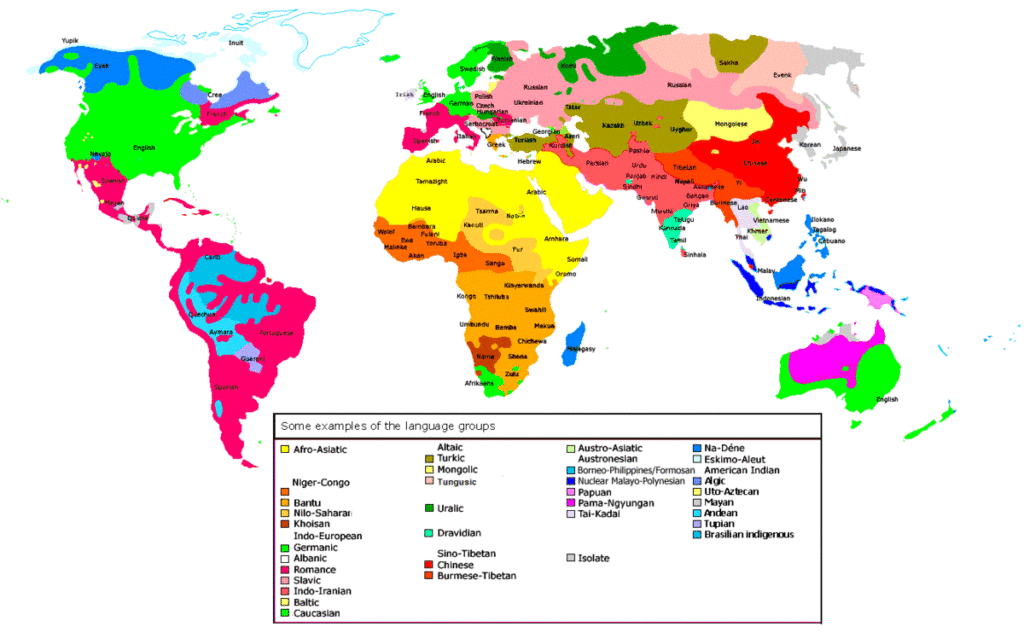
Language shapes our world in fascinating ways, and the diversity of linguistic families reveals much about human history. Did you know that Afro-Asiatic, Dravidian, and Indo-European are examples of major language families that illustrate this diversity? Each family carries unique characteristics and cultural significance, reflecting the regions they originate from.
Afro-Asiatic Dravidian and Indo-European Are Examples Of
Afro-Asiatic, Dravidian, and Indo-European represent major language families with unique features. These families illustrate the diversity of human communication across different regions.
Afro-Asiatic Languages
Afro-Asiatic includes languages like Arabic and Hebrew. Arabic is spoken by over 400 million people worldwide. This family reveals connections between cultures in North Africa and the Middle East.
Dravidian Languages
Dravidian languages such as Tamil and Telugu are primarily found in Southern India. Tamil has a rich literary tradition dating back over 2,000 years. These languages showcase the cultural heritage of their speakers.
Indo-European Languages
Indo-European encompasses a vast array of languages including English, Spanish, and Hindi. English alone has around 1.5 billion speakers globally. This family reflects historical migrations and interactions among diverse groups.
These three language families exemplify how linguistic structures shape identities and societies around the world. Each provides insight into the complex tapestry of human history through language.
Language Families Overview
Language families provide insight into the evolution and diversity of human communication. Afro-Asiatic, Dravidian, and Indo-European are prominent examples that illustrate how languages connect cultures across different regions.
Historical Background
Afro-Asiatic languages date back to ancient civilizations in Africa and the Middle East. They encompass various branches, including Semitic languages like Arabic and Hebrew. Similarly, Dravidian languages emerged around 3,000 years ago in Southern India. This family includes Tamil, which boasts a rich literary history dating back over 2,000 years. Indo-European languages originated from a common ancestor spoken thousands of years ago in Eurasia.
