Imagine you’re diving into the world of Spanish verbs, and suddenly you hit a roadblock with those tricky ar imperfect endings. Understanding how to use these endings can transform your ability to communicate in past scenarios. The imperfect tense allows you to describe ongoing actions or habitual activities, giving depth to your storytelling.
Understanding Ar Imperfect Endings
Mastering ar imperfect endings is essential for expressing past actions in Spanish. These endings help convey ongoing situations and habitual activities, enriching your storytelling abilities.
Definition and Importance
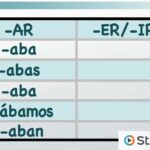
Ar imperfect endings refer to the specific verb conjugations used in the imperfect tense for -ar verbs. The forms include -aba, -abas, -aba, -ábamos, -abais, and -aban. This tense captures actions that were continuous or recurring in the past, such as “I was talking” or “We used to play.” Understanding these forms enhances your ability to discuss events with context and detail.
Common Usage in Language
You often use ar imperfect endings to describe background information or settings in narratives. Consider these examples:
These sentences illustrate how the imperfect tense describes actions without a defined beginning or end, adding depth to conversations about past experiences.
Conjugation Rules for Ar Imperfect Endings
Understanding ar imperfect endings is crucial for effective communication in past contexts. These endings allow you to convey ongoing actions and habitual activities, enhancing your storytelling abilities.
Regular Verb Structure
Regular -ar verbs follow a predictable pattern in the imperfect tense. The conjugations include:
- Yo hablaba (I was talking)
- Tú hablabas (You were talking)
- Él/Ella/Usted hablaba (He/She/You formal were talking)
- Nosotros/Nosotras hablábamos (We were talking)
- Vosotros/Vosotras hablabais (You all were talking)
- Ellos/Ellas/Ustedes hablaban (They/You all formal were talking)
This structure remains consistent across regular -ar verbs, making it easier to learn and apply.
Irregular Verb Variations
While most -ar verbs are regular, some may exhibit irregularities. However, in the case of the imperfect tense, very few -ar verbs deviate from the standard endings. Notable exceptions typically arise in other tenses rather than the imperfect.
For example:
- The verb “ir” becomes “iba,” “ibas,” “iba,” etc.
Recognizing these variations helps you maintain accuracy when using less common verbs in conversation or writing.
Examples of Ar Imperfect Endings in Sentences
Understanding ar imperfect endings enhances your ability to express past actions. Here are several examples showcasing how these endings function in sentences.
Constructing Meaningful Sentences
- Yo hablaba con mis amigos cada tarde.
- Tú jugabas fútbol en el parque durante los veranos.
- Él estudiaba para sus exámenes todos los días.
- Nosotros viajábamos a la playa cada año.
- Vosotros comíais juntos en casa de abuela.
Each sentence illustrates ongoing or habitual actions, emphasizing the continuity of these experiences over time.
Contextual Usage of the Endings
Using ar imperfect endings conveys background information effectively. Consider these scenarios:
- Describing childhood activities: “Cuando era niño, yo nadaba en la piscina.”
- Relating a past routine: “Cada domingo, tú ibas al cine.”
- Sharing memories: “Mientras ellos conversaban, yo escuchaba música.”
These examples highlight how ar imperfect endings enrich narratives by providing context and depth to past experiences.
Teaching Strategies for Ar Imperfect Endings
Understanding ar imperfect endings enhances your ability to convey past actions effectively. Focus on practical teaching strategies that engage learners and facilitate mastery of these conjugations.
Approaches for Educators
- Interactive Activities: Utilize games like conjugation bingo or flashcards to reinforce the forms: -aba, -abas, -aba, -ábamos, -abais, and -aban. These activities encourage participation while solidifying knowledge.
- Storytelling Exercises: Encourage students to create stories using ar imperfect endings. This allows them to practice contextually and see how these forms enrich narratives.
- Role-Playing Scenarios: Implement role-playing exercises where students describe daily routines or past events using the imperfect tense. This fosters conversational skills and real-life application.
- Visual Aids: Use charts that display conjugation patterns alongside example sentences. Visual representation aids retention and understanding.
Resources for Learners
Utilize diverse resources to support learning ar imperfect endings:
- Online Conjugation Tools: Websites like Conjugemos provide interactive conjugation practice tailored to various levels.
- Language Apps: Apps such as Duolingo or Babbel offer structured lessons focusing on verb tenses, including the imperfect tense.
- Worksheets and Quizzes: Printable materials from educational sites can help reinforce concepts through targeted exercises.
- Video Tutorials: Platforms like YouTube feature educators explaining the nuances of Spanish verb conjugations with visual examples.
These resources enhance comprehension and provide opportunities for independent study, ensuring you grasp ar imperfect endings thoroughly.