this benefit. It’s crucial to consider the entire lifecycle of biomass use when assessing sustainability.
Economic Factors
Economic factors significantly influence the adoption of biomass energy. The initial investment for setting up biomass facilities can be high, which deters some investors and small-scale farmers. Additionally, fluctuating prices for raw materials like agricultural residues affect profitability.
Market demand also plays a role; if fossil fuel prices drop, it becomes harder for biomass solutions to compete economically. Accessing funding or subsidies can alleviate some financial burdens but varies widely across regions and policies. Understanding these economic dynamics is essential for stakeholders in the biomass sector.