Geographic Distribution
Geographically speaking, Afro-Asiatic languages spread primarily across North Africa and parts of the Middle East. Countries such as Egypt and Ethiopia showcase these linguistic ties. The Dravidian family mainly resides in Southern India; Tamil Nadu is particularly notable for its cultural significance. In contrast, Indo-European languages dominate Europe and South Asia; English, Spanish, Hindi, and many others serve as key examples reflecting historical migrations across these regions.
Linguistic Features
The linguistic features of Afro-Asiatic, Dravidian, and Indo-European families reveal their unique characteristics. Understanding these features enhances your grasp of the languages within these families.
Phonetic Characteristics
Phonetics varies significantly across these language families. For instance:
- Afro-Asiatic languages often feature emphatic consonants, which are pronounced with a strong articulation.
- Dravidian languages utilize retroflex sounds, produced by curling the tongue back against the roof of the mouth.
- Indo-European languages exhibit a wide range of vowel distinctions, contributing to their diverse phonetic systems.
These phonetic traits contribute to distinct pronunciations and accents among speakers in different regions.
Grammatical Structures
Grammatical structures differ markedly among these families. Consider the following examples:
- Afro-Asiatic languages typically use root-and-pattern morphology, where roots convey core meanings modified by patterns.
- Dravidian languages employ agglutinative structures, combining multiple affixes to convey complex grammatical relationships.
- Indo-European languages showcase inflectional morphology, altering word endings to express tense or case.
These grammatical variations shape how speakers construct sentences and convey meaning effectively.
Cultural Significance
Linguistic families like Afro-Asiatic, Dravidian, and Indo-European significantly shape cultural identities and heritage. These languages reflect the histories of their speakers and contribute to diverse cultures around the world.
Influence on Identity
Afro-Asiatic, Dravidian, and Indo-European languages influence group identity profoundly. For instance:
- Afro-Asiatic: Speakers of Arabic often share cultural practices based on shared linguistic roots.
- Dravidian: Tamil speakers connect through a rich literary tradition that fosters regional pride in Southern India.
- Indo-European: Languages like Hindi create bonds among various ethnic groups across South Asia.
Each language carries unique expressions of community values, traditions, and beliefs. How does your language shape your sense of belonging?
Literature and Folklore
Literature plays a crucial role in preserving the essence of each language family. Consider these examples:
- Afro-Asiatic: The Quran showcases the eloquence of Arabic literature.
- Dravidian: The Sangam literature highlights ancient Tamil poetry’s beauty.
- Indo-European: Works by Shakespeare or Tagore demonstrate the depth of English and Bengali literature respectively.
Folklore also thrives in these languages, enriching cultural narratives. From fables to epics, each story reflects societal norms and values within its community. What stories do you cherish from your own culture?
Comparative Analysis
The comparative analysis of Afro-Asiatic, Dravidian, and Indo-European language families reveals both commonalities and unique characteristics that illustrate their richness. Each family carries significant cultural weight and historical context.
Similarities and Differences
Afro-Asiatic, Dravidian, and Indo-European languages share some structural traits but differ notably in sounds and grammar. For instance, all three families exhibit a wide range of vocabulary influenced by their respective cultures.
- Phonetics: Afro-Asiatic languages use emphatic consonants; Dravidian has retroflex sounds; Indo-European features diverse vowel distinctions.
- Grammar Structures: Afro-Asiatic employs root-and-pattern morphology while Dravidian uses agglutinative structures. In contrast, Indo-European showcases inflectional morphology.
These differences contribute to distinct pronunciations among speakers from various regions.
Language Evolution
Language evolution plays a crucial role in understanding these families’ histories. Each family shows unique development patterns rooted in ancient civilizations or migrations.
For example:
- Afro-Asiatic languages trace back thousands of years to early North African societies.
- Dravidian languages emerged around 3,000 years ago with Tamil boasting over 2,000 years of literary history.
- Indo-European languages reflect interactions stemming from numerous migratory movements across Europe and South Asia.
This evolutionary path illustrates how language adapts over time while retaining cultural significance.