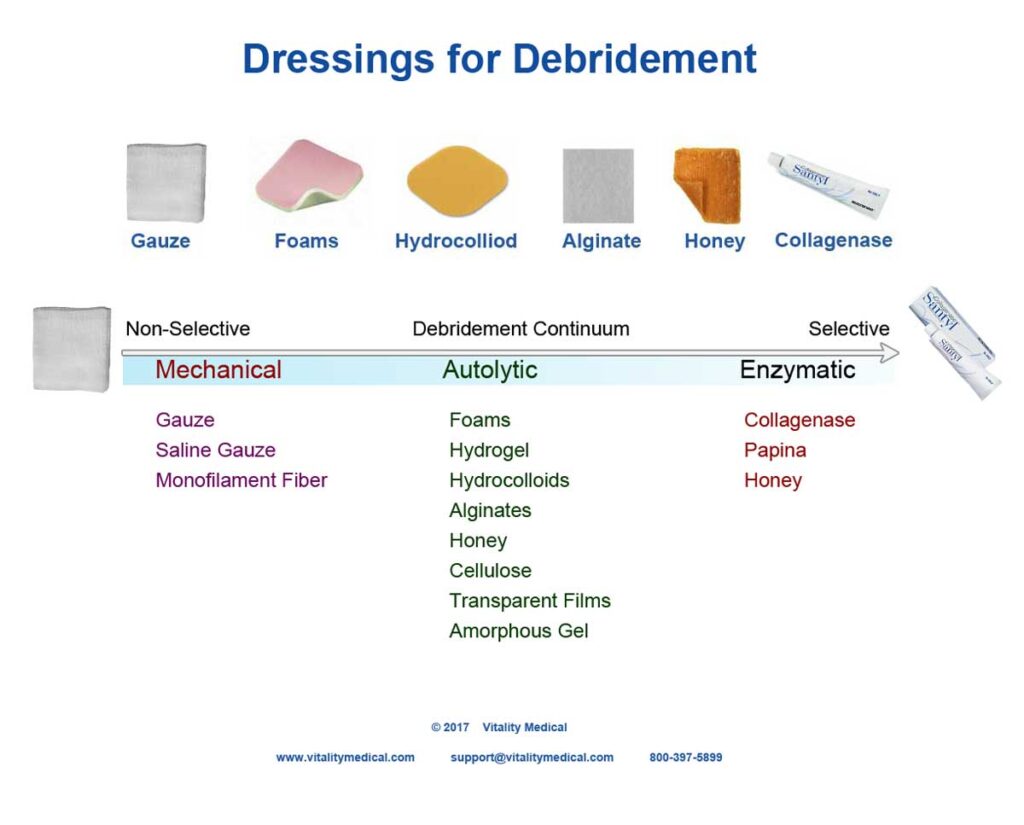
When it comes to wound care, you might be wondering what options are best for promoting healing. Alginate dressing has emerged as a top choice in modern medical practices due to its unique properties and effectiveness. Derived from seaweed, this innovative dressing not only absorbs excess moisture but also creates an optimal healing environment.
Overview of Alginate Dressing
Alginate dressing is a highly effective wound care product derived from brown seaweed. It offers multiple benefits that enhance the healing process.
One key feature is its exceptional absorbency. Alginate dressing can absorb up to 20 times its weight in exudate, making it ideal for moderate to heavily draining wounds. This ability helps maintain a moist environment, which is crucial for optimal healing.
Another important aspect involves its biocompatibility. Alginate dressing interacts positively with wound tissues, promoting cell migration and granulation tissue formation. This interaction supports faster recovery times.
You may find alginate dressings in various forms, including:
The versatility of these forms allows you to choose the best option for your specific wound type. Whether treating surgical wounds, pressure ulcers, or venous leg ulcers, alginate dressings play a vital role in modern wound management.
Moreover, <strong.alginate dressings facilitate easy removal without damaging new tissue. Their gentle adherent properties minimize trauma during changes while ensuring patient comfort. So when selecting a dressing for your needs, consider the unique advantages offered by alginates.
Composition and Properties
Alginate dressing consists of natural polysaccharides derived from brown seaweed. These dressings effectively absorb moisture and provide a conducive environment for wound healing.
Natural Sources of Alginate
Alginate is primarily extracted from two species of brown seaweed: Laminaria and Ascophyllum. These algae grow in coastal regions, thriving in cold waters. Each type offers varying properties, which can influence the effectiveness of alginate dressings.
Physical and Chemical Properties
Alginate possesses unique physical and chemical attributes that make it suitable for wound care. It forms a gel when in contact with moisture, helping to maintain a moist wound environment. Additionally, its high absorption capacity allows it to hold up to 20 times its weight in exudate, reducing the risk of maceration around wounds.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Absorption Capacity | Up to 20 times its weight |
| Gel Formation | Creates a moist environment |
| Biocompatibility | Promotes positive interactions with tissues |
| Forms Available | Sheets, granules, pads |
These properties contribute significantly to faster recovery times by facilitating cell migration and supporting granulation tissue formation.
Mechanism of Action
Alginate dressings operate through distinct mechanisms that enhance wound healing. Their unique properties facilitate effective management of various types of wounds.
Absorption of Exudate
Alginate dressings absorb exudate efficiently, up to 20 times their weight. This high absorption capacity keeps the wound environment moist, preventing maceration and promoting healing. For instance, in cases of venous leg ulcers or pressure sores, alginate dressings manage excess fluid while maintaining optimal conditions for tissue regeneration. The presence of sodium ions in alginate also encourages gel formation when it comes into contact with moisture, further enhancing absorption capabilities.
Promotion of Healing
Alginate dressings promote healing by supporting cellular activities essential for recovery. They encourage cell migration and granulation tissue formation through their biocompatibility. In surgical wounds or diabetic ulcers, this promotes faster closure and reduces infection risks. Additionally, alginates can release calcium ions that stimulate fibroblast activity, which is crucial for collagen synthesis and overall wound strength. By creating a favorable environment for these processes, alginate dressings significantly contribute to improved patient outcomes.
Clinical Applications
Alginate dressings play a crucial role in wound care, particularly due to their versatility and effectiveness across various applications.
Wound Types
Alginate dressings are suitable for multiple wound types, including:
- Surgical wounds: Their high absorption capacity aids in managing post-operative exudate.
- Pressure ulcers: They help maintain a moist environment, essential for healing these challenging wounds.
- Venous leg ulcers: The ability to absorb significant amounts of fluid supports treatment in chronic conditions.
These examples illustrate the adaptability of alginate dressings in treating different wound scenarios effectively.
Advantages over Other Dressings
Choosing alginate dressings offers several advantages compared to traditional options.
- Moisture management: Alginate’s ability to absorb up to 20 times its weight keeps the wound moist while preventing maceration.
- Biocompatibility: These dressings promote positive interactions with tissues, which can speed up healing processes.
- Easy removal: Alginate dressings facilitate painless changes without disrupting new tissue growth.
Overall, these benefits make alginate dressing a preferred choice for healthcare professionals aiming to enhance patient outcomes.
Potential Limitations
Alginate dressings, while beneficial, do present some limitations that you should consider. Understanding these challenges can help in making informed decisions regarding wound care.
Cost Considerations
Costs associated with alginate dressings can be higher than traditional bandages. Depending on the brand and form, prices may vary significantly. For example:
- Sheet forms might range from $5 to $20 per unit.
- Granules could cost between $10 and $30 for a standard package.
These costs add up, especially for long-term treatment of chronic wounds. Insurance coverage might not fully account for these specialized dressings.
Application Challenges
Applying alginate dressings requires specific techniques to ensure effectiveness. First, you must clean the wound adequately before application. Also, if excessive exudate is present and not managed properly, it can compromise the dressing’s performance.
Furthermore:
- Moisture management is crucial; too little moisture can lead to adhesion issues.
- Skin irritation may occur if the dressing remains in place longer than recommended.
These factors necessitate careful monitoring during use to maintain optimal healing conditions.