Imagine you’re diving into the world of programming and suddenly come across the term array example. It sounds simple, but understanding arrays can unlock a whole new level of efficiency in your coding journey. Whether you’re managing data or organizing information, arrays are fundamental structures that help you store multiple values in a single variable.
Overview of Array Examples
Arrays serve as powerful tools in programming. They simplify data management by grouping related values together. Here are a few common examples of arrays:
- Integer Arrays: You can store a series of numbers, like scores in a game or temperatures recorded throughout the week.
- String Arrays: This type holds text values, such as names of students or product titles.
- Multi-dimensional Arrays: These allow for complex data structures, like matrices used in mathematical computations.
Using arrays enhances efficiency and organization. For instance, if you need to access a student’s score from an array, simply refer to its index rather than searching through multiple variables.
You might wonder how arrays differ between programming languages. In Python, you use lists; while in JavaScript, you work with native array objects. Each language has its syntax but maintains the fundamental concepts.
Consider these practical applications:
- Storing user preferences
- Managing inventory items
- Tracking daily expenses
Understanding various array examples lays the groundwork for efficient coding. By mastering arrays, you’re better equipped to handle larger datasets and improve your software’s performance.
Types of Arrays
Arrays come in various types, each serving distinct purposes in programming. Understanding these types can enhance your ability to manage and manipulate data effectively.
One-Dimensional Arrays
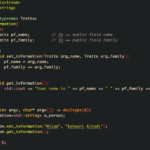
One-dimensional arrays store a single list of items. They allow you to access elements using a single index value. For example, an integer array can hold scores like this:
scores = [85, 92, 78, 90]
You retrieve the first score with scores[0]. These arrays are ideal for simple collections such as names or ages.
Multi-Dimensional Arrays
Multi-dimensional arrays extend one-dimensional arrays by adding more dimensions. This enables you to create complex structures like matrices or tables. For instance, a two-dimensional array may represent a grid:
matrix = [[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6],
[7, 8, 9]]
Accessing an element requires two indices: matrix[1][2] returns the value 6. Such arrays are useful for handling data that naturally forms rows and columns.
Practical Applications of Array Examples
Arrays serve numerous practical applications in programming and everyday data management. They streamline data processing, making it easier for you to handle multiple values efficiently.
Programming and Data Structures
In programming, arrays are essential for managing collections of related items. You can use them to create lists, queues, stacks, and more. For instance, integer arrays store numerical scores for a game or grades for students. String arrays might hold names or product descriptions. Multi-dimensional arrays like matrices effectively manage complex datasets such as images or grids in games.
Real-World Use Cases
Arrays find extensive use in various real-world scenarios:
- Storing User Preferences: You can keep user settings in string arrays, allowing quick access during application runtime.
- Managing Inventory Items: Businesses often utilize integer arrays to track quantities of products available.
- Tracking Daily Expenses: By using float or decimal arrays, individuals can record daily spending and categorize expenses.
These examples demonstrate how understanding array concepts enhances your ability to develop efficient software solutions while organizing data logically.
Best Practices for Using Arrays
Using arrays effectively enhances your coding efficiency. Here are some best practices to keep in mind:
- Choose the right type of array: Different programming languages offer various array types. Make sure you select the one that fits your data needs, like lists in Python or native arrays in JavaScript.
- Initialize arrays properly: Always initialize your arrays before use. This practice prevents unexpected behavior and makes debugging easier.
- Use meaningful variable names: Descriptive names help clarify what the array contains. For example, instead of naming an integer array “arr,” consider using “scores” for better context.
- Keep track of indices: When working with multi-dimensional arrays, maintain proper indexing to prevent errors. Mismanagement can lead to accessing wrong elements.
- Avoid magic numbers: Use constants instead of hardcoding values for array lengths or indices. It increases code readability and maintainability.
Following these practices leads to cleaner, more efficient code when working with arrays. You’ll streamline your data management tasks and enhance overall performance in your applications.