Imagine stepping back in time, shedding the weight of adult responsibilities to embrace the carefree spirit of childhood. Age regression is a fascinating phenomenon that allows individuals to experience and express themselves as younger versions of themselves. Whether it’s through playful activities, imaginative play, or simply adopting a childlike mindset, age regression offers a unique escape from everyday stressors.
In this article, you’ll explore various examples of age regression and how they manifest in different contexts. From therapeutic practices that promote healing to creative outlets like art and storytelling, age regression can be both a coping mechanism and a form of self-exploration. Are you curious about how tapping into your inner child might transform your life? Join us as we delve deeper into this intriguing concept and uncover its potential benefits for emotional well-being and personal growth.
Understanding Age Regression
Age regression involves individuals reconnecting with their childhood through playful activities and a childlike mindset. This practice can occur in various contexts, providing emotional benefits and personal growth opportunities.
Definition of Age Regression
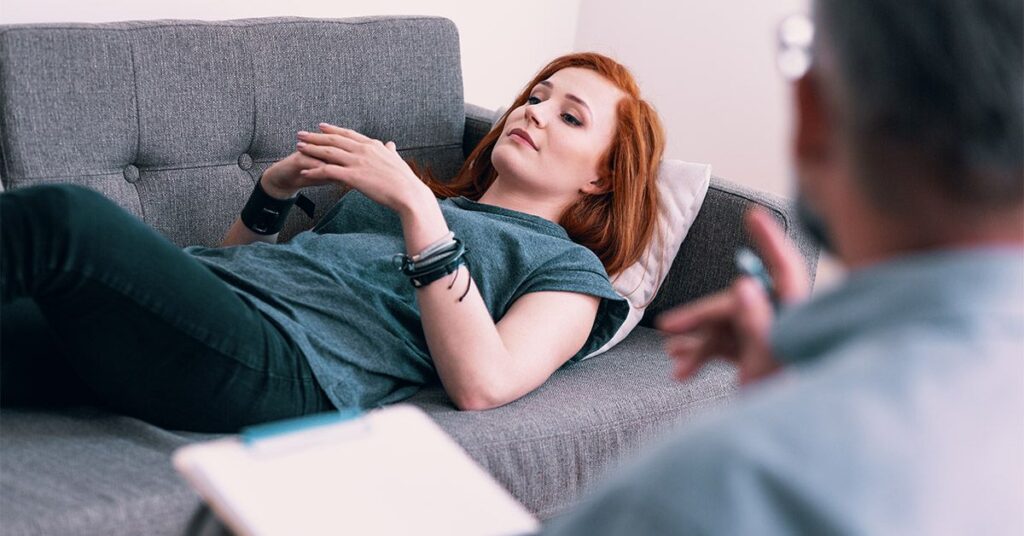
Age regression refers to the psychological phenomenon where an individual reverts to behaviors or attitudes characteristic of a younger age. This might manifest during stress or as a coping mechanism. It can serve therapeutic purposes, allowing individuals to explore unresolved issues from childhood.
- Therapeutic Age Regression: Used in therapy, this type helps clients access repressed memories or emotions.
- Voluntary Age Regression: Individuals engage in childlike activities for fun, such as coloring, playing games, or watching cartoons.
- Roleplay/Community-Based: In communities like “Adult Baby” (ABDL), members embrace infantile roles as part of shared experiences.
Understanding these types clarifies how age regression can be both a personal journey and a social activity.
The Psychology Behind Age Regression
Age regression involves a complex interplay of psychological mechanisms and therapeutic applications. Understanding these aspects reveals how reconnecting with one’s inner child can facilitate emotional healing and personal growth.
Mechanisms of Age Regression
Age regression functions primarily as a coping mechanism. When faced with stress or trauma, you might subconsciously revert to behaviors from childhood. This response often provides a temporary escape from adult responsibilities. Some key mechanisms include:
- Emotional Release: Engaging in childlike activities can help release pent-up emotions.
- Safe Space Creation: Regressing allows for the creation of a safe mental space where you feel secure.
- Cognitive Flexibility: Adopting a younger mindset enhances creativity and problem-solving.
By utilizing these mechanisms, individuals can navigate difficult feelings more effectively.
Therapeutic Uses
Therapists often incorporate age regression techniques into treatment plans. Here are some common therapeutic uses:
- Memory Recall: Therapeutic age regression helps clients access repressed memories, aiding in trauma recovery.
- Emotional Exploration: It encourages exploration of unresolved childhood emotions, facilitating healing.
- Play Therapy: Many practitioners use play therapy to engage clients in childlike scenarios that promote emotional expression.
Through these methods, therapists harness the power of age regression to foster deeper connections between past experiences and current challenges.
Age Regression in Pop Culture
Age regression manifests prominently in pop culture, influencing various media forms. You can see this theme portrayed through films, television shows, and literature that explore childhood memories or experiences.
Representation in Media
Many films incorporate age regression to highlight characters’ emotional journeys. For example:
- “Inside Out” showcases the personification of emotions as childlike figures representing core feelings from childhood.
- “Big,” starring Tom Hanks, features a young boy who magically transforms into an adult while retaining his childlike perspective and wonder.
Television series also depict age regression. Shows like “Stranger Things” embrace themes of nostalgia and the importance of friendship during adolescence.
Public Perception
Public perception of age regression varies widely. Some people view it as a healthy coping mechanism for stress relief, while others regard it with skepticism.
Surveys indicate that:
- About 45% find engaging in childlike activities beneficial for mental health.
- Approximately 30% express concern about adults participating in such behaviors.
These statistics highlight how societal attitudes toward age regression influence its acceptance and practice within communities. As discussions around mental health evolve, perceptions may shift towards greater understanding and acceptance of this phenomenon.
Benefits and Risks of Age Regression
Age regression presents both advantages and disadvantages that can impact mental health and emotional well-being. Understanding these factors helps you make informed choices about engaging in age regression practices.
Positive Aspects
Engaging in age regression offers multiple benefits.
- Emotional relief: You might experience significant stress reduction through playful activities that evoke childhood memories.
- Creativity boost: Allowing your inner child to emerge can enhance creative thinking, leading to innovative problem-solving.
- Improved self-awareness: By reconnecting with past experiences, you may gain insights into unresolved emotions or patterns from your childhood.
- Enhanced coping mechanisms: Age regression provides a temporary escape from adult responsibilities, allowing for relaxation and rejuvenation.
These aspects show how embracing a childlike mindset promotes emotional healing and personal growth.
Potential Drawbacks
However, consider the potential risks associated with age regression.
- Social stigma: Engaging in childlike behaviors may attract judgment or misunderstanding from others, impacting social relationships.
- Escapism tendency: Relying too heavily on age regression could hinder your ability to cope with adult challenges effectively.
- Dependency issues: You might develop an unhealthy attachment to regressive behaviors as a means of avoiding reality rather than addressing underlying problems.
Recognizing these drawbacks ensures a balanced approach when exploring age regression practices